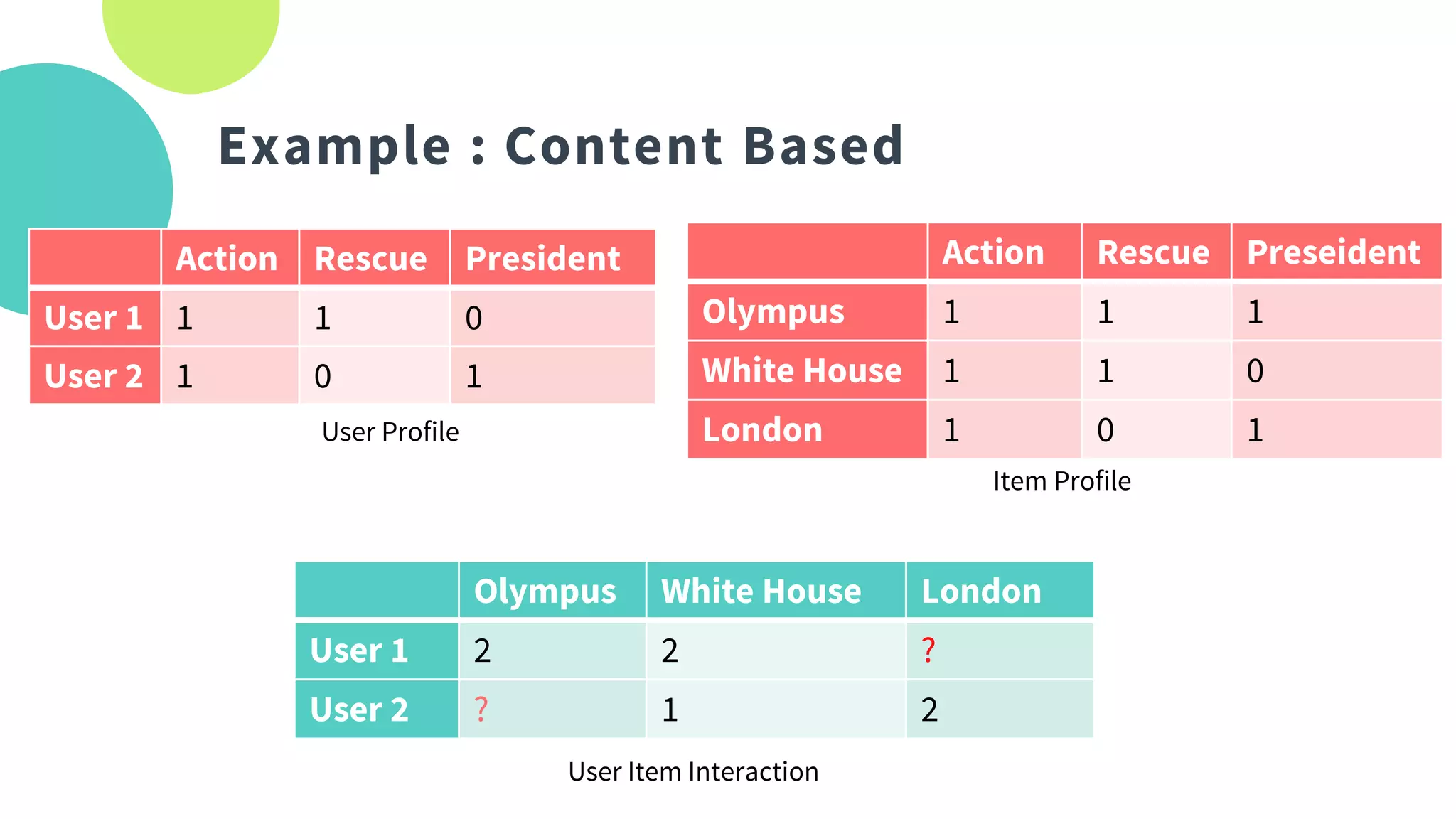
