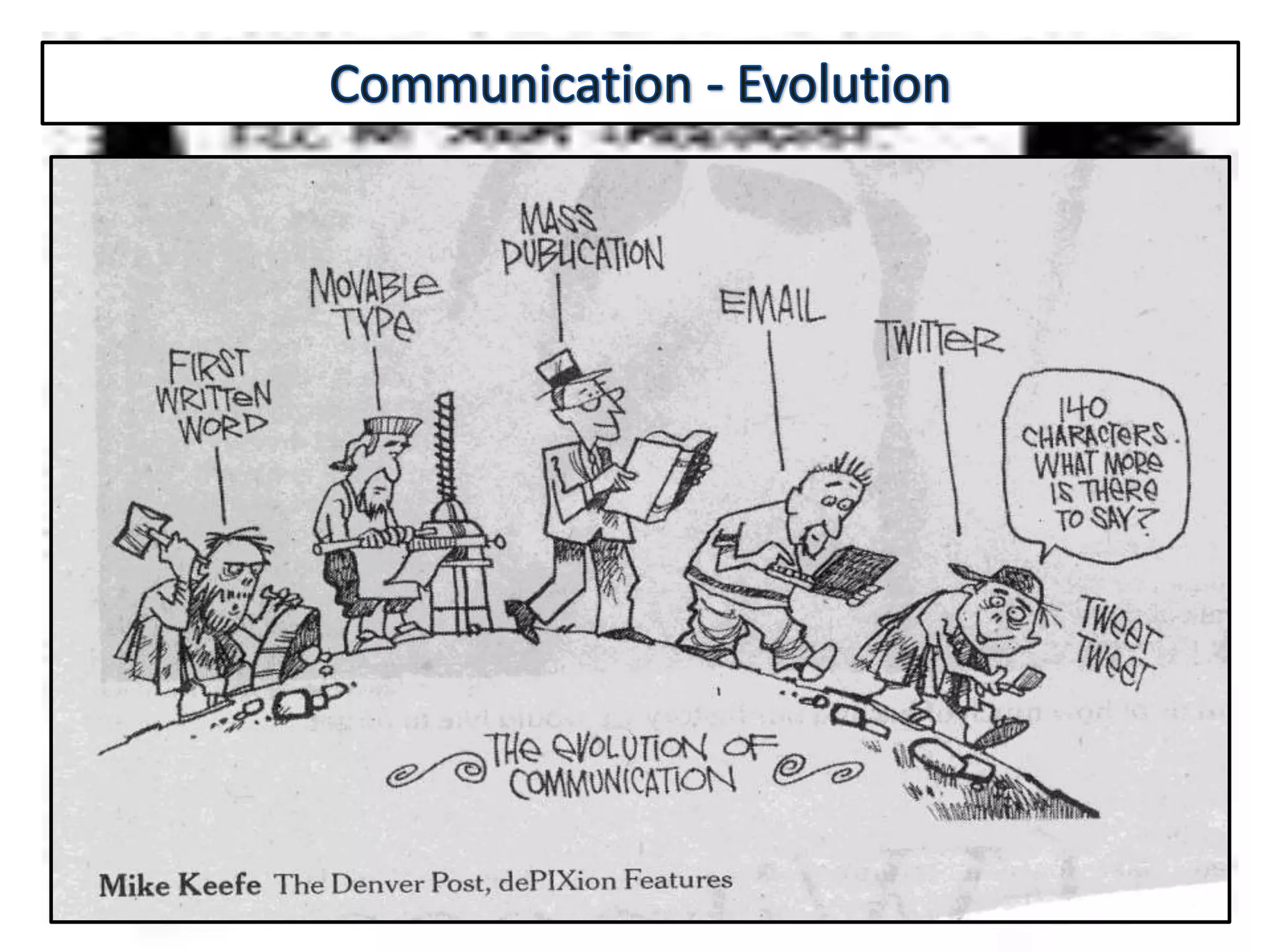
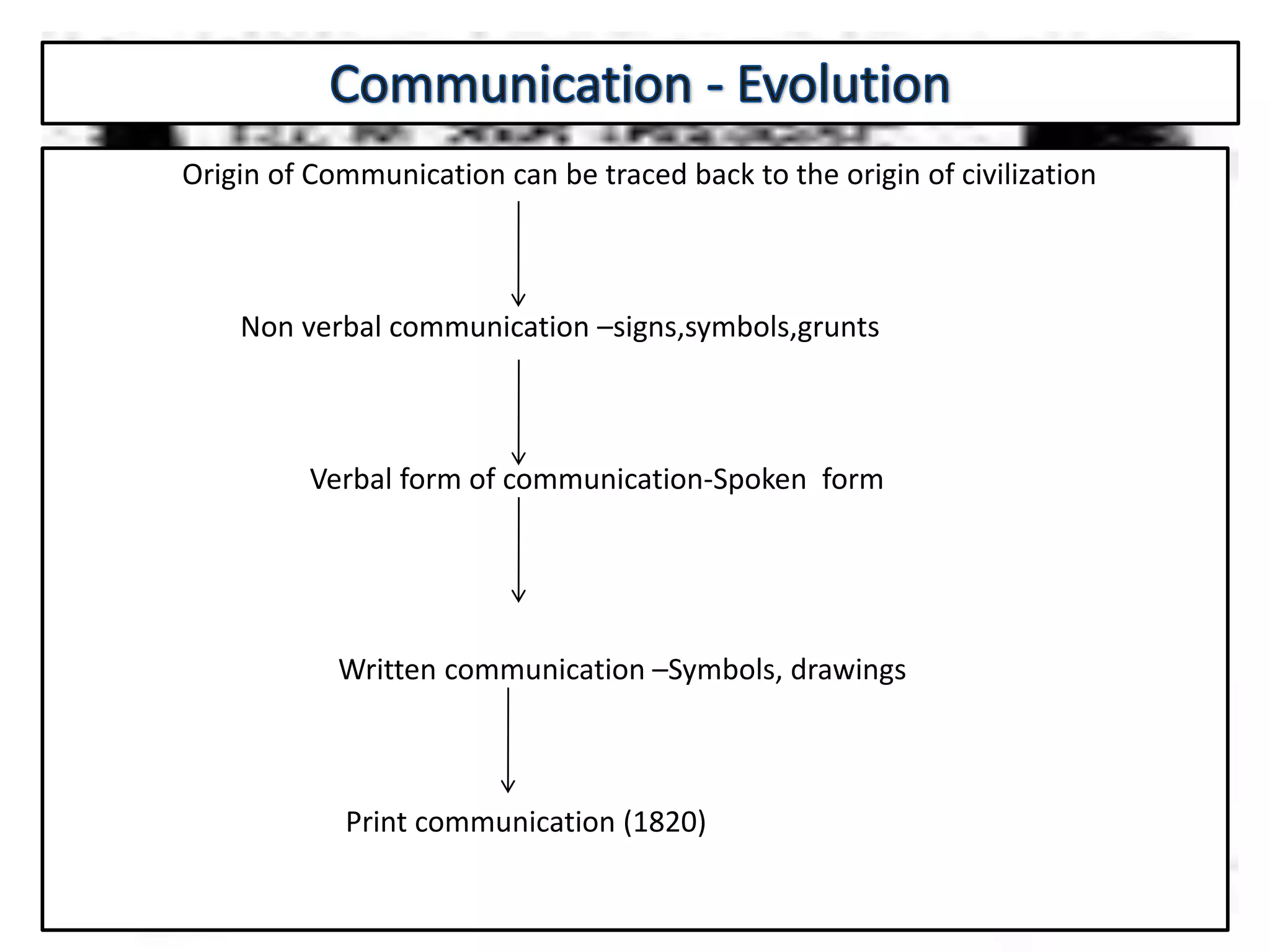
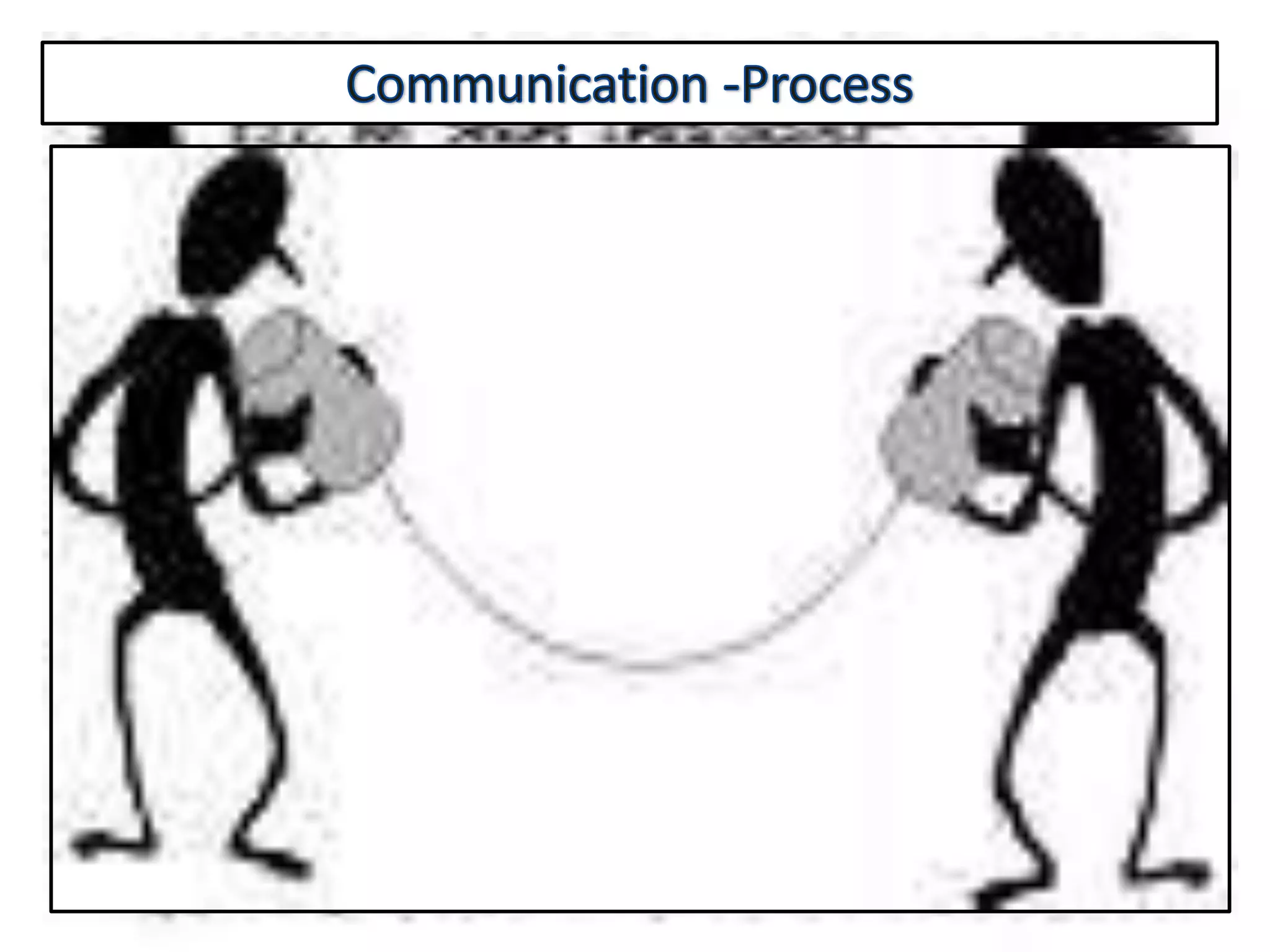
