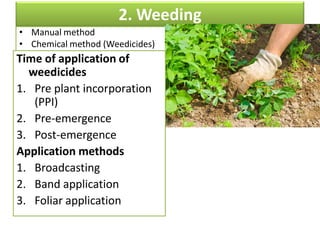
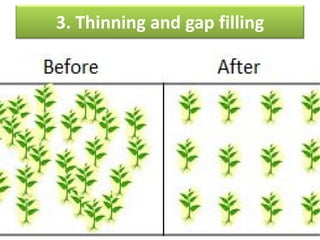
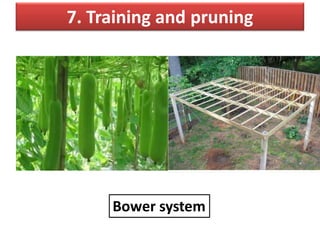
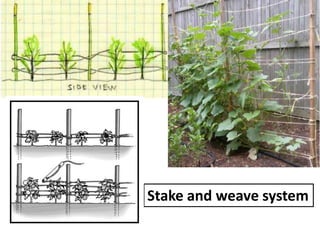
This document provides an overview of 14 intercultural operations for vegetable crops: 1) transplanting and hardening off, 2) weeding, 3) thinning and gap filling, 4) irrigation, 5) staking, 6) manures and fertilizer application, 7) training and pruning, 8) mulching, 9) application of plant growth regulators, 10) insect pest and disease control, 11) earthing up, 12) dehaulming, 13) blanching, and 14) nipping. For each operation, common techniques are described, such as manual and chemical weeding methods, types of irrigation and fertilization, and controls for insects and diseases.