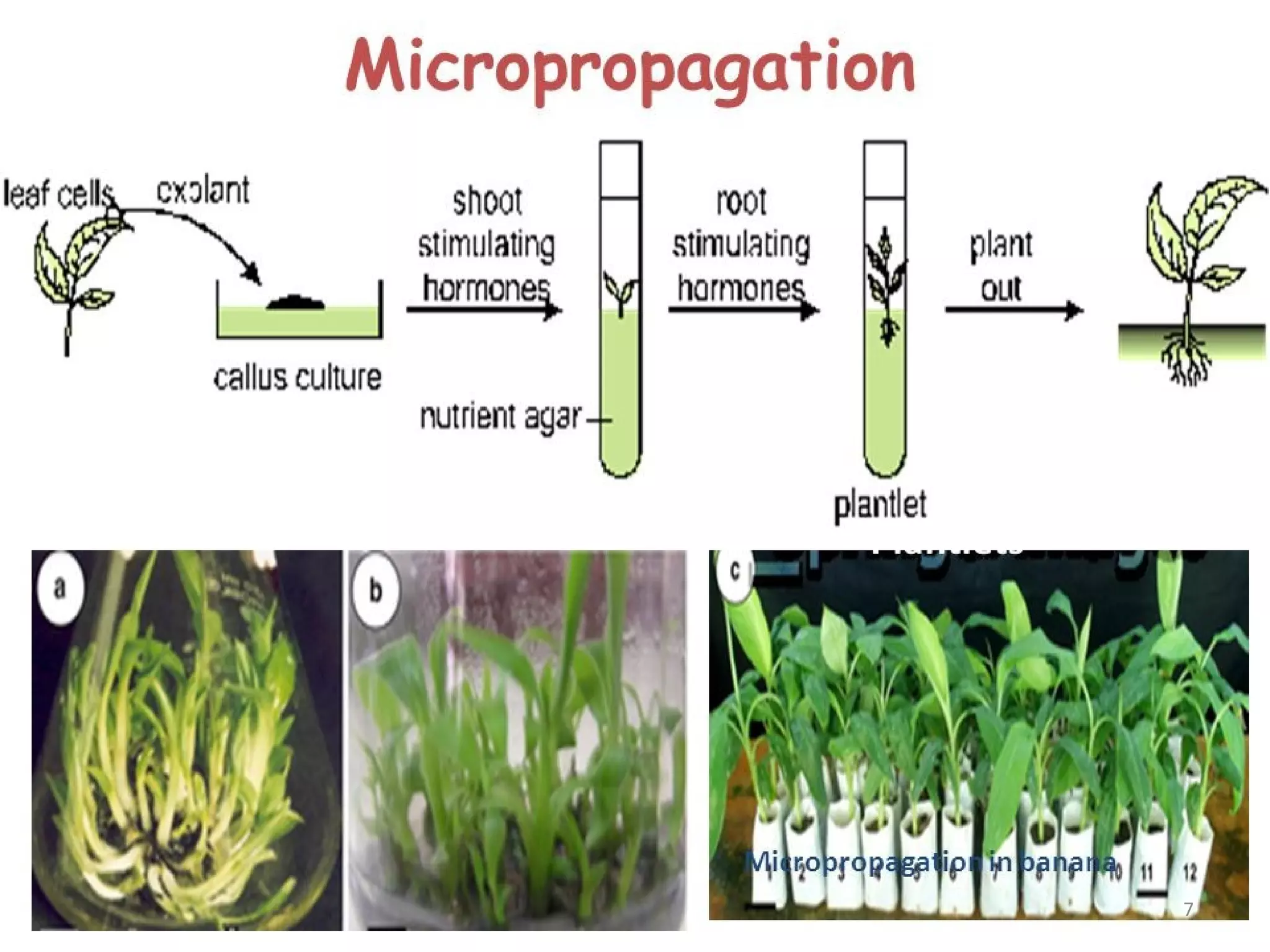
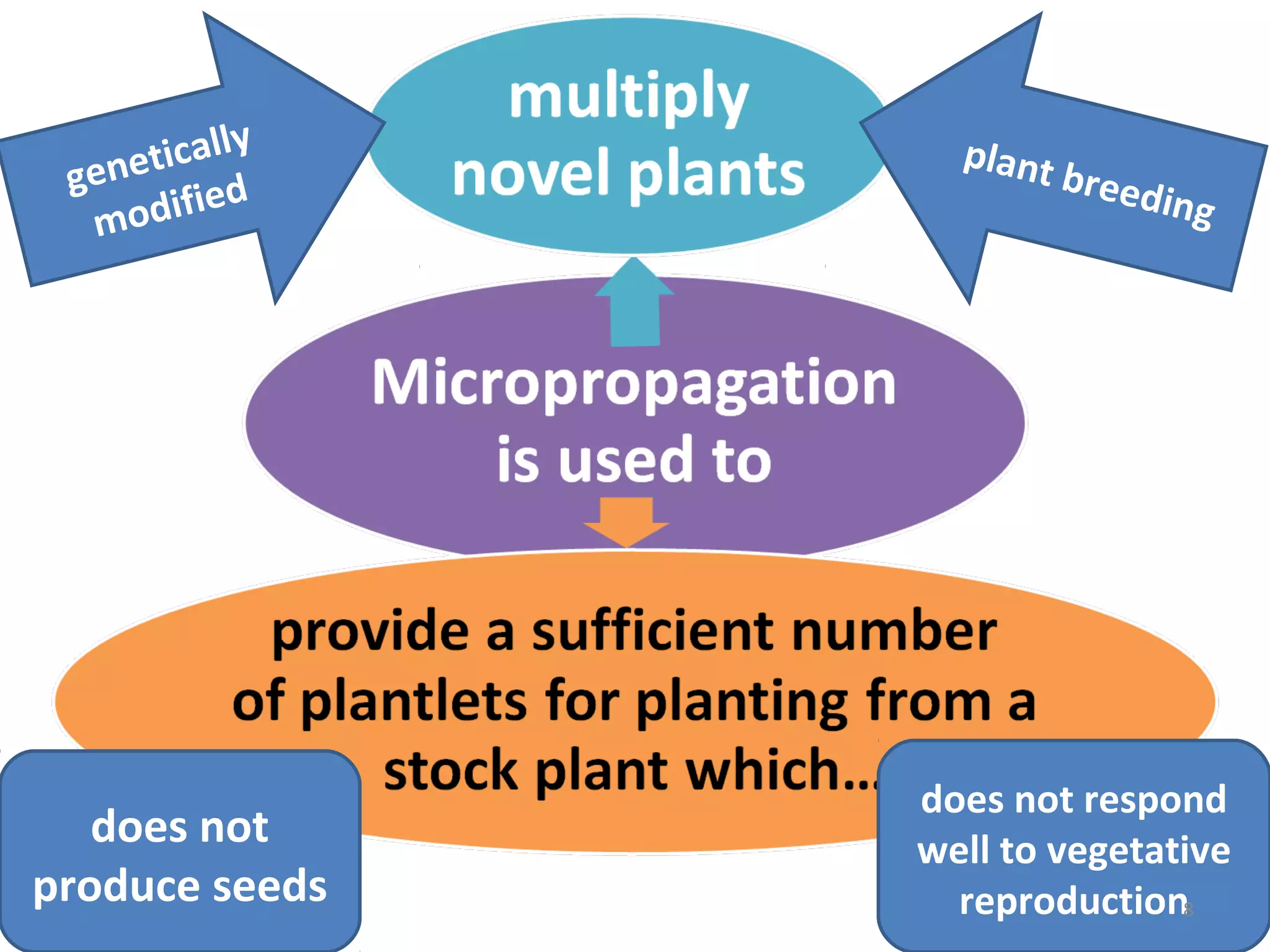
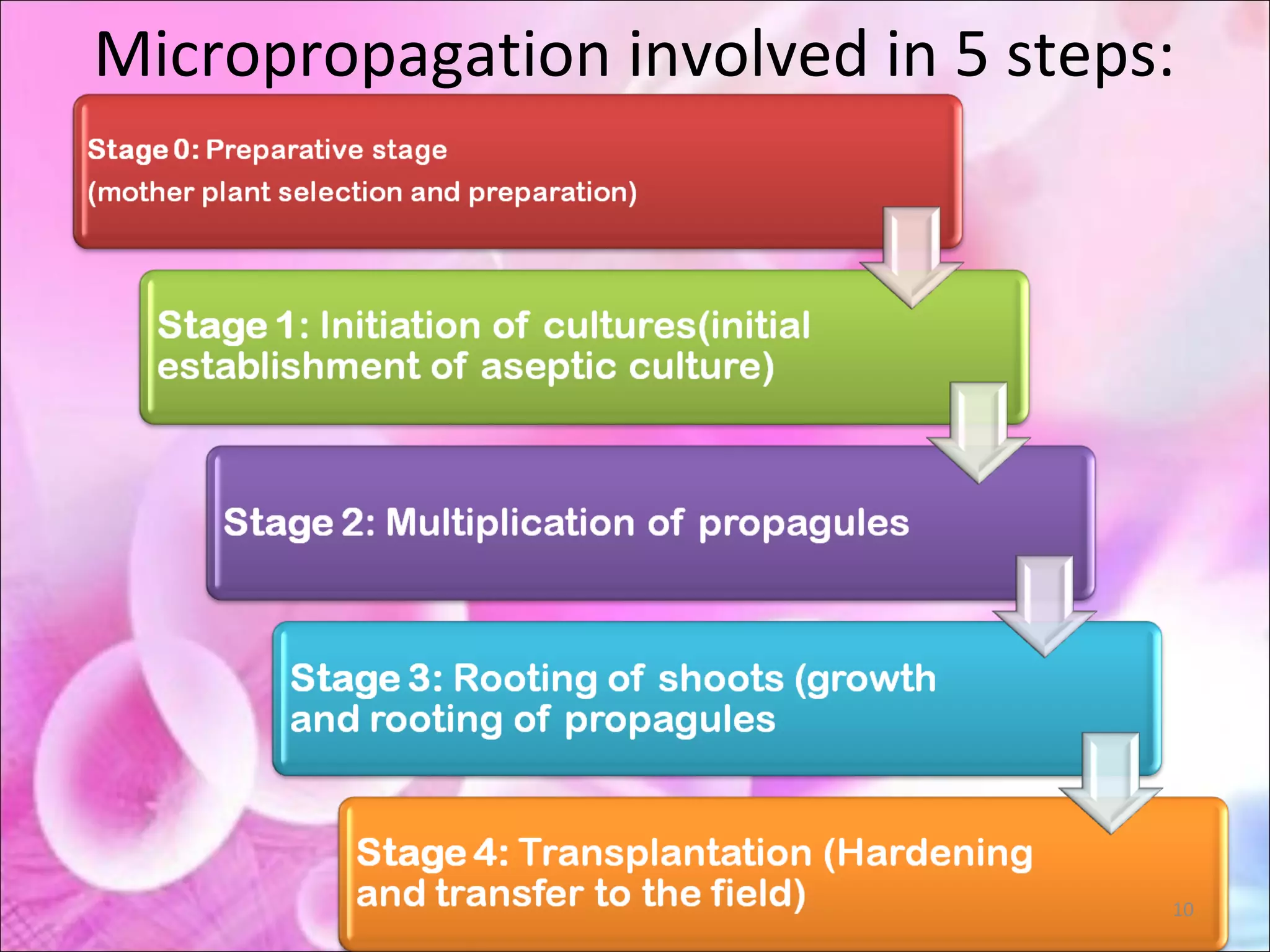