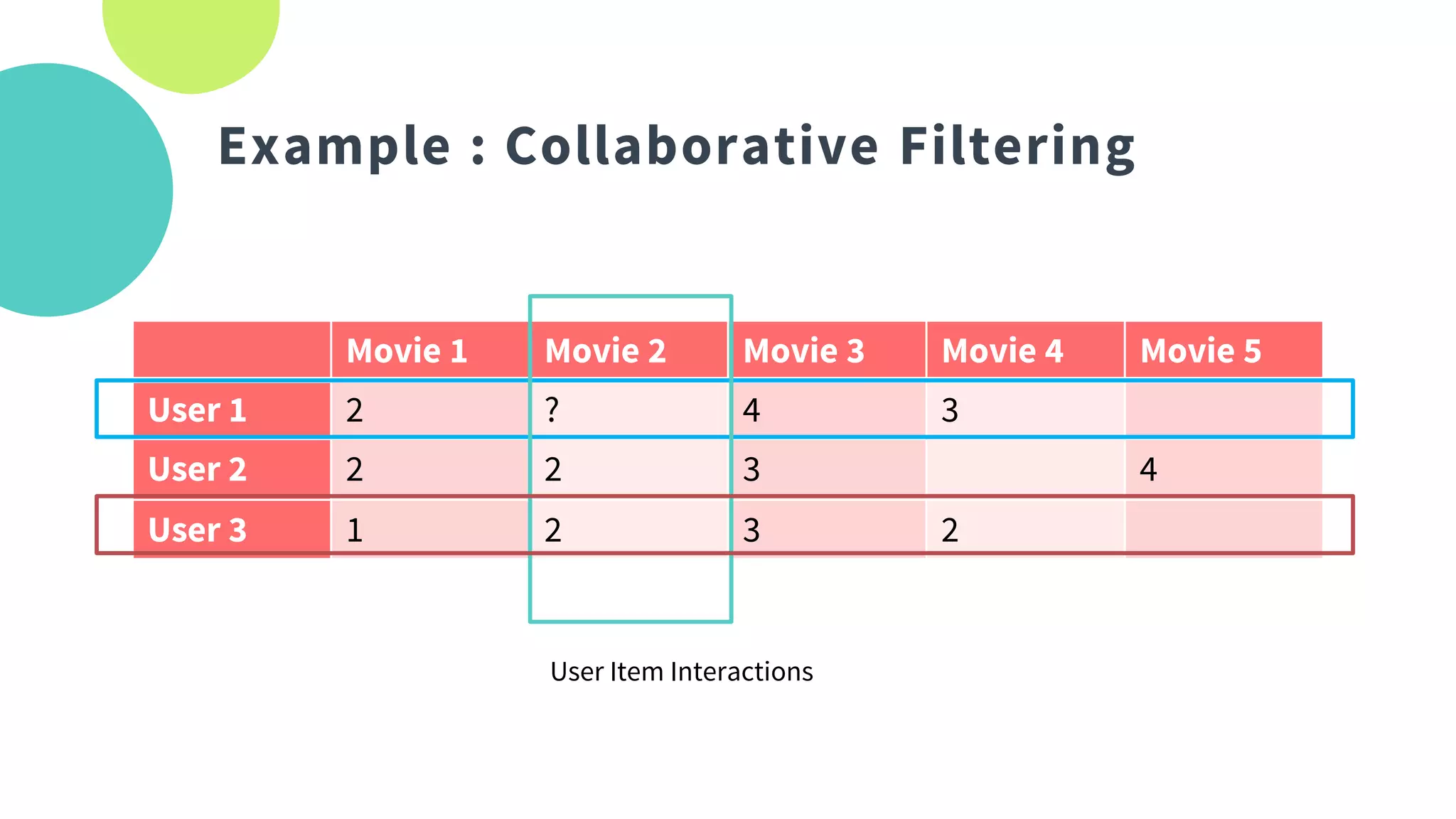
