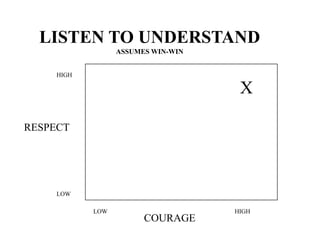
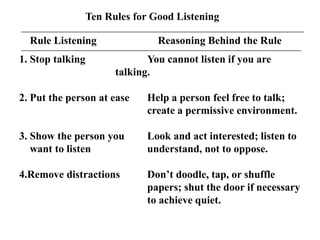
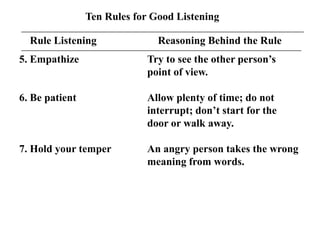
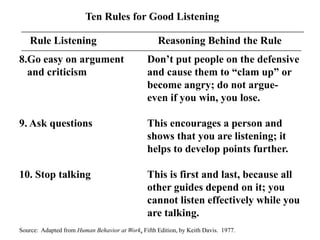
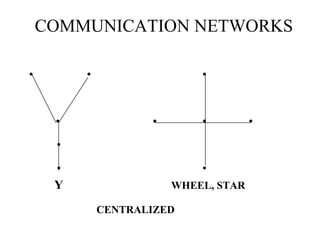
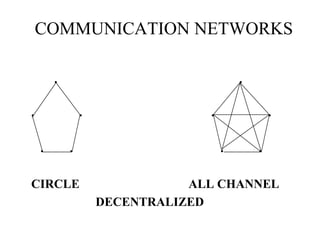
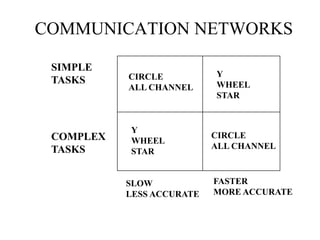
The document discusses common barriers to communication and effective listening. It identifies 12 common barriers including semantics, channel choice, distractions, emotions, perceptions, and poor listening. It provides tips for overcoming barriers such as using feedback, understanding others' perspectives, and direct communication. The document also outlines characteristics of supportive communication and effective listening techniques including paraphrasing, reflecting feelings, and not giving advice. Lastly, it discusses organizational communication and the impact of network structure on information flow.