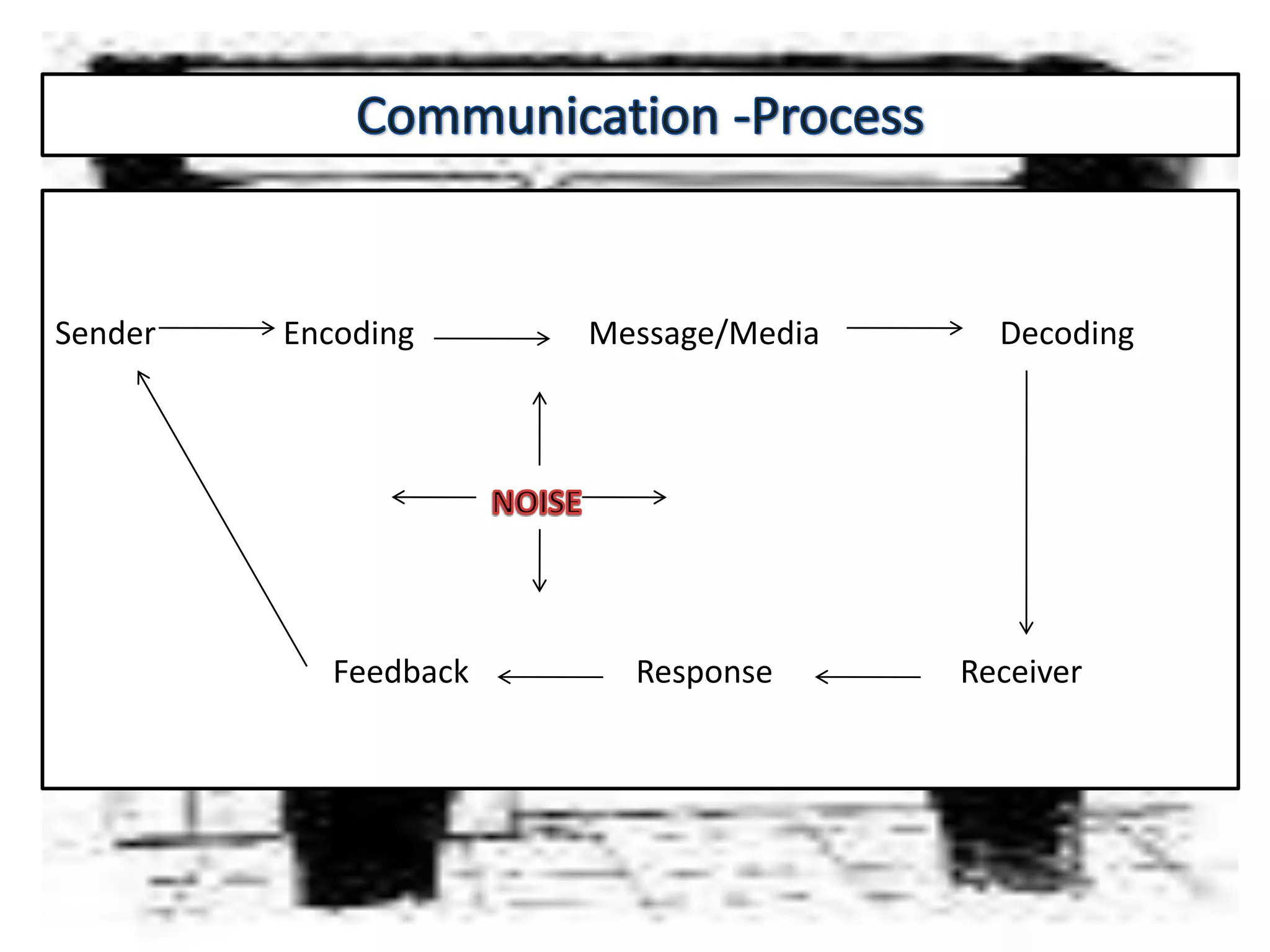
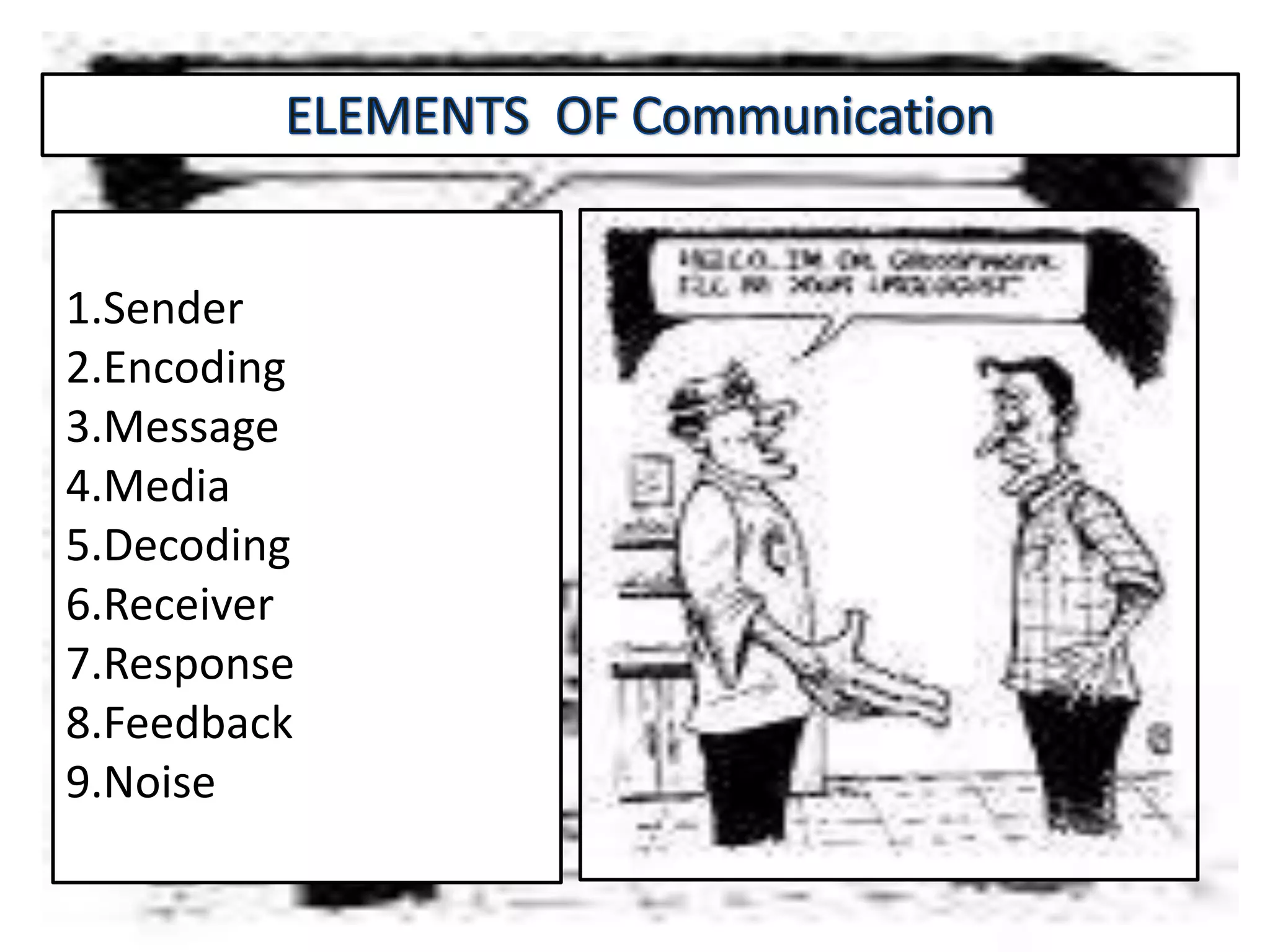
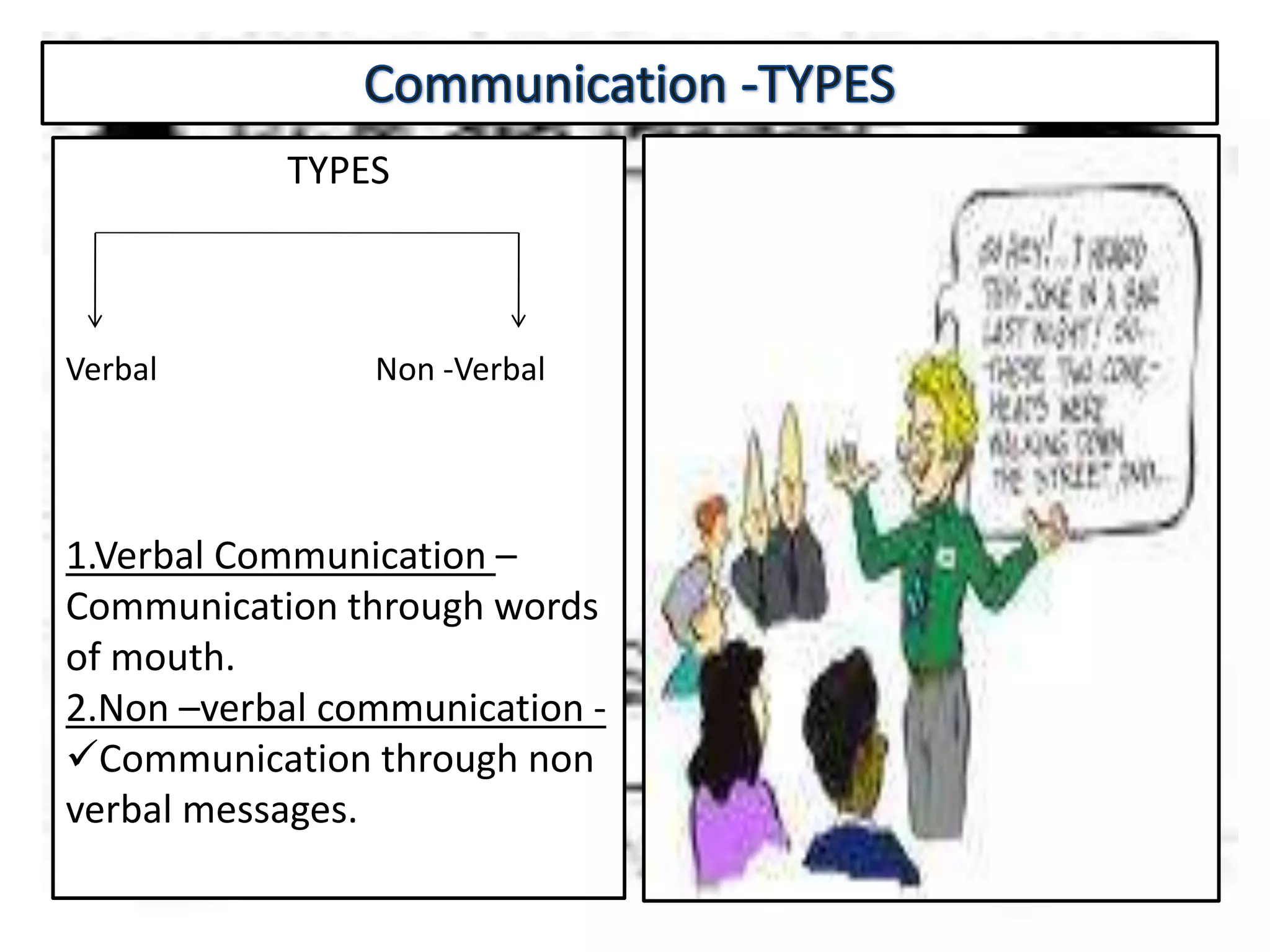
