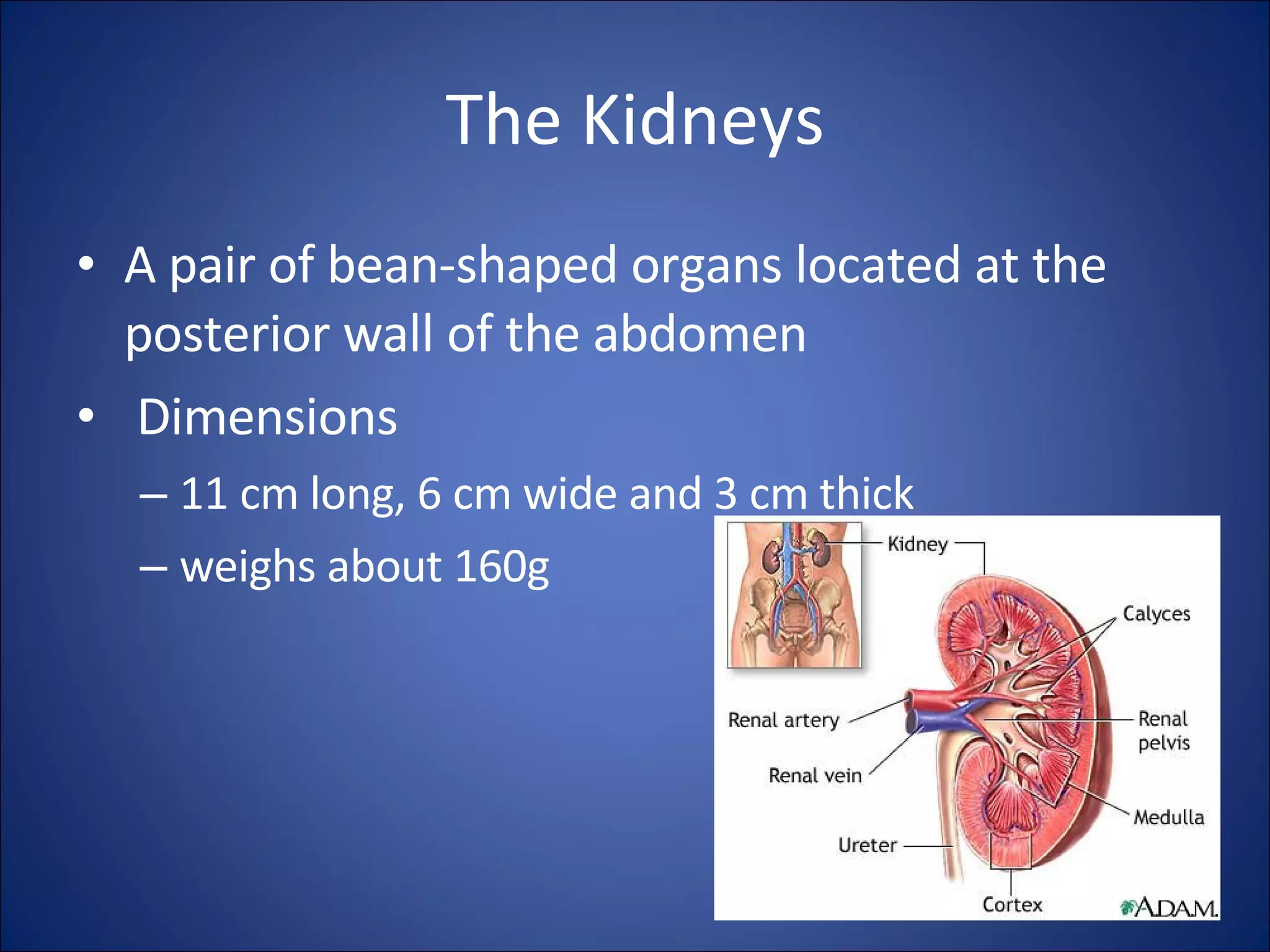
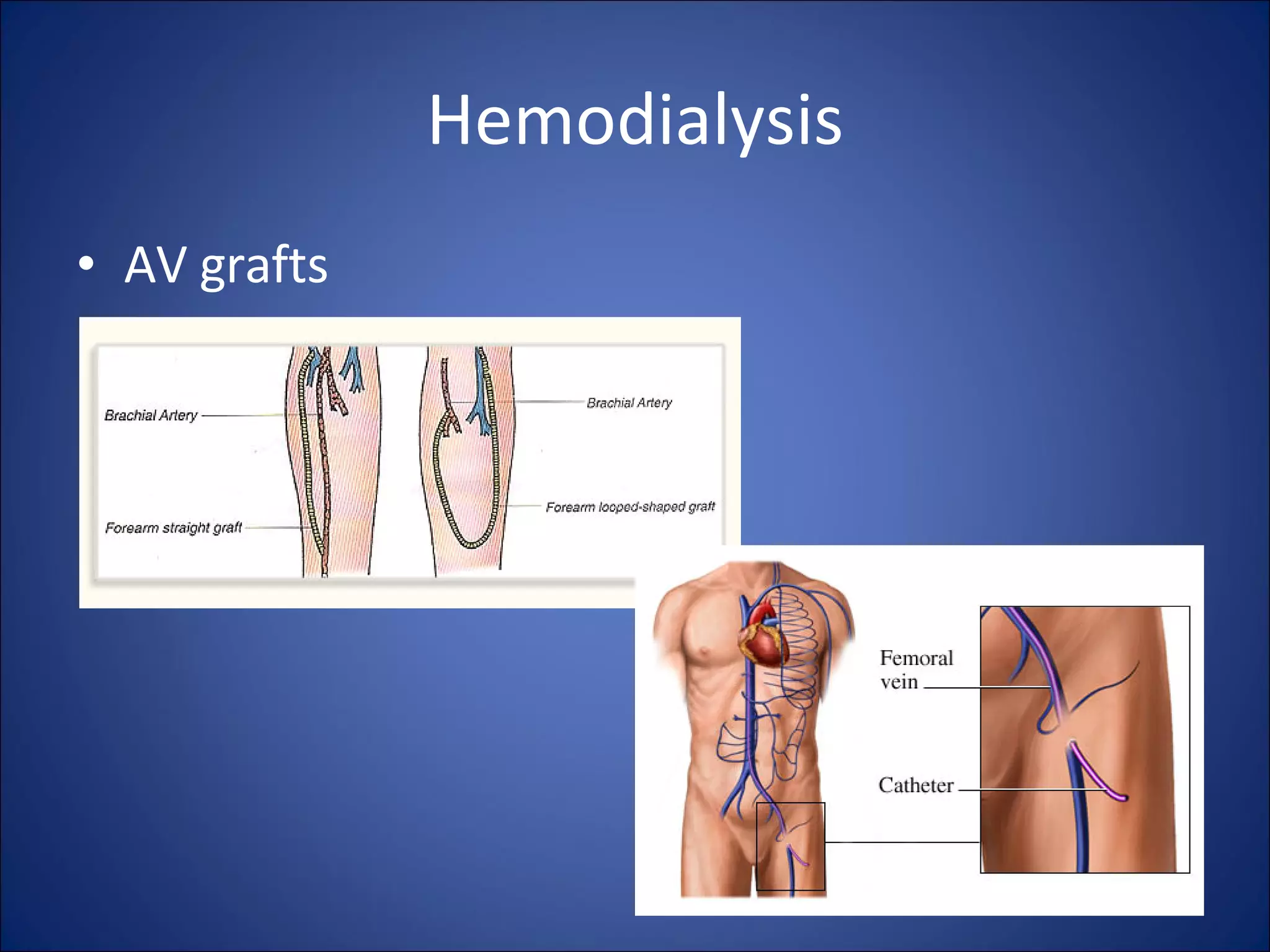
The document discusses the kidneys and their functions, as well as common kidney diseases and treatments for kidney failure. The kidneys filter waste from the blood and produce hormones. When the kidneys fail, waste builds up and dialysis or transplantation is needed. Common causes of kidney failure include diabetes, high blood pressure, glomerulonephritis, polycystic kidney disease and long term painkiller use. Dialysis options include hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, while transplantation provides the best outcomes.
















































![References Kidney Dialysis Foundation (2007). Normal Kidney Functions. Health Guide [Online]. Available: http://www.kdf.org.sg/health.php (2008, June 01). National Kidney Foundation (2007). Common Kidney Diseases. Education [Online]. Available: http://www.nkfs.org/index.php (2008, June 01).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kidney-for-presentation-1213194952210318-9/75/Common-Kidney-Diseases-51-2048.jpg)