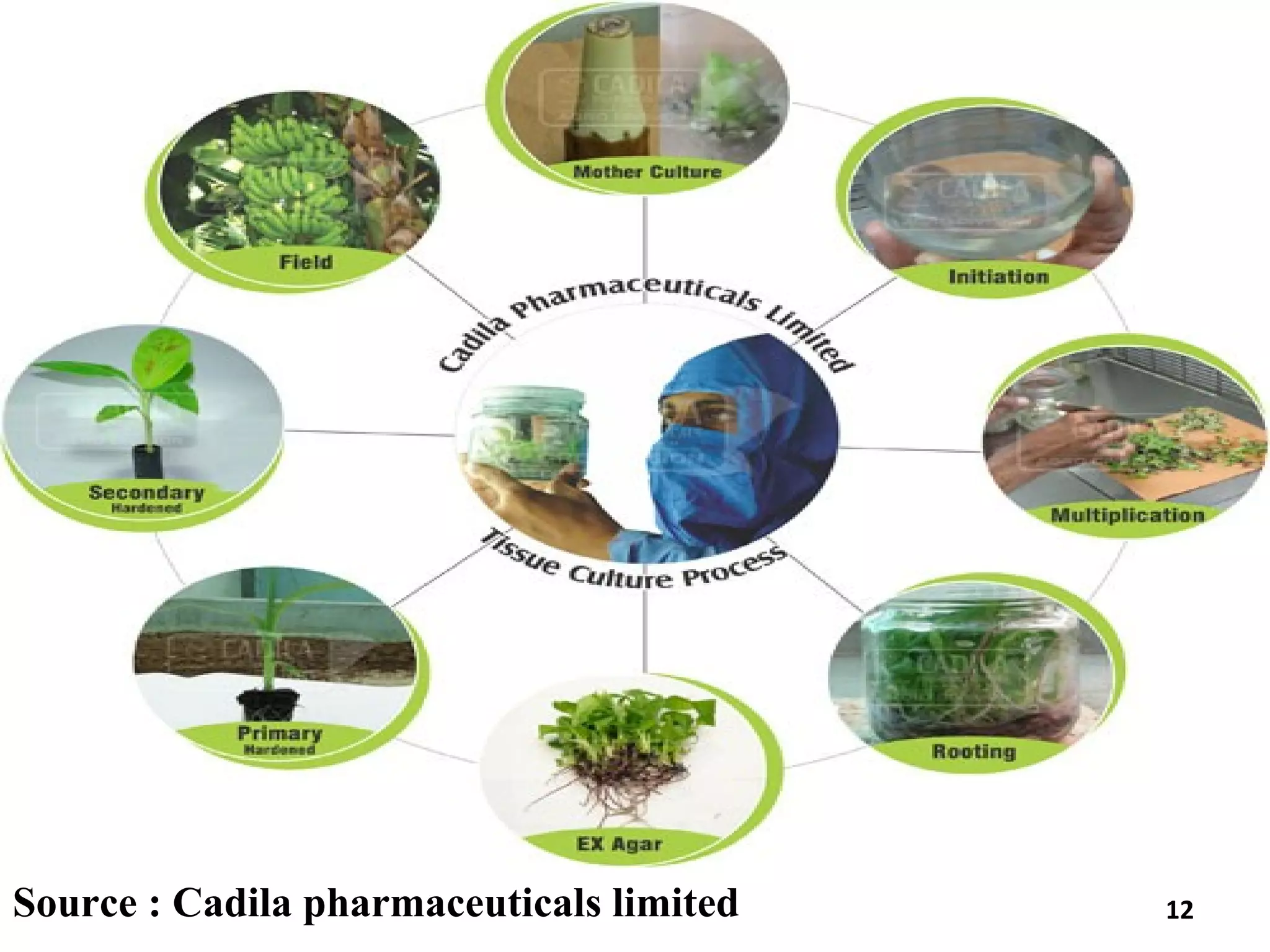
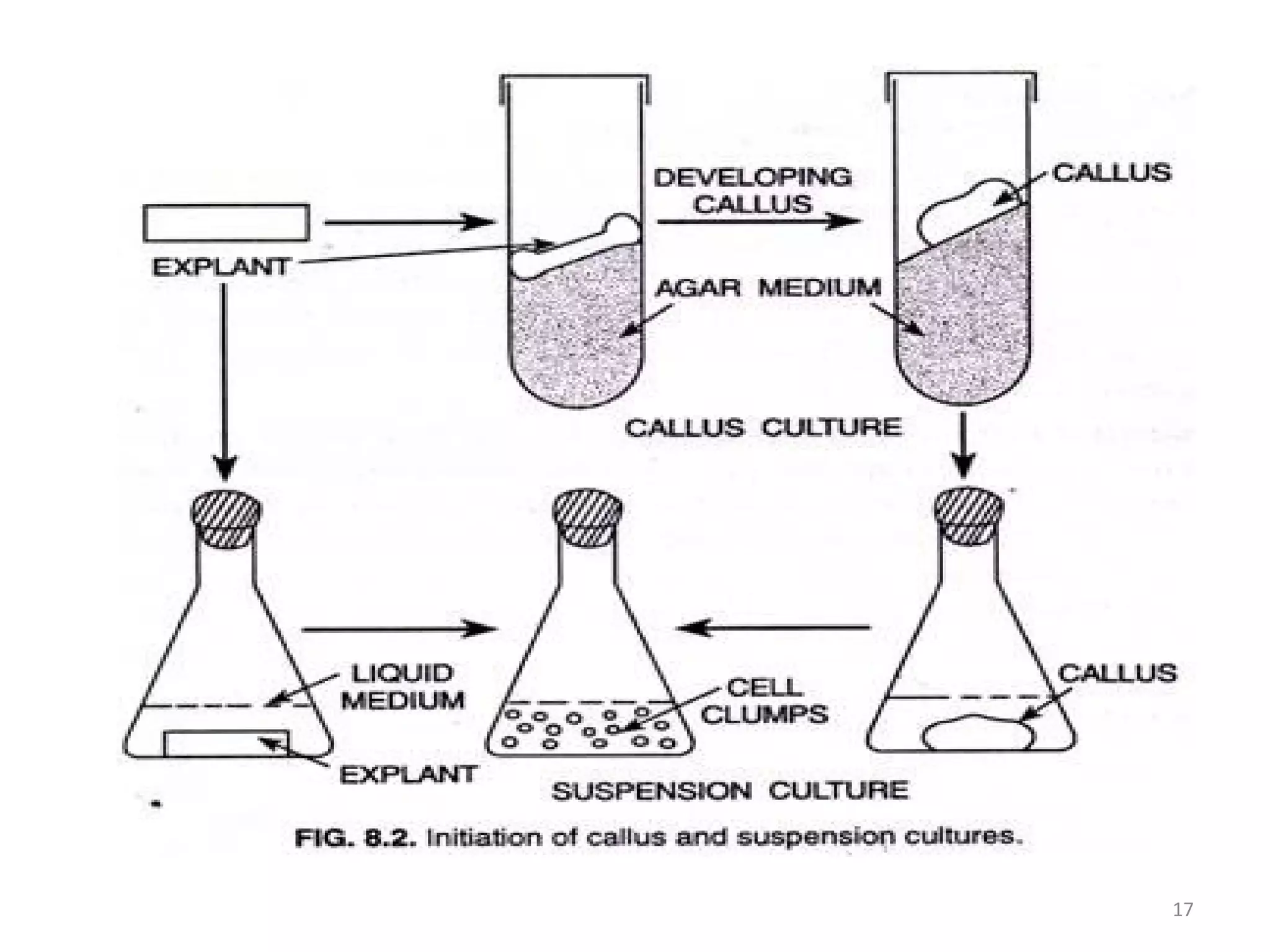
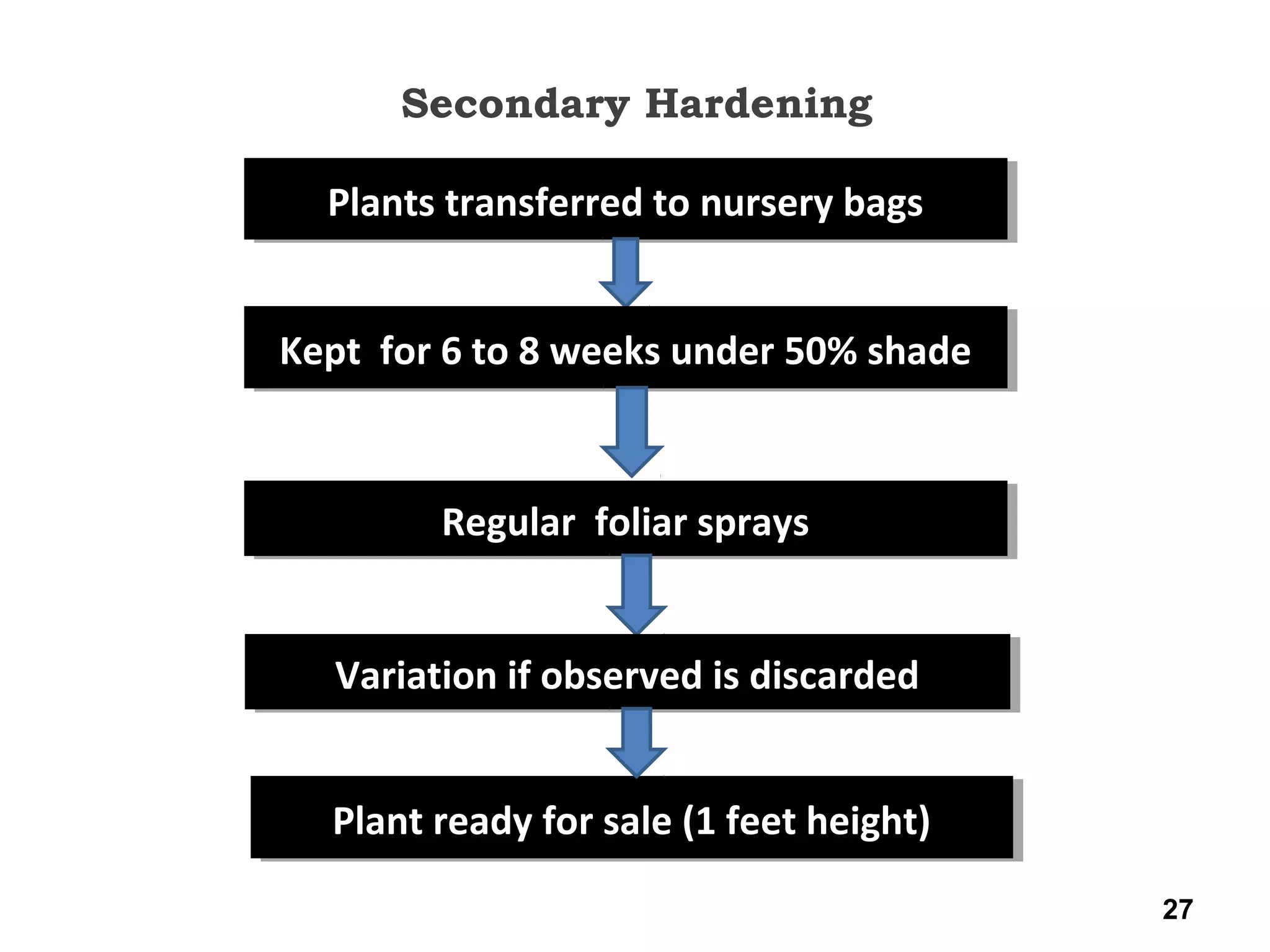
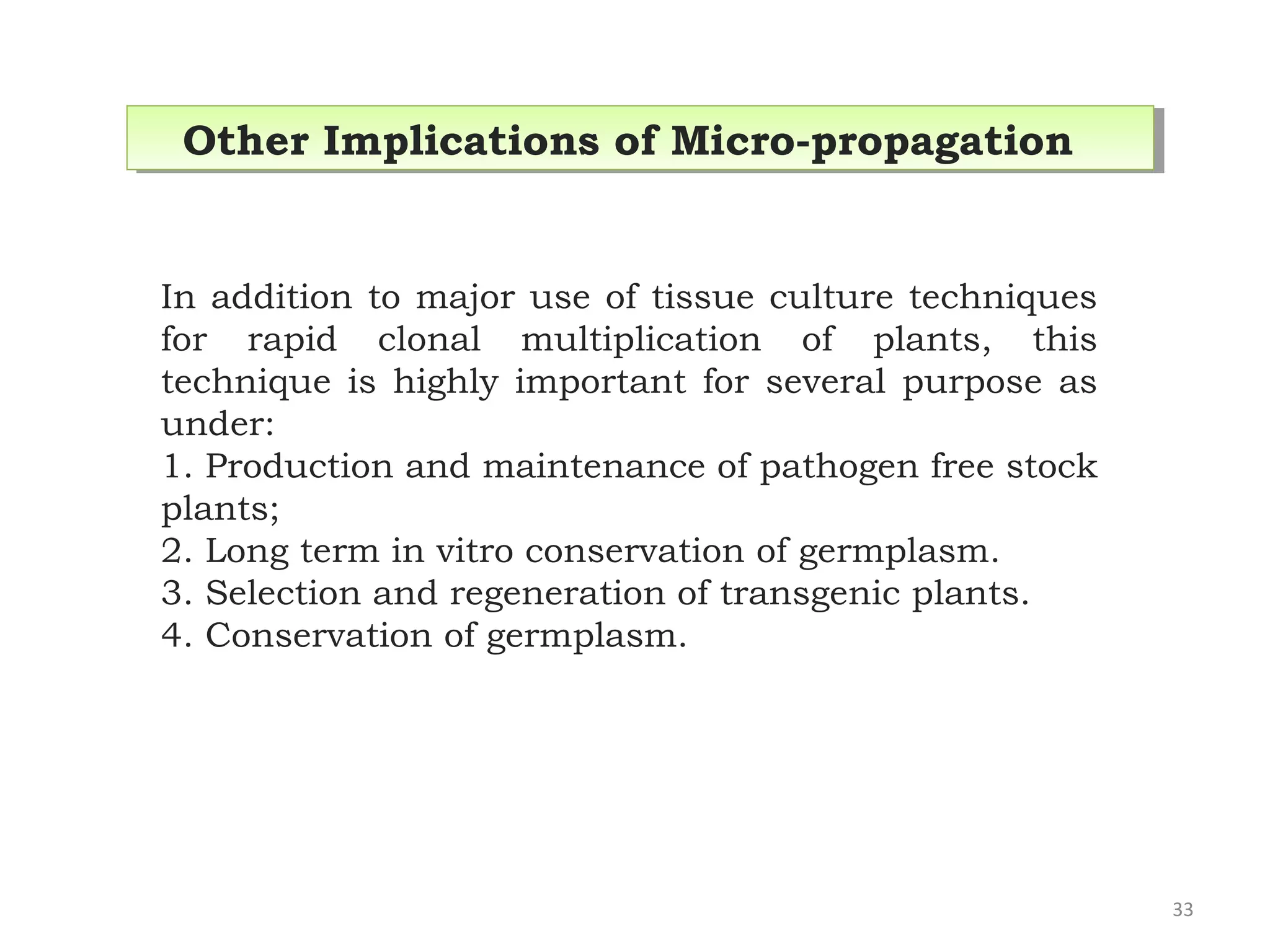
