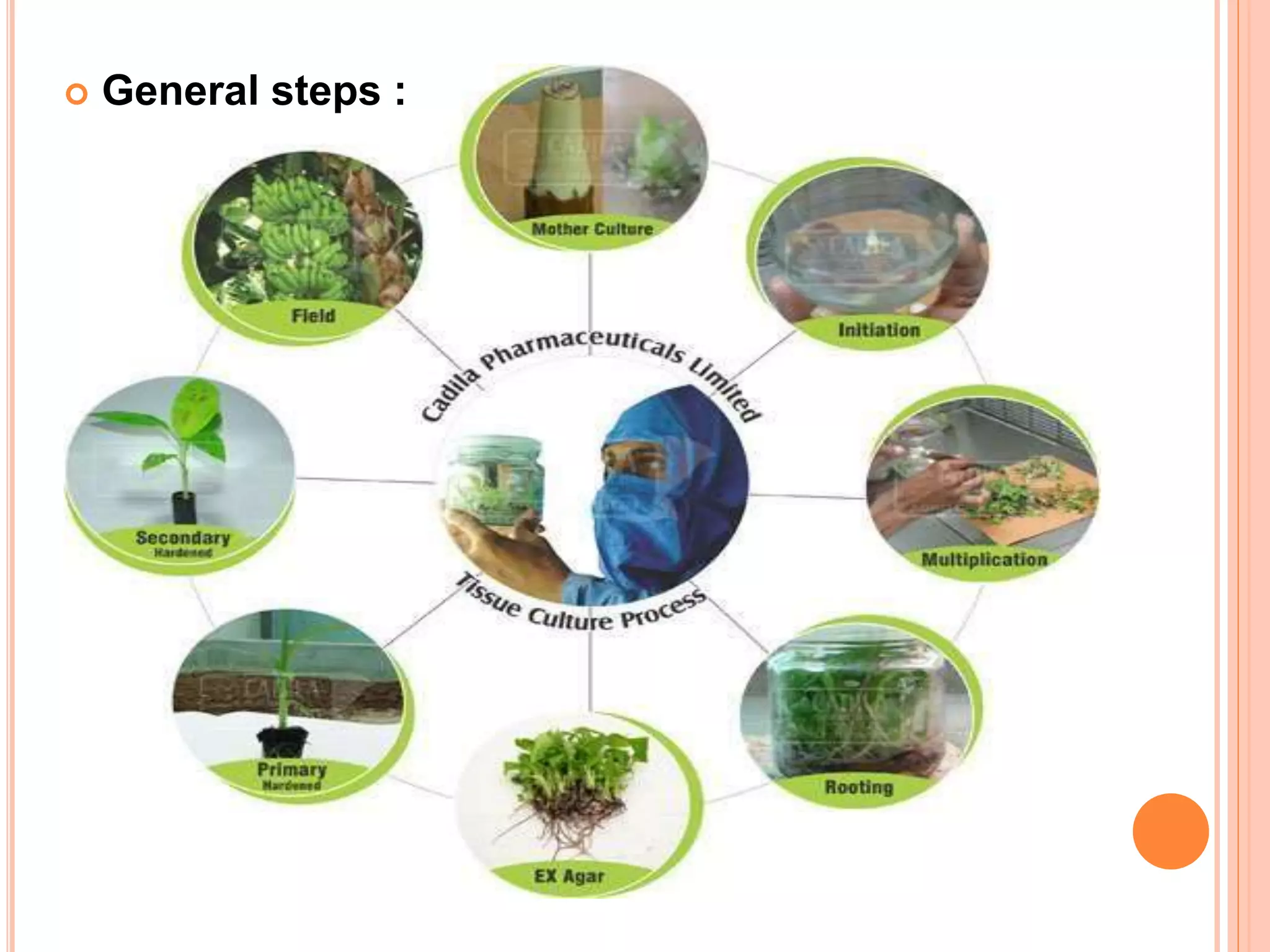
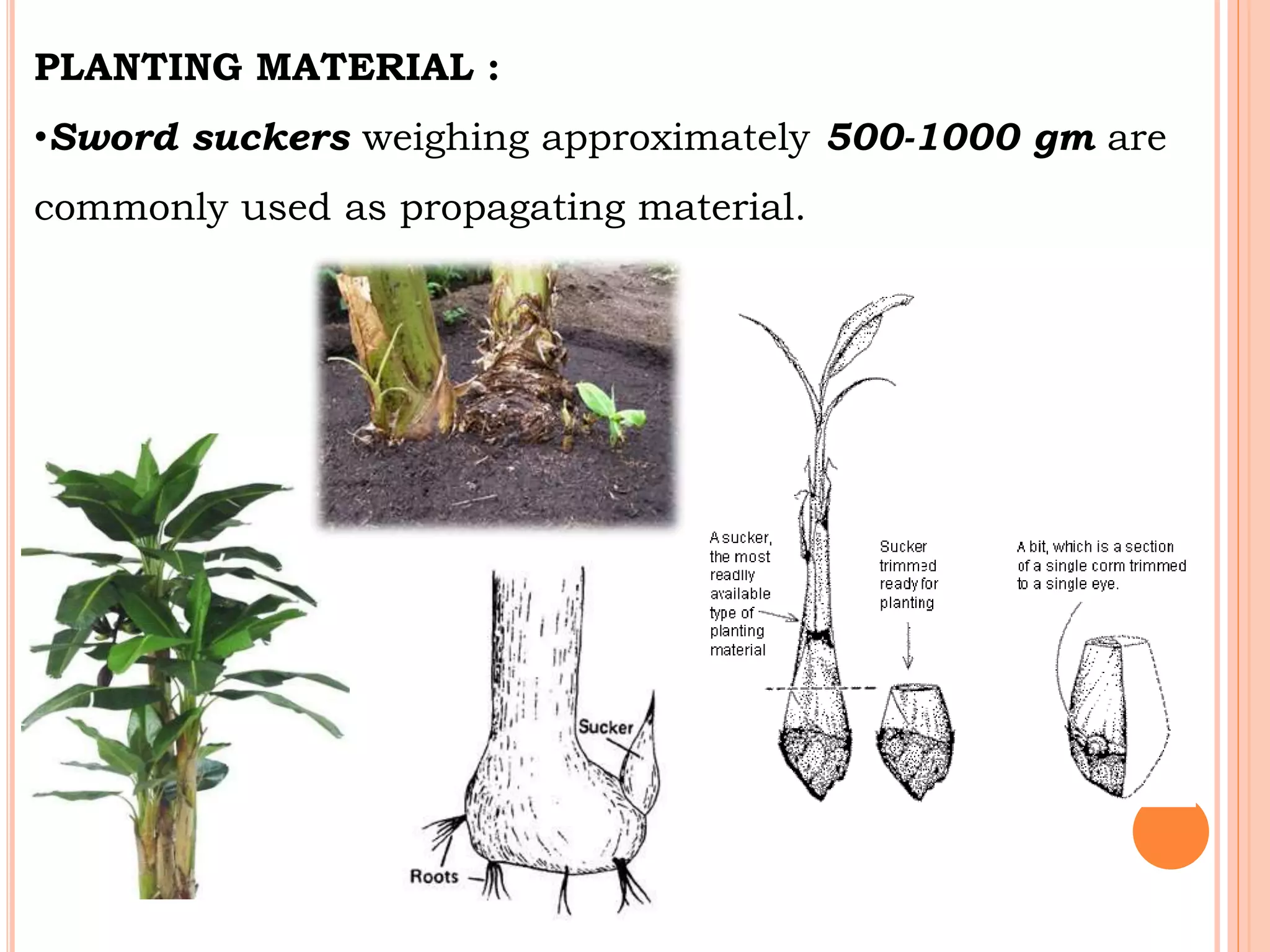
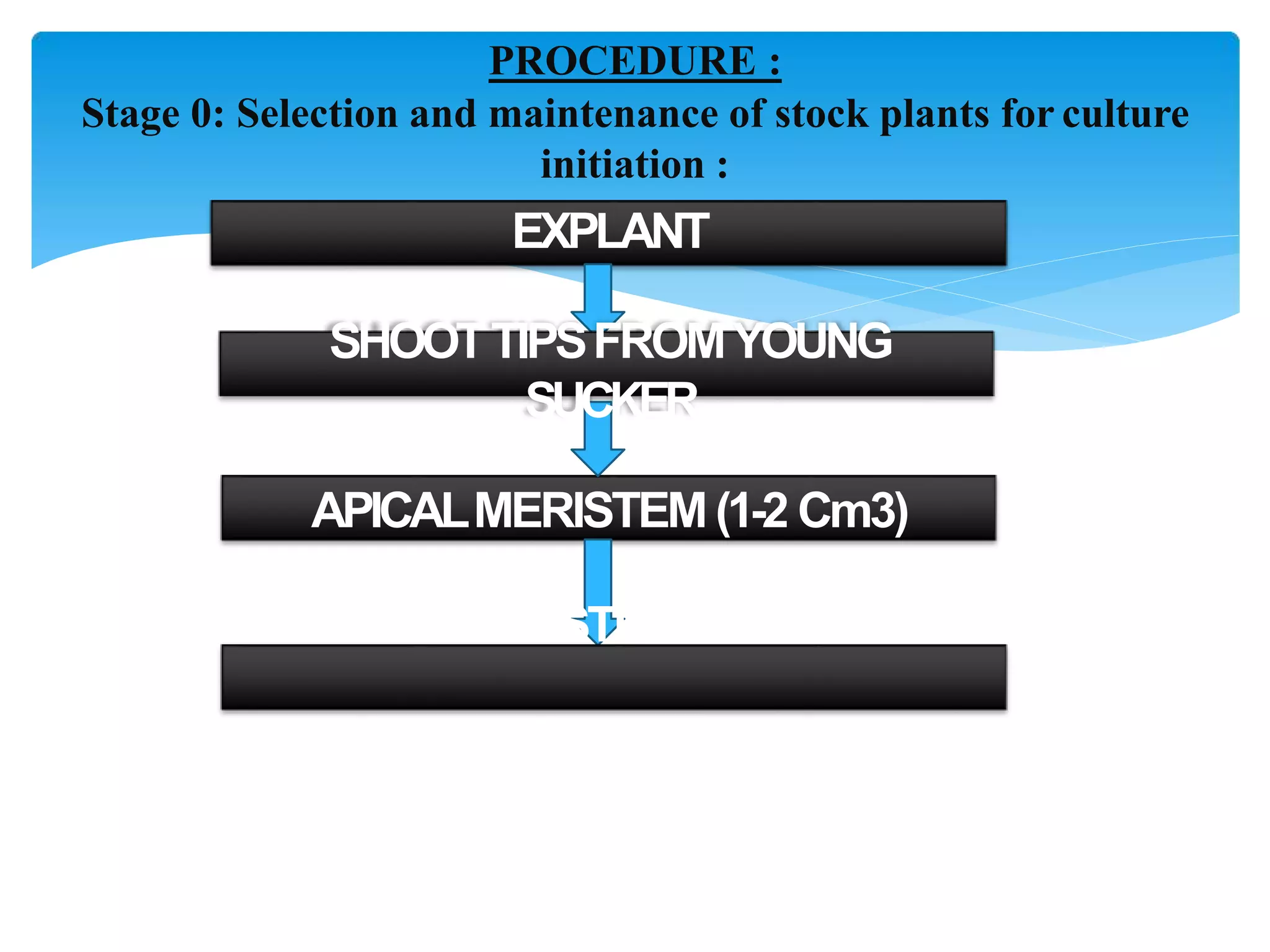
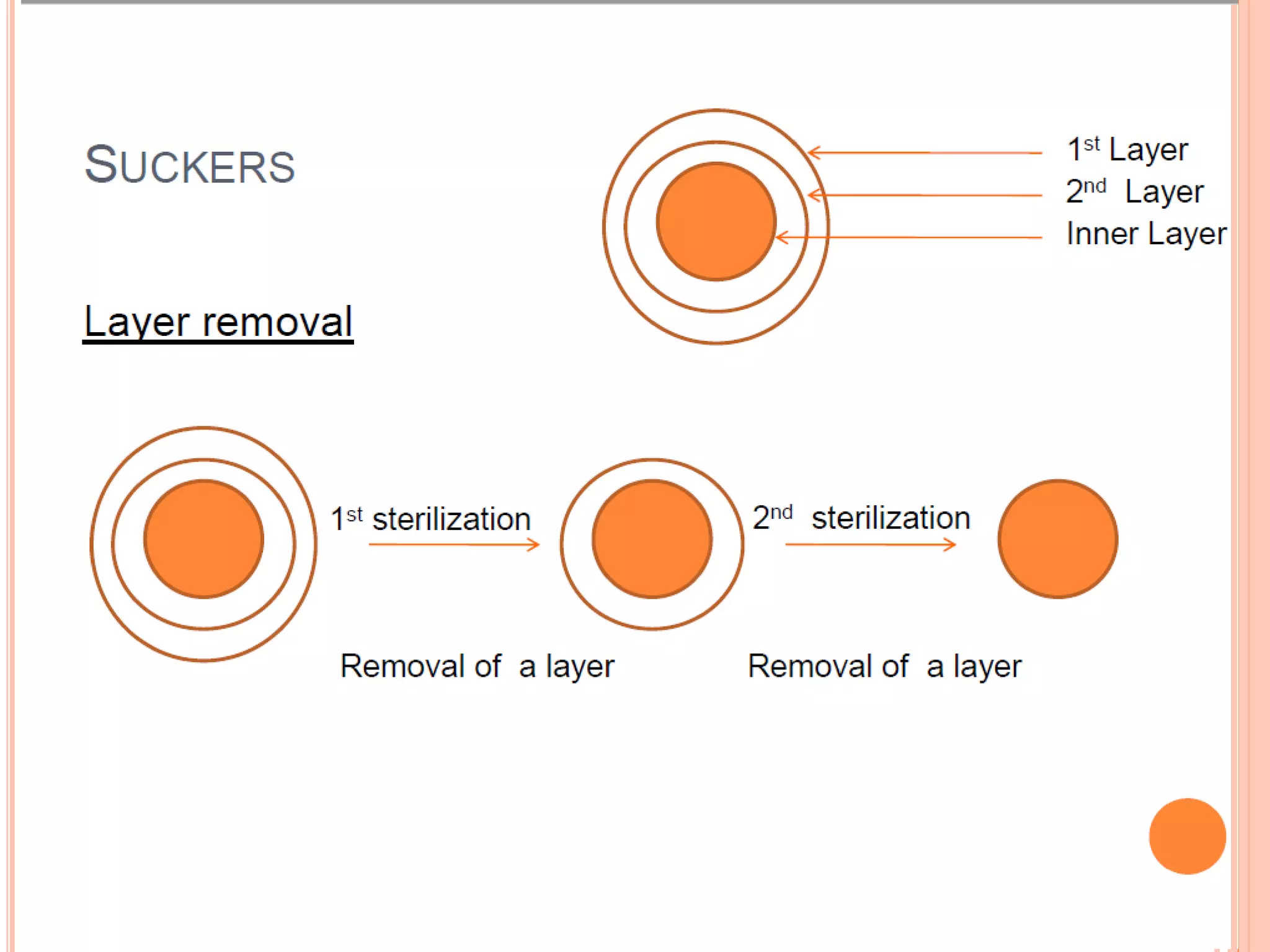
