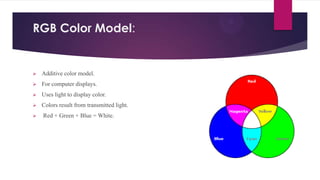
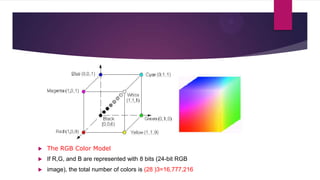
Color is a sensation produced by the human visual system. The two most common color models are RGB, used for computer displays, and CMYK, used for printing. RGB is an additive model that uses combinations of red, green, and blue light to produce colors. CMYK is a subtractive model that uses combinations of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks to produce colors. Both models represent colors using three numeric values corresponding to the intensities of the primary colors.