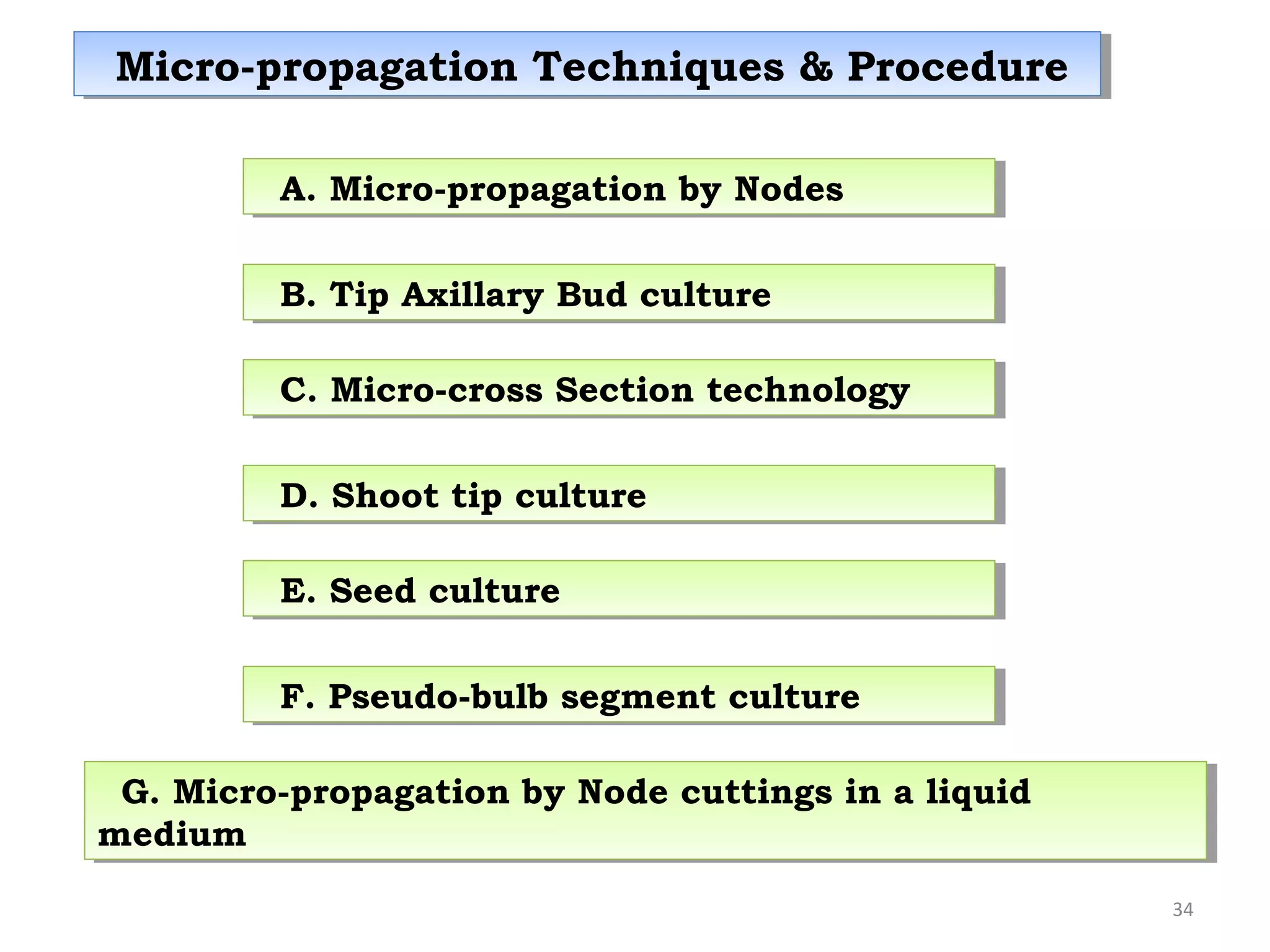
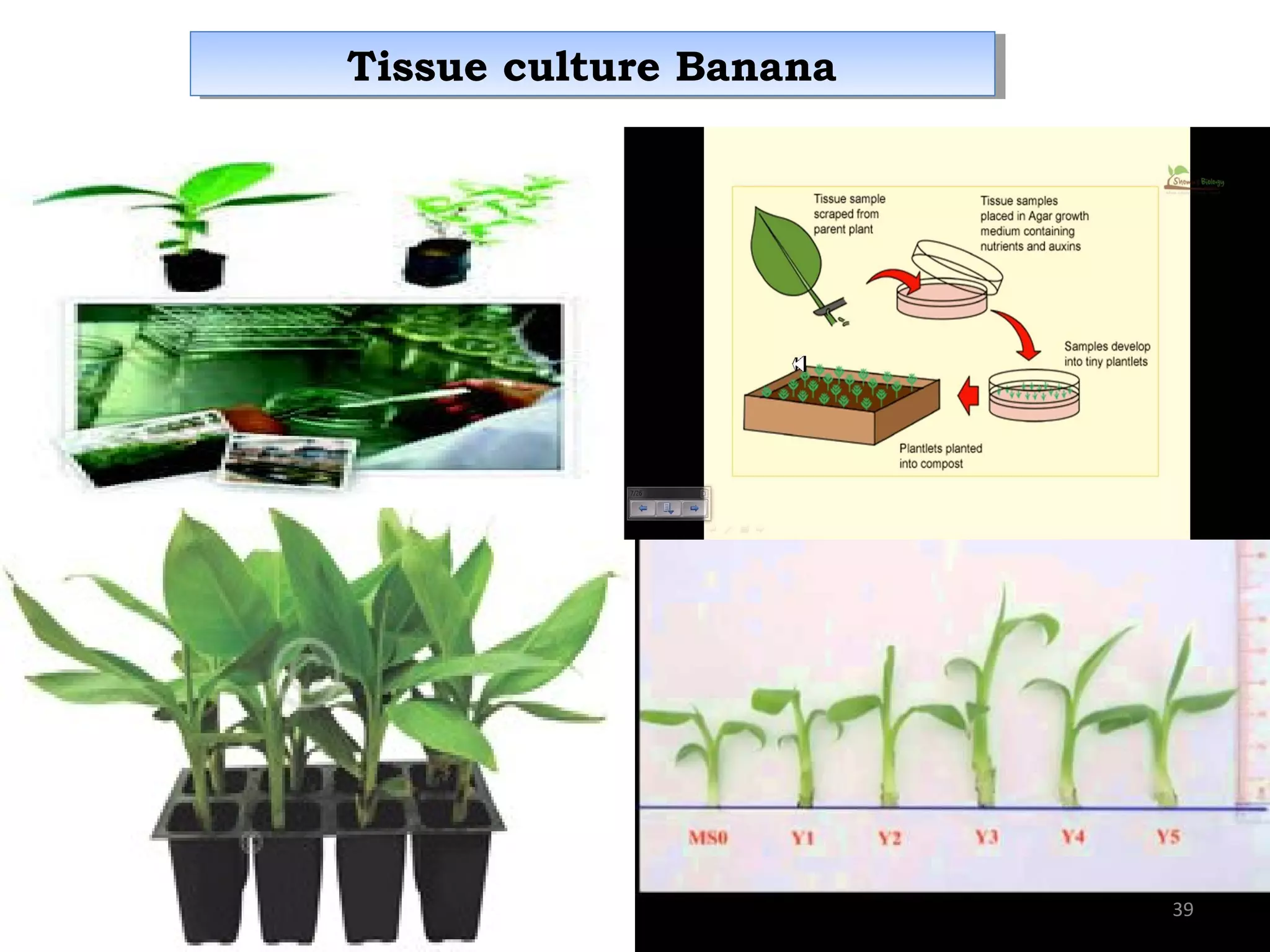
Micropropagation is a tissue culture technique where plantlets are regenerated from small plant parts like shoot tips, nodes, and meristems. It allows for the rapid multiplication of plant materials in a relatively short period of time compared to traditional propagation methods. The process involves sterilizing and culturing explants on nutrient media, multiplying shoots through subculture, rooting the shoots, and acclimatizing the plantlets. Micropropagation has various advantages like producing disease-free plants, conserving germplasm, and facilitating the export of plants. It has been commercialized for many horticultural crops in India like banana, citrus, grapes, guava, papaya, and strawberry through research institutes.