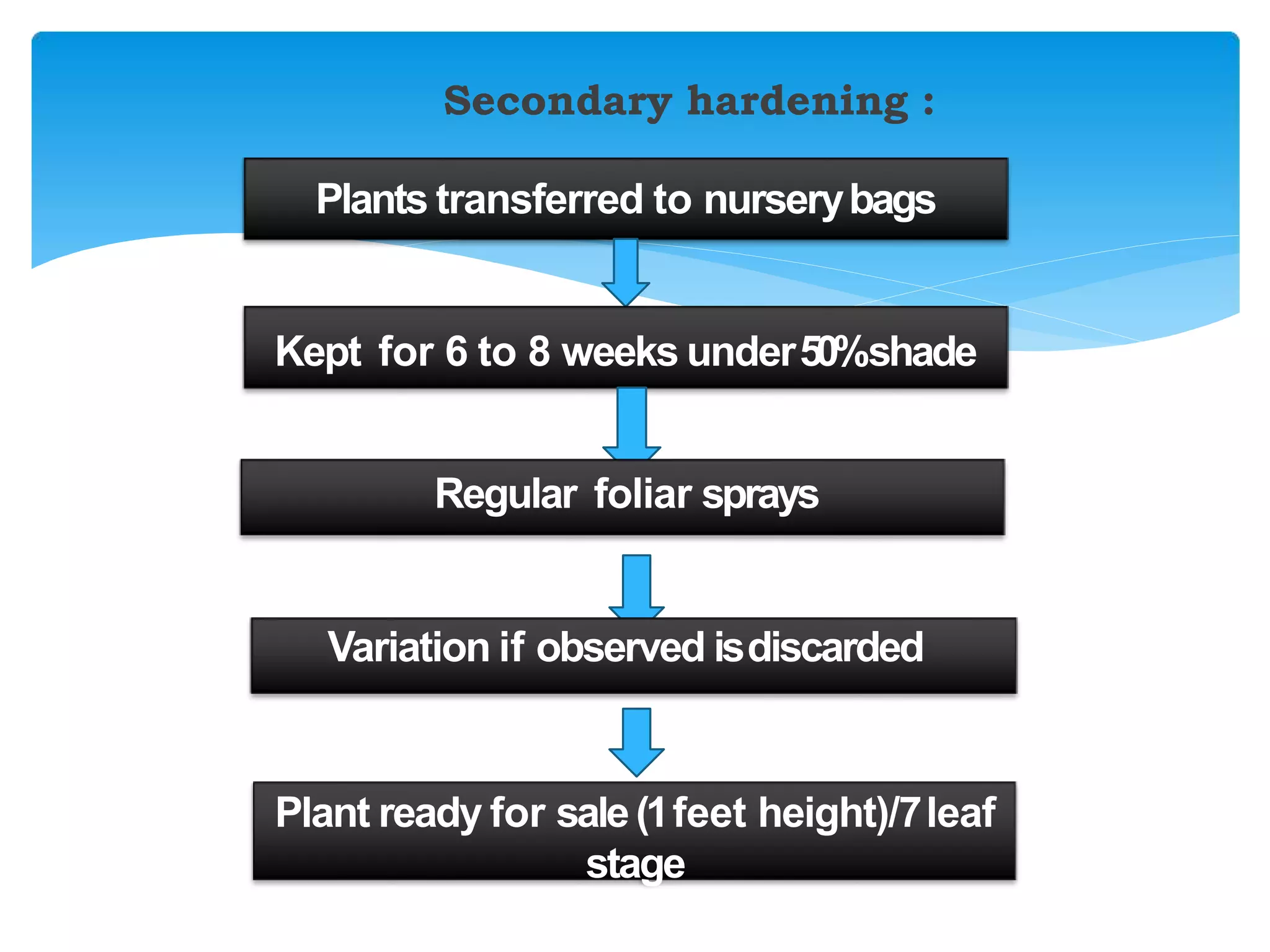
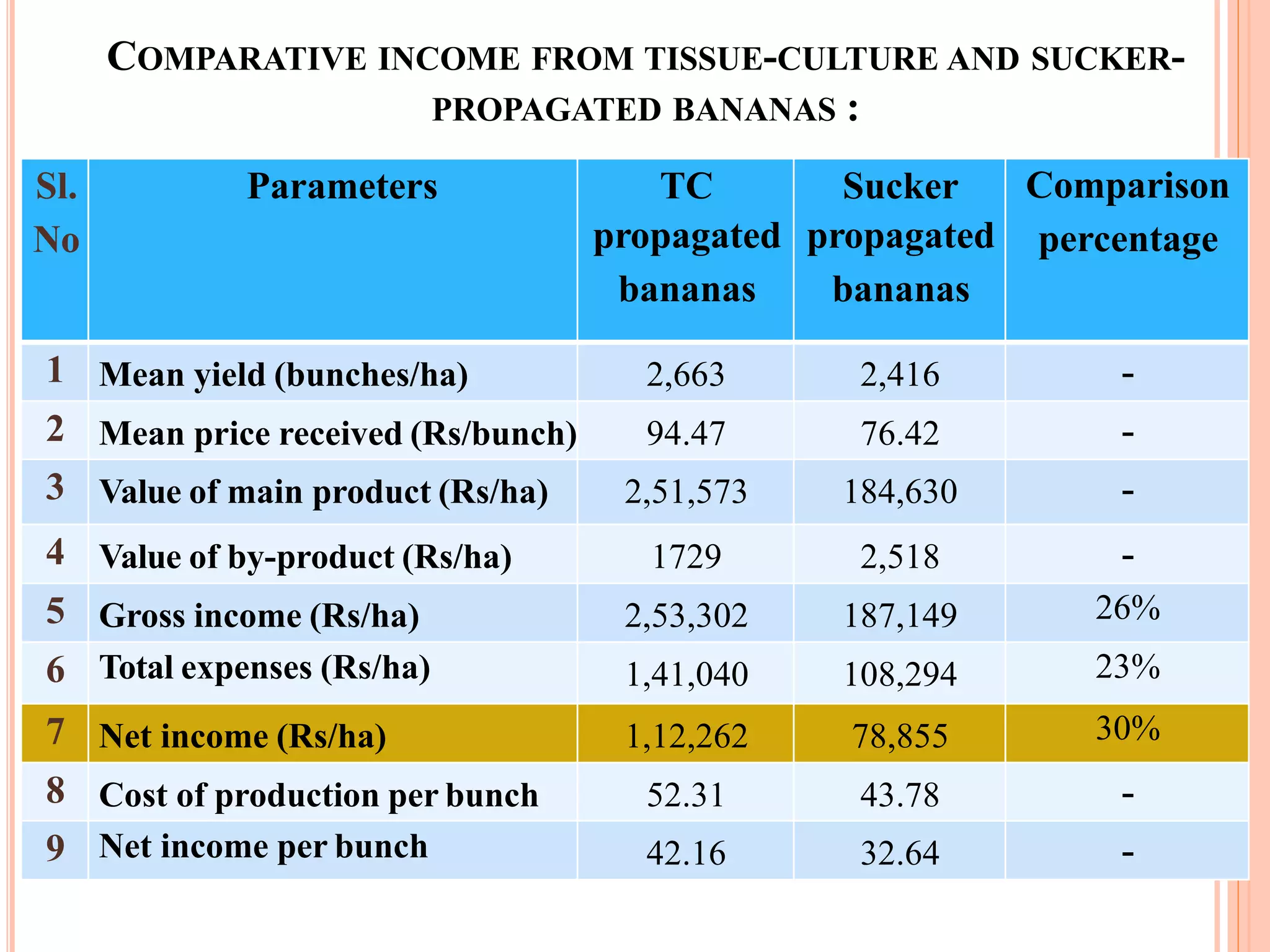
Micropropagation is a technique used to rapidly multiply plant materials under sterile conditions. The document discusses micropropagation of banana and pomegranate. For banana, tissue culture is used to produce disease-free planting materials for year-round availability and improved yields. Explants from banana suckers are sterilized and cultured on media to induce shoot formation. Shoots are then rooted and hardened for planting. For pomegranate, shoot tips are used as explants and cultured on MS media supplemented with growth regulators and compounds. This allows for mass production of true-to-type pomegranate plants.