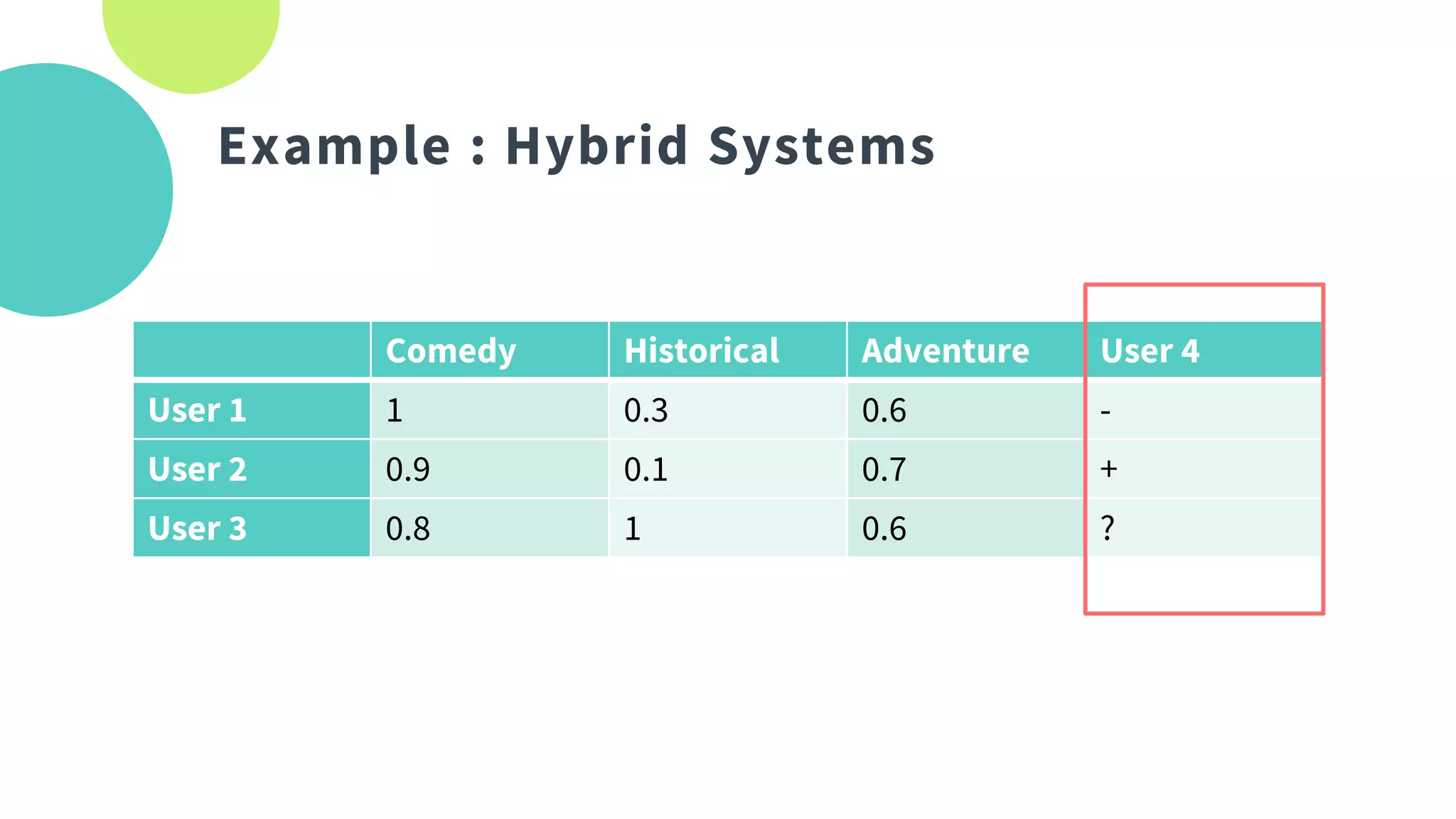
