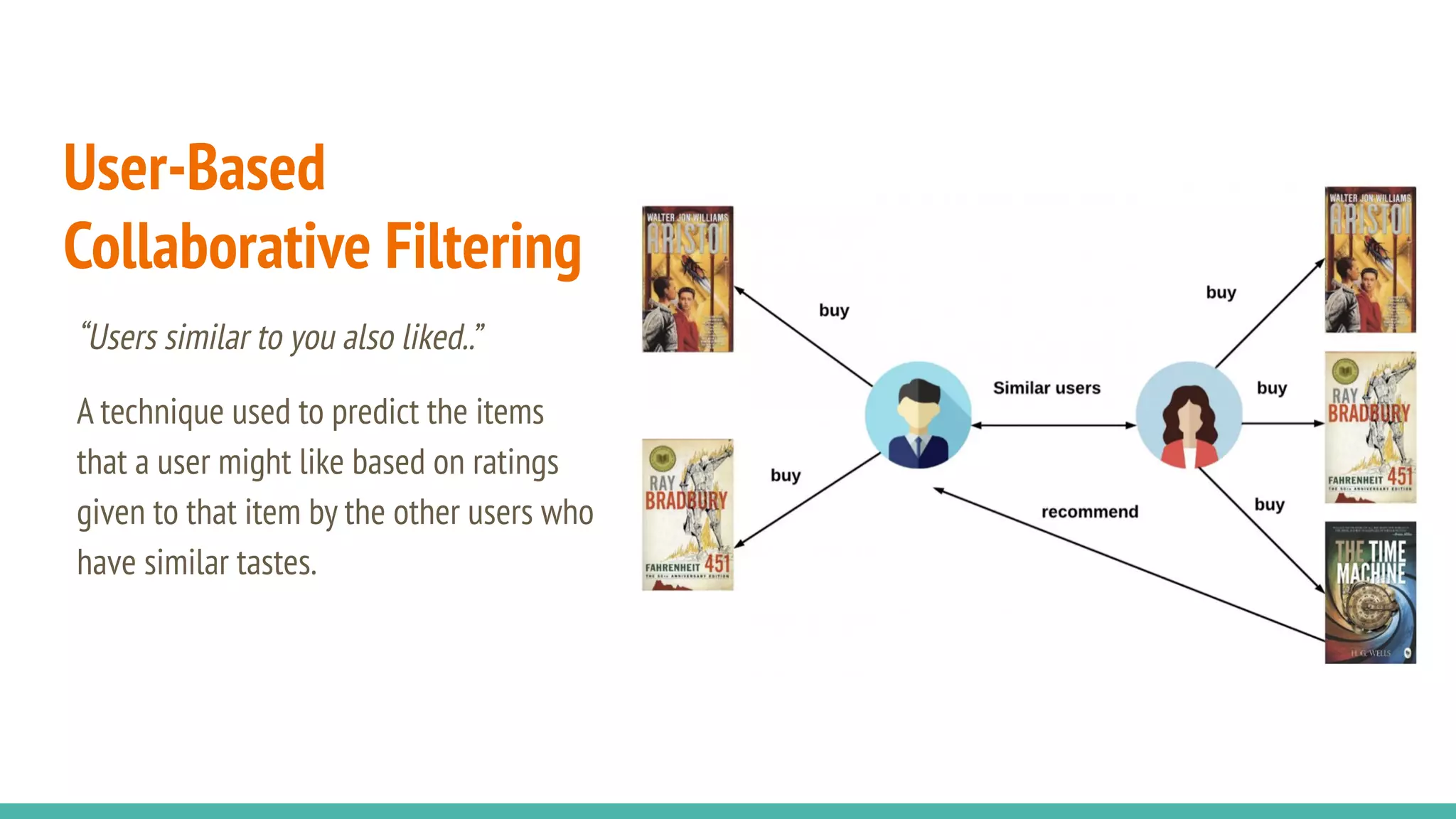
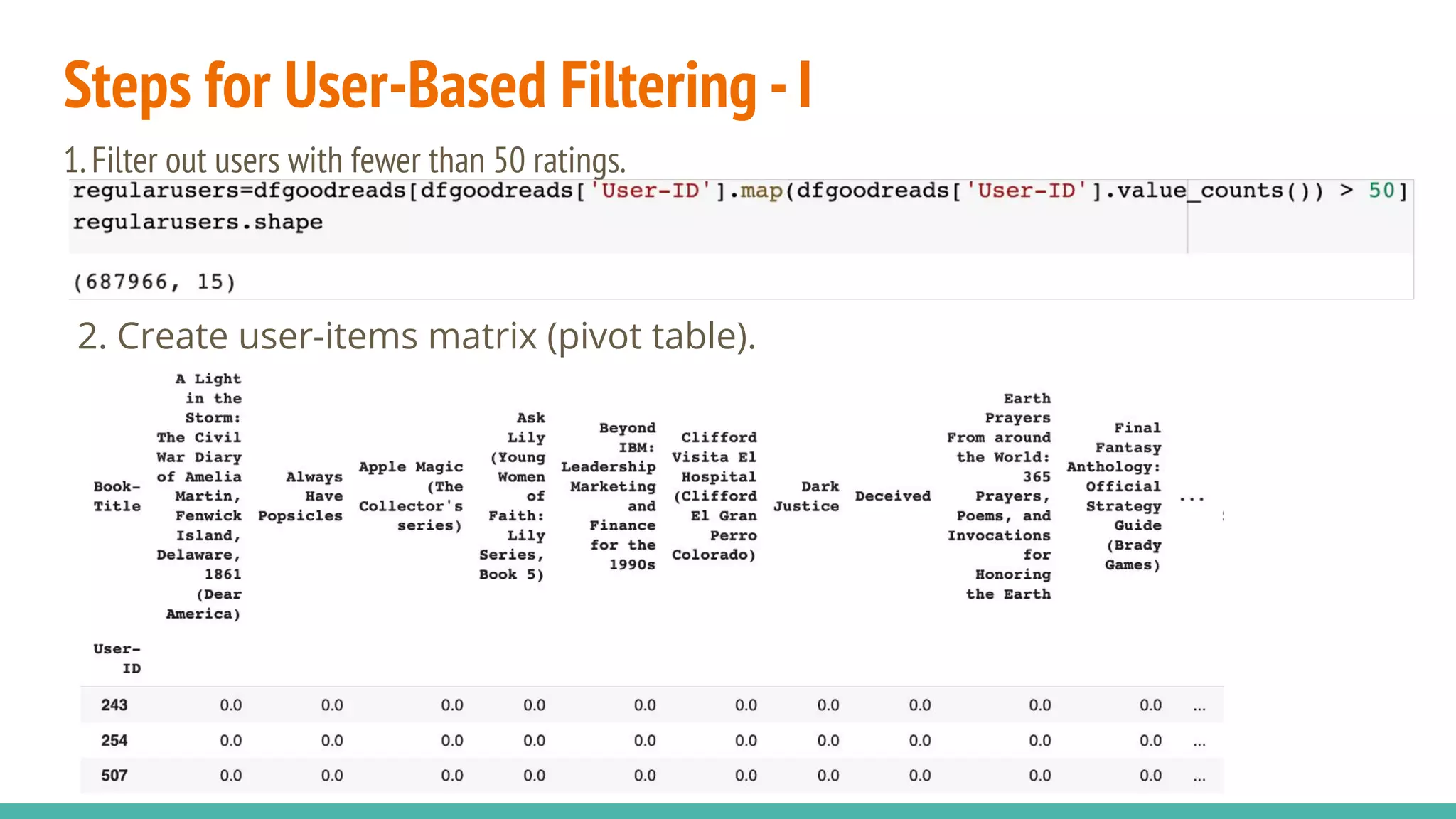
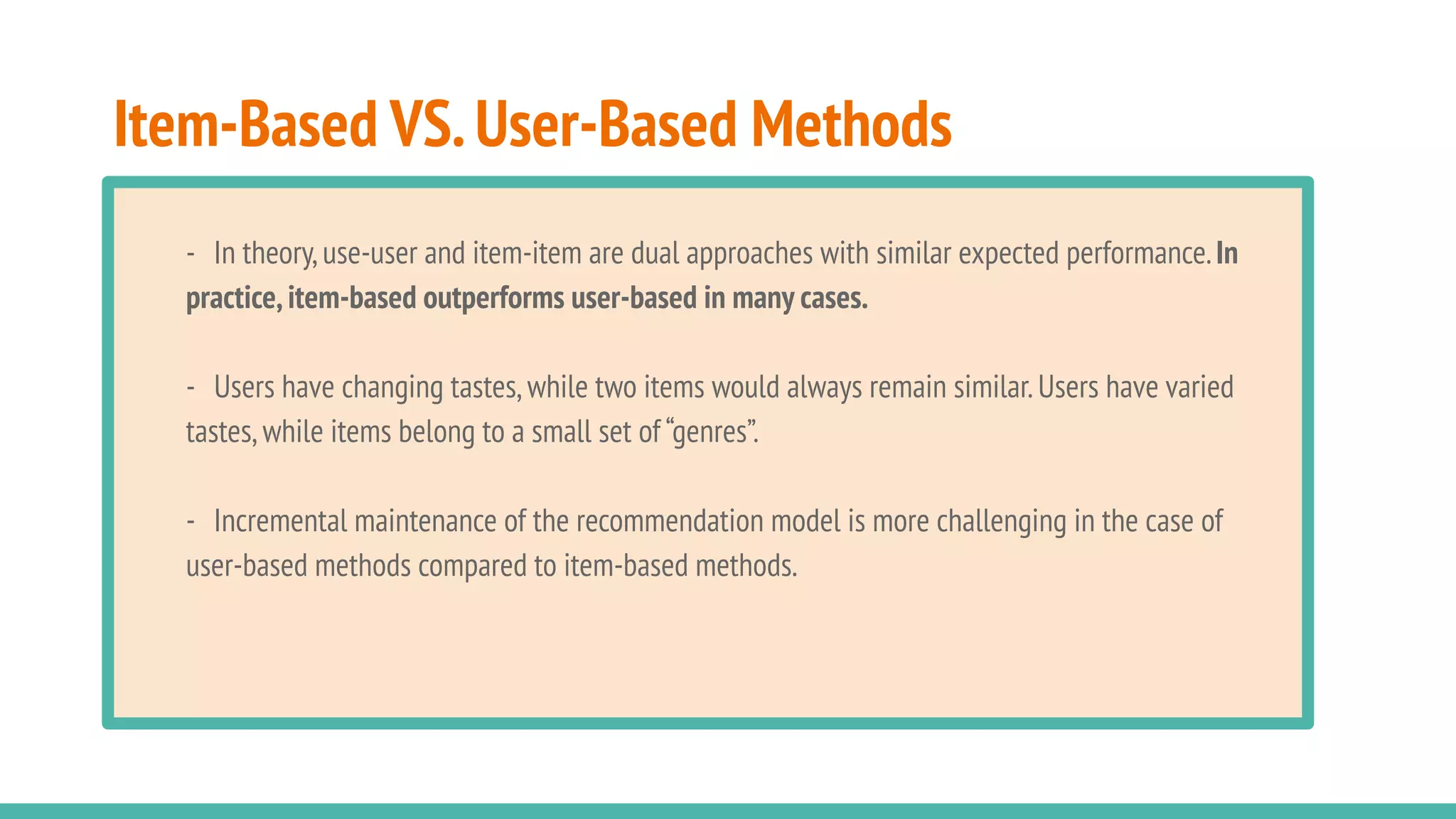
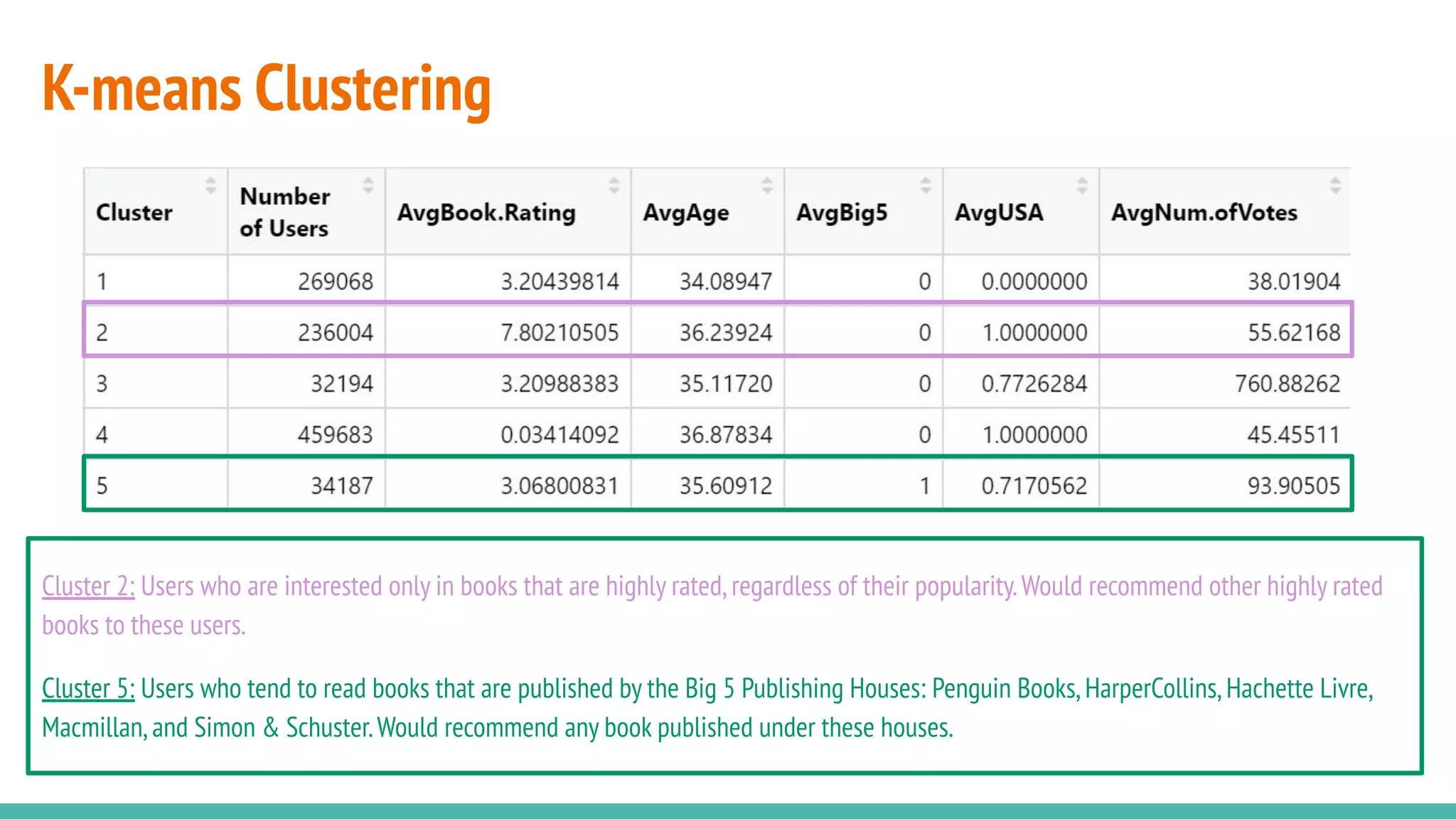
This document describes a book recommendation engine created using Goodreads ratings data. It discusses exploring collaborative filtering, item-based filtering, user-based filtering and content-based filtering approaches. Item-based collaborative filtering using cosine similarity is presented as the primary recommendation method. The document also discusses evaluating recommendation results, addressing challenges, future improvements like using hybrid recommendation techniques, and the potential business value.