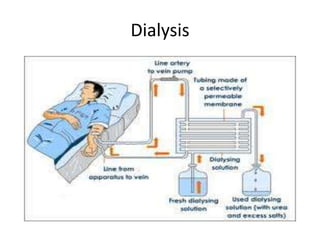
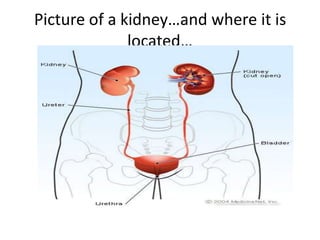
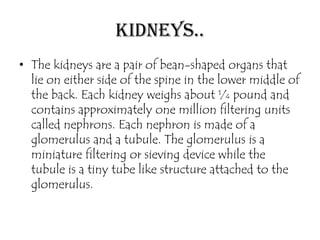
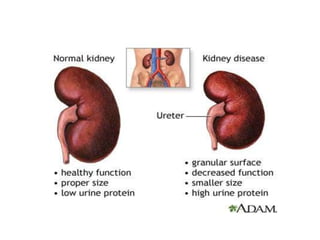
The document summarizes kidney function and chronic kidney disease. It discusses how the kidneys filter waste from the blood and produce important hormones. Chronic kidney disease is a progressive loss of renal function over time that can be caused by conditions like diabetes or hypertension. Symptoms of worsening kidney function are nonspecific but may include fatigue. Dialysis is needed when the kidneys fail completely, which works to remove waste but cannot replace all kidney functions.





![CKD
• Chronic kidney disease (CKD), also known
as chronic renal disease, is a progressive loss
in renal function over a period of months or years. The
symptoms of worsening kidney function are unspecific,
and might include feeling generally unwell and
experiencing a reduced appetite. Often, chronic kidney
disease is diagnosed as a result of screening of
people known to be at risk of kidney problems, such
as those with high blood pressure or diabetesand
those with a blood relative with chronic kidney
disease. Chronic kidney disease may also be
identified when it leads to one of its recognized
complications, such as cardiovascular
disease, anemia or pericarditis.[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/18-kidneyproblemsanddialysis-120106181129-phpapp02/85/18-kidney-problems-and-dialysis-9-320.jpg)