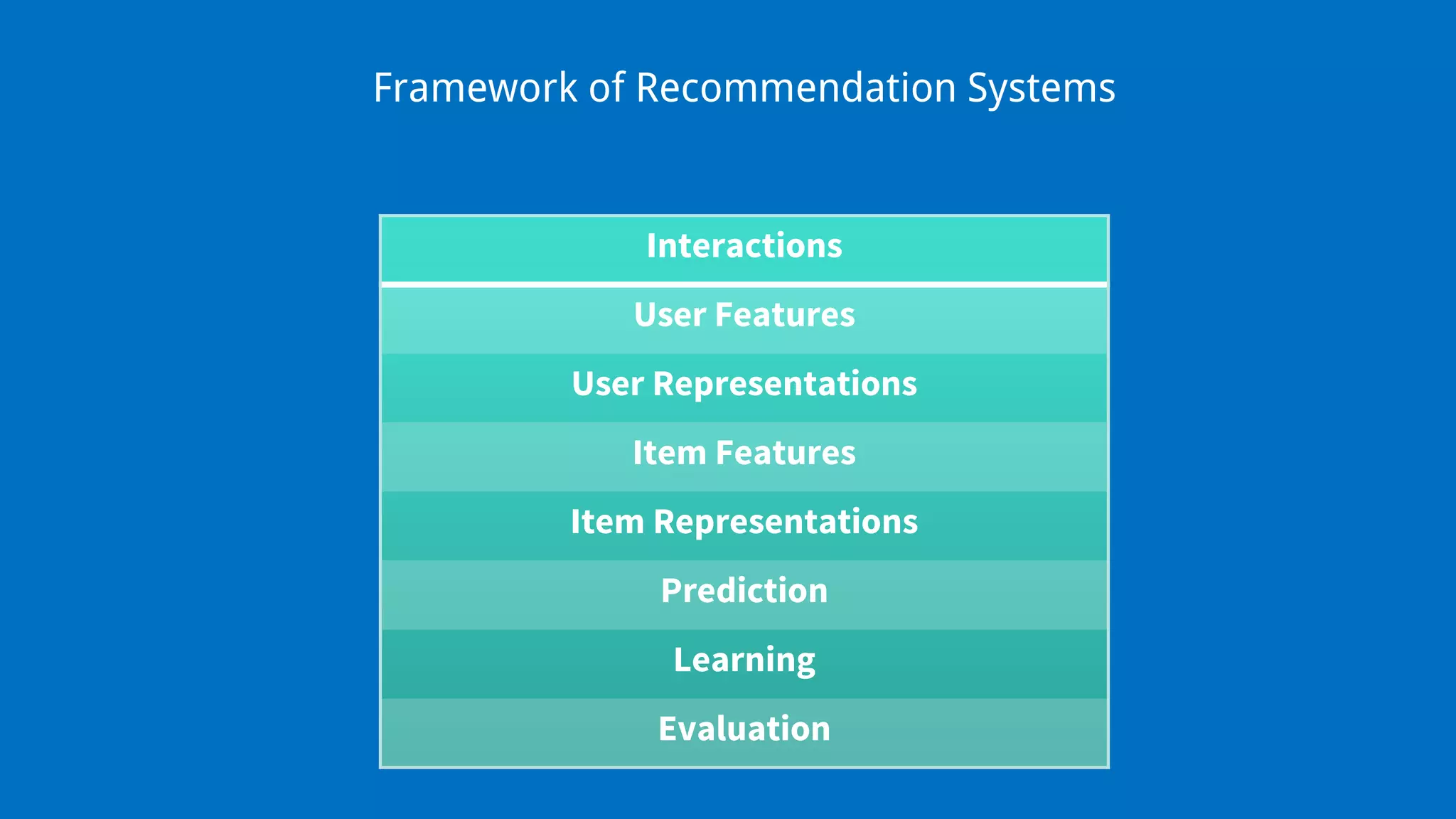