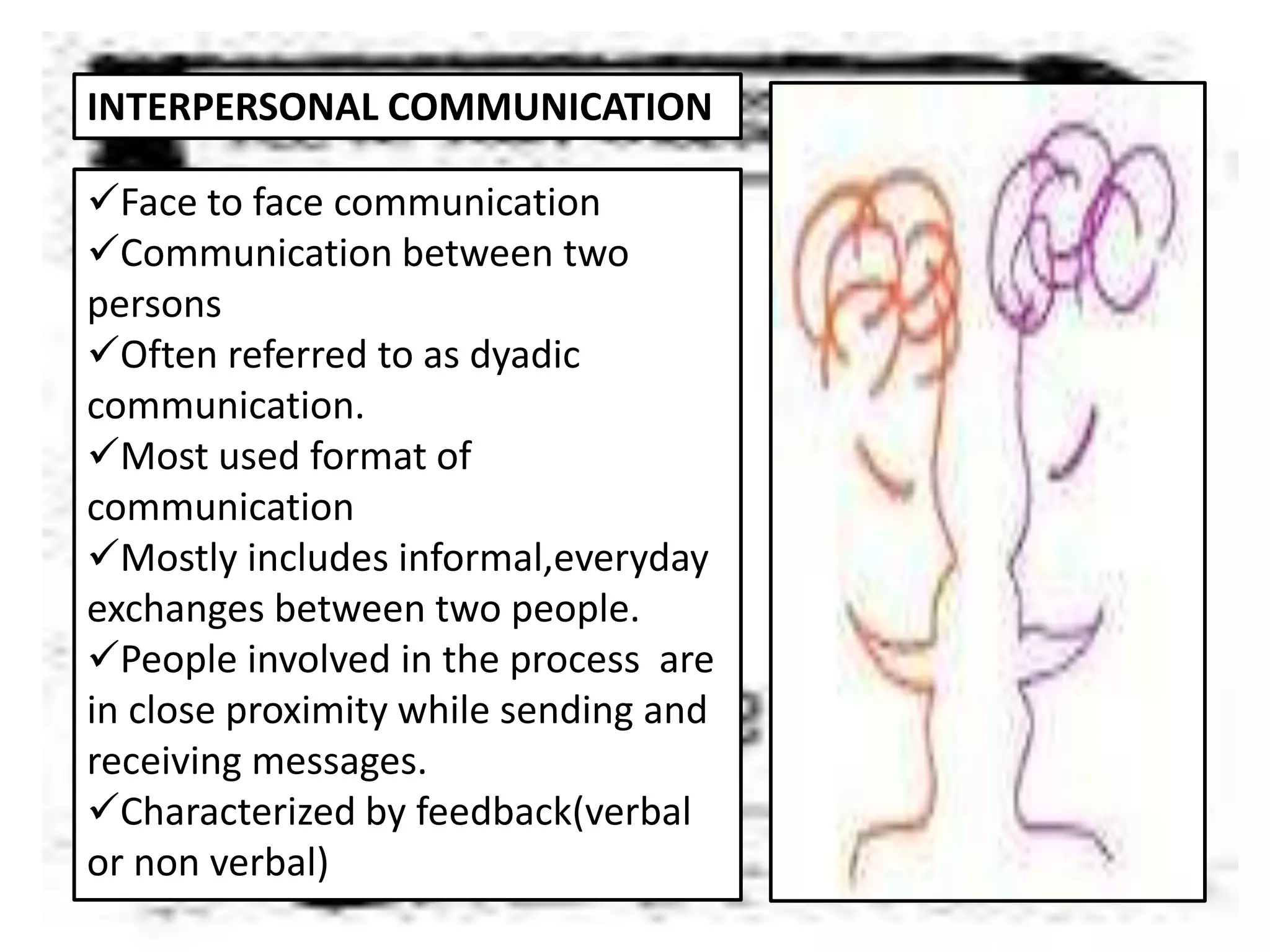
Communication is the process of exchanging ideas, feelings, and information between two or more people to reach mutual understanding. It involves a sender encoding a message, transmitting it through a medium, which is then decoded by the receiver. Effective communication requires clarity, consistency, and credibility. The document discusses various types of communication including intrapersonal, interpersonal, group, public, and mass communication. Non-verbal communication complements verbal communication through body language, facial expressions, touch, space, and other cues.