Embed presentation
Downloaded 77 times





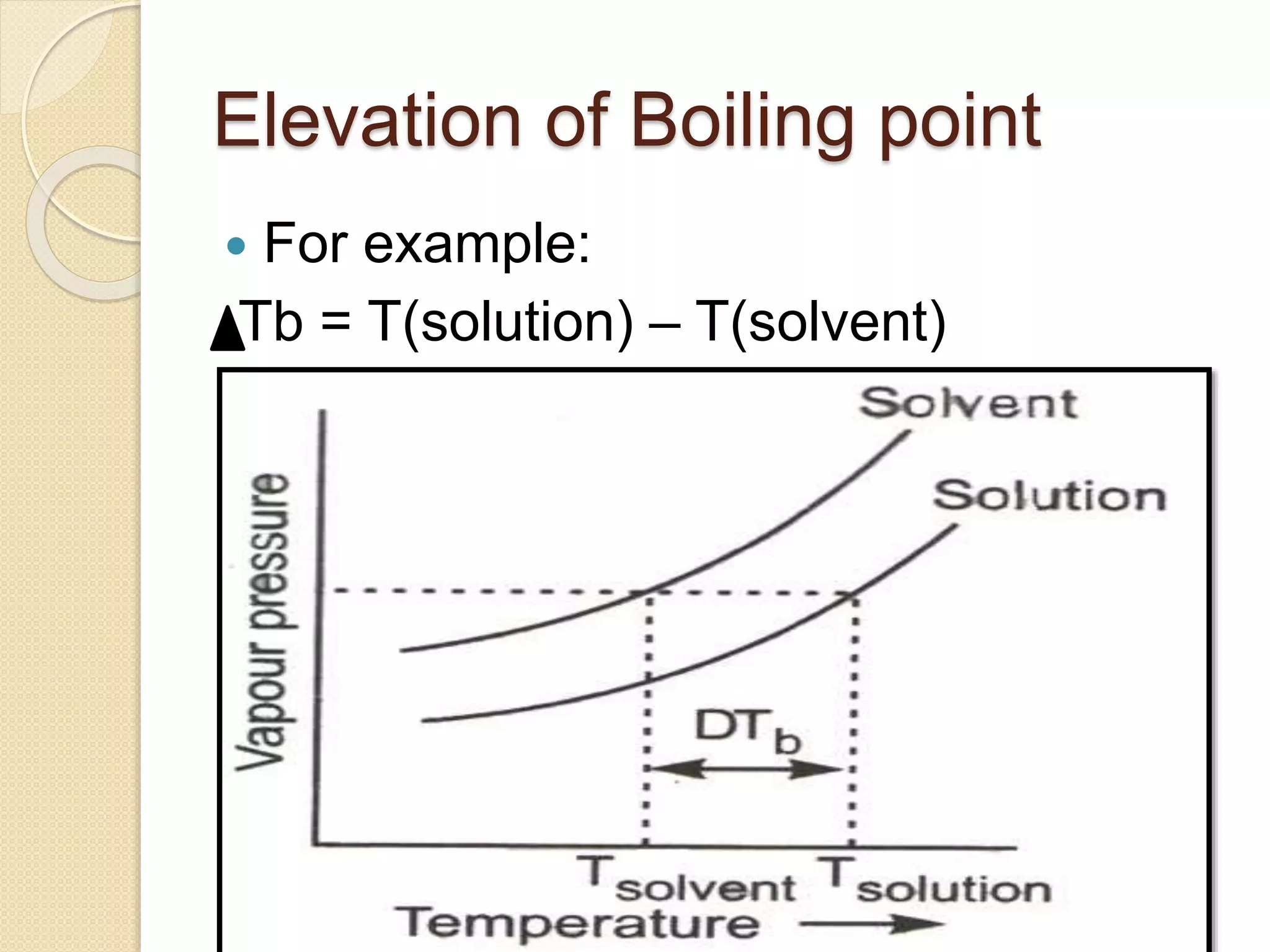





This document discusses the colligative property of boiling point elevation. It defines boiling point as the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure. When a non-volatile solute is added to a solvent, its boiling point increases from the original boiling point. This elevation in boiling point (ΔTb) is directly proportional to the molarity of the solution, as shown by the equation ΔTb = Kb × m, where Kb is the ebullioscopic constant specific to the solvent and m is the molality of the solution. The increased boiling point is due to the solute particles interfering with the vaporization of the solvent molecules.










