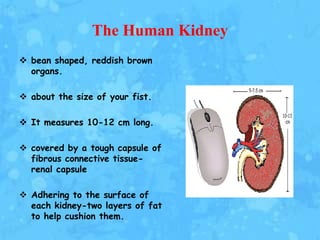
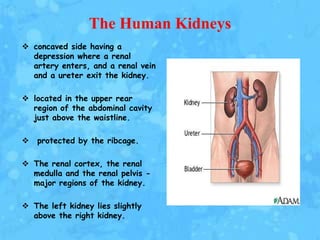
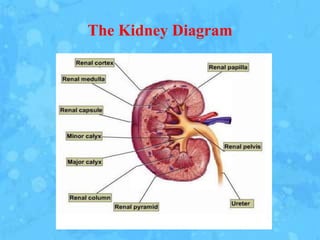
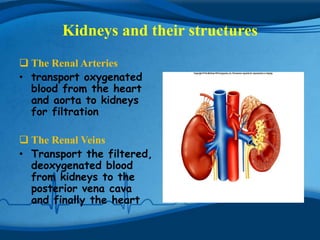
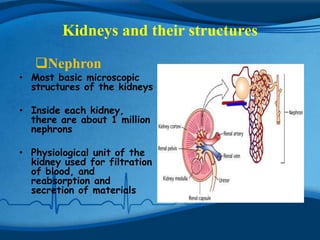
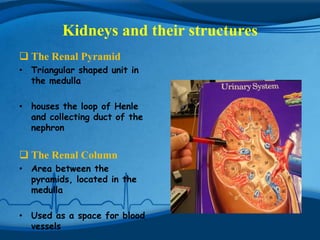
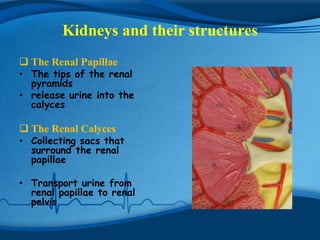
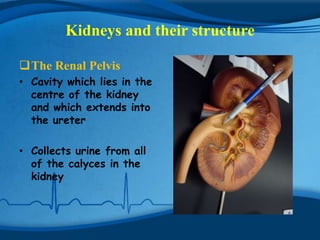
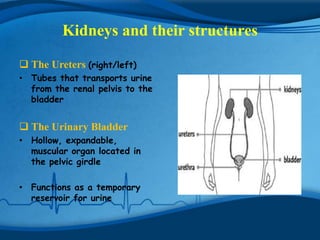
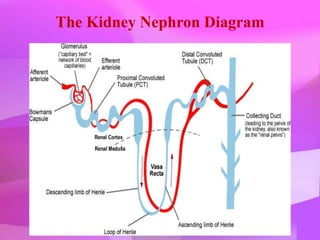
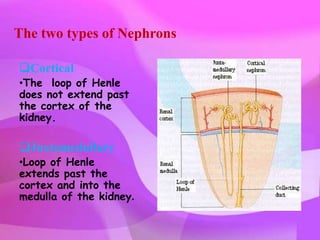
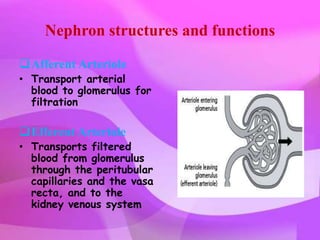
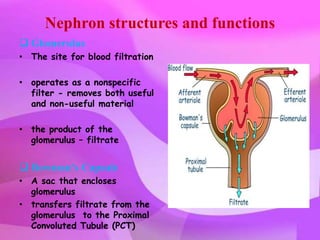
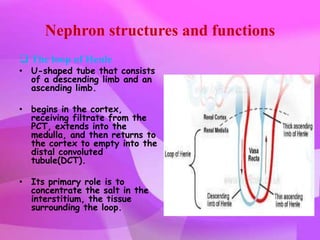
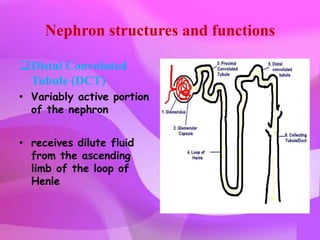
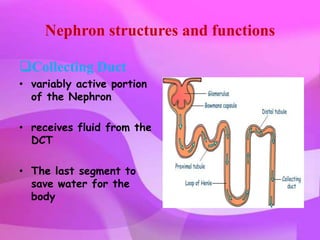
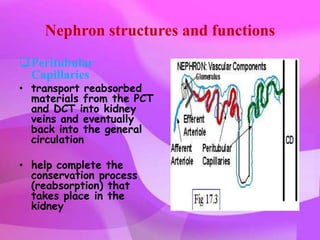
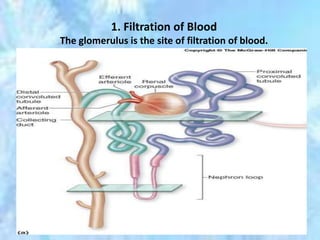
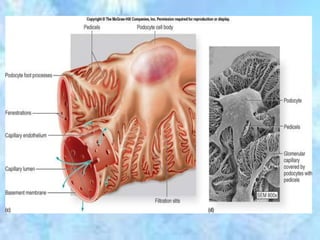
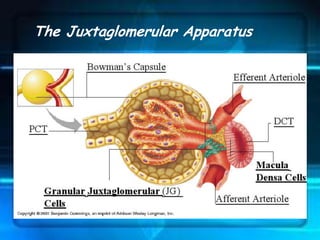
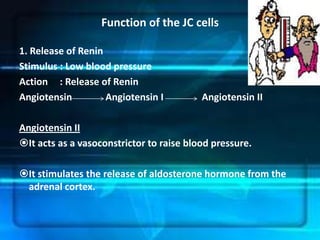
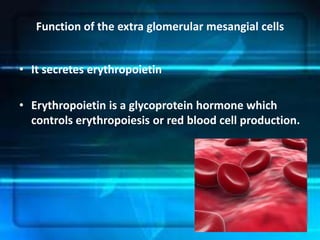
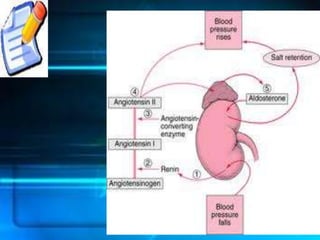
