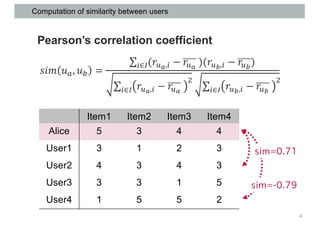
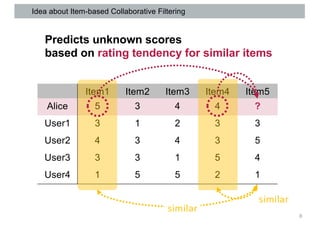
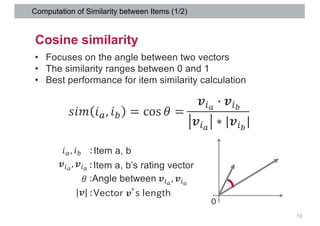
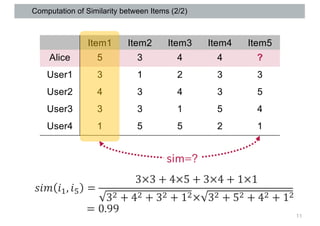
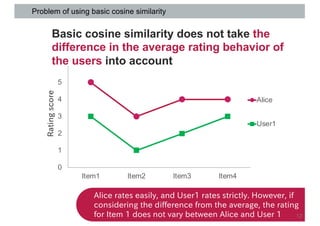
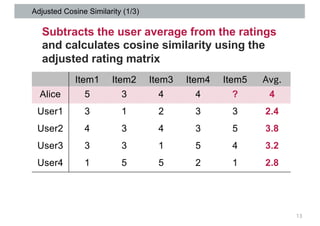
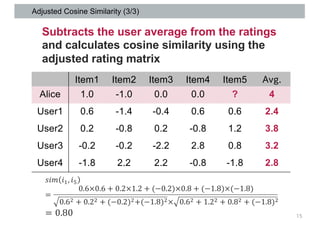
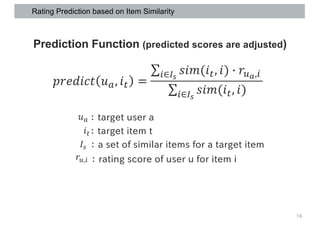
This document discusses item-based collaborative filtering for recommender systems. It describes how item-based collaborative filtering works by predicting a target user's rating for an item based on the ratings of similar items. It highlights advantages over user-based filtering like lower computational cost and more stable similarity computations. Key aspects covered include using cosine similarity to calculate item similarities, adjusting for individual rating biases, selecting the top K similar items, and predicting ratings based on similar items' ratings.