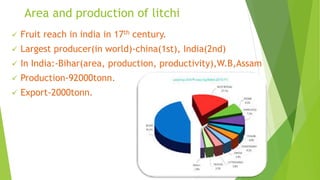
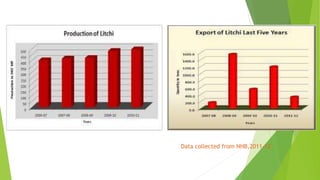
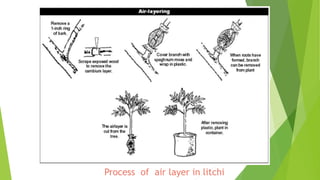
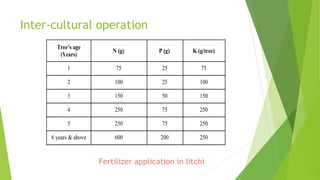
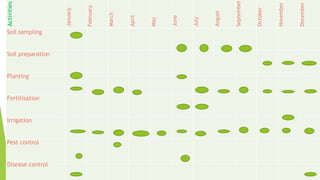
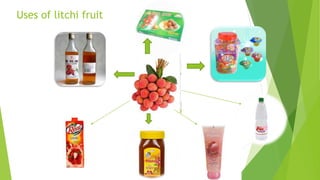
This document provides information about litchi cultivation. It discusses the botanical description of litchi, including its origin in South China. It details litchi production in India, with Bihar being the largest producer. The document outlines optimal climate and soil conditions for litchi growth. It also describes propagation methods, cultivation practices like planting, irrigation, fertilization and pest management. Maturity indices, harvesting, yield and storage of litchi are summarized. Finally, the document lists some future directions to improve litchi cultivation.