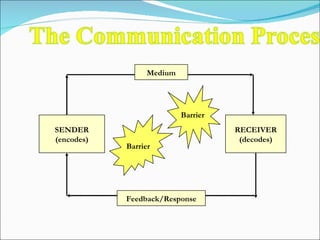
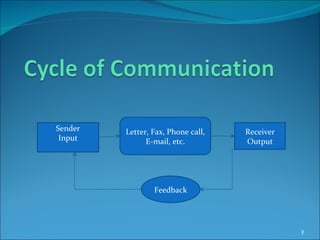
The document discusses various aspects of communication including defining communication, understanding the communication process, overcoming barriers, and improving verbal and non-verbal skills. It covers different types of communication such as written, oral, visual, and computer-based. Tips are provided for effective listening and overcoming communication barriers. The importance of language, tone, body language, and other factors in ensuring clear transmission of information are also highlighted.