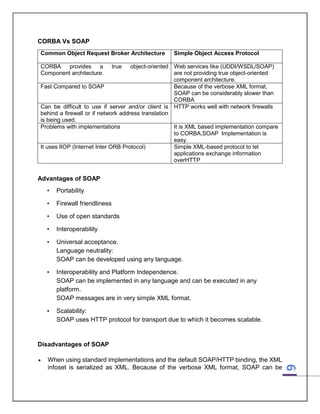
SOAP is a protocol specification for exchanging structured information between applications, typically in a decentralized, distributed environment. It uses XML as its message format and relies on other protocols like HTTP for message negotiation and transmission.
SOAP has a basic structure that includes an envelope, header, body, and optional fault element. It allows for lightweight communication between applications across different operating systems and programming languages. While it provides advantages like portability and interoperability through open standards, SOAP can be slower than other middleware technologies due to its verbose XML format.


![Introduction to SOAP
SOAP:
SOAP is a protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the
implementation of Web Services in computer networks. It relies on Extensible Markup
Language (XML) for its message format, and usually relies on other Application Layer
protocols, most notably Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Simple Mail Transfer
Protocol (SMTP), for message negotiation and transmission. The following is the structure
of SOAP Envelope,
It is important for application development to allow Internet
communication
between
programs.
Today's
applications
communicate using Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) between
objects like DCOM and CORBA, but HTTP was not designed for
this. RPC represents a compatibility and security problem;
firewalls and proxy servers will normally block this kind of traffic.
A better way to communicate between applications is over HTTP,
because HTTP is supported by all Internet browsers and servers. SOAP was created to
accomplish this. SOAP provides a way to communicate between applications running on
different operating systems, with different technologies and programming languages.
Where did it come from?
SOAP was designed as an object-access protocol in 1998 by Dave Winer, Don Box, Bob
Atkinson, and Mohsen Al-Ghosein for Microsoft where Atkinson and Al-Ghosein were
working at the time.[1] The SOAP specification is currently maintained by the XML Protocol
Working Group of the World Wide Web Consortium.
SOAP Specification
Lightweight communication protocol
•
For communication between application
•
Designed to communicate via HTTP
•
Not tied to any component technology and any programming language
•
Based on XML](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soapreport-140108055852-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-SOAP-3-320.jpg)
![Basic Structure of SOAP
Element
Description
Required
Envelope Identifies the XML document as a SOAP message.
Yes
Header
Contains header information.
No
Body
Contains call and response information.
Yes
Fault
Provides information about errors that occurred while processing the message.
No
SOAP Building Block [2]
SOAP Contains Four Parts
•
An extensible envelope expressing (mandatory)
•
•
who should deal with them,
•
•
what features and services are represented in a message;
Whether they are optional or mandatory.
A set of encoding rules for data (optional)
•
•
•
Exchange instances of application-defined data types and directed graphs
Uniform model for serializing abstract data models that cannot directly be
expressed in XML schema
A Convention for representation RPC (optional)
•
•
How to make calls and responses
A protocol binding to HTTP and HTTP-EF (optional)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soapreport-140108055852-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-SOAP-4-320.jpg)


![•
considerably slower than competing middleware technologies such as CORBA or ICE
This may not be an issue when only small messages are sent.[3] To improve
performance for the special case of XML with embedded binary objects, the Message
Transmission Optimization Mechanism was introduced.
Too much reliance on HTTP
•
Statelessness
•
Serialization by value and not by reference](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soapreport-140108055852-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-SOAP-8-320.jpg)