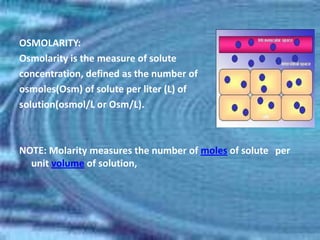
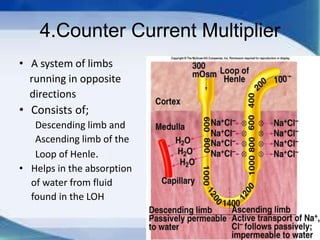
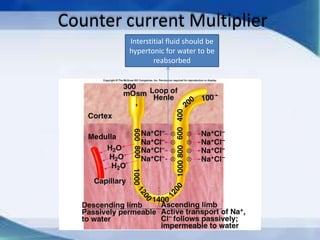
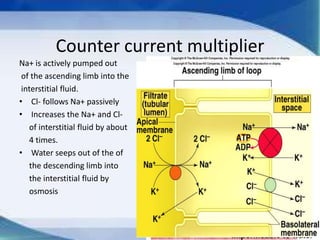
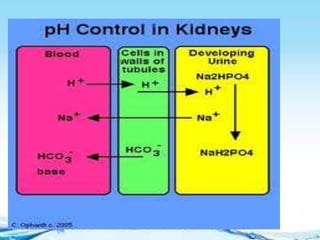
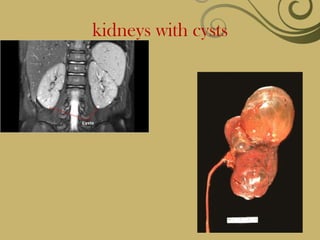
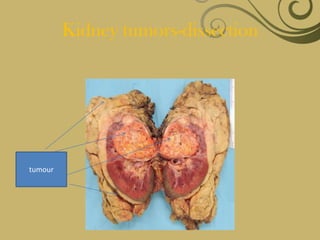
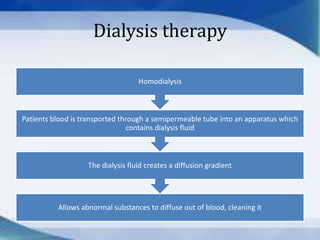
The kidneys are essential excretory organs that filter waste from the blood to produce urine. The kidneys contain over 1 million tiny filtering units called nephrons. Blood enters nephrons via the glomerulus and is filtered, then most water and nutrients are reabsorbed. The loop of Henle and countercurrent mechanism allow concentration of urine. Hormones regulate water and electrolyte balance. The kidneys maintain acid-base balance and blood pressure while filtering wastes and drugs for excretion. Kidney disorders occur if filtration, reabsorption or other functions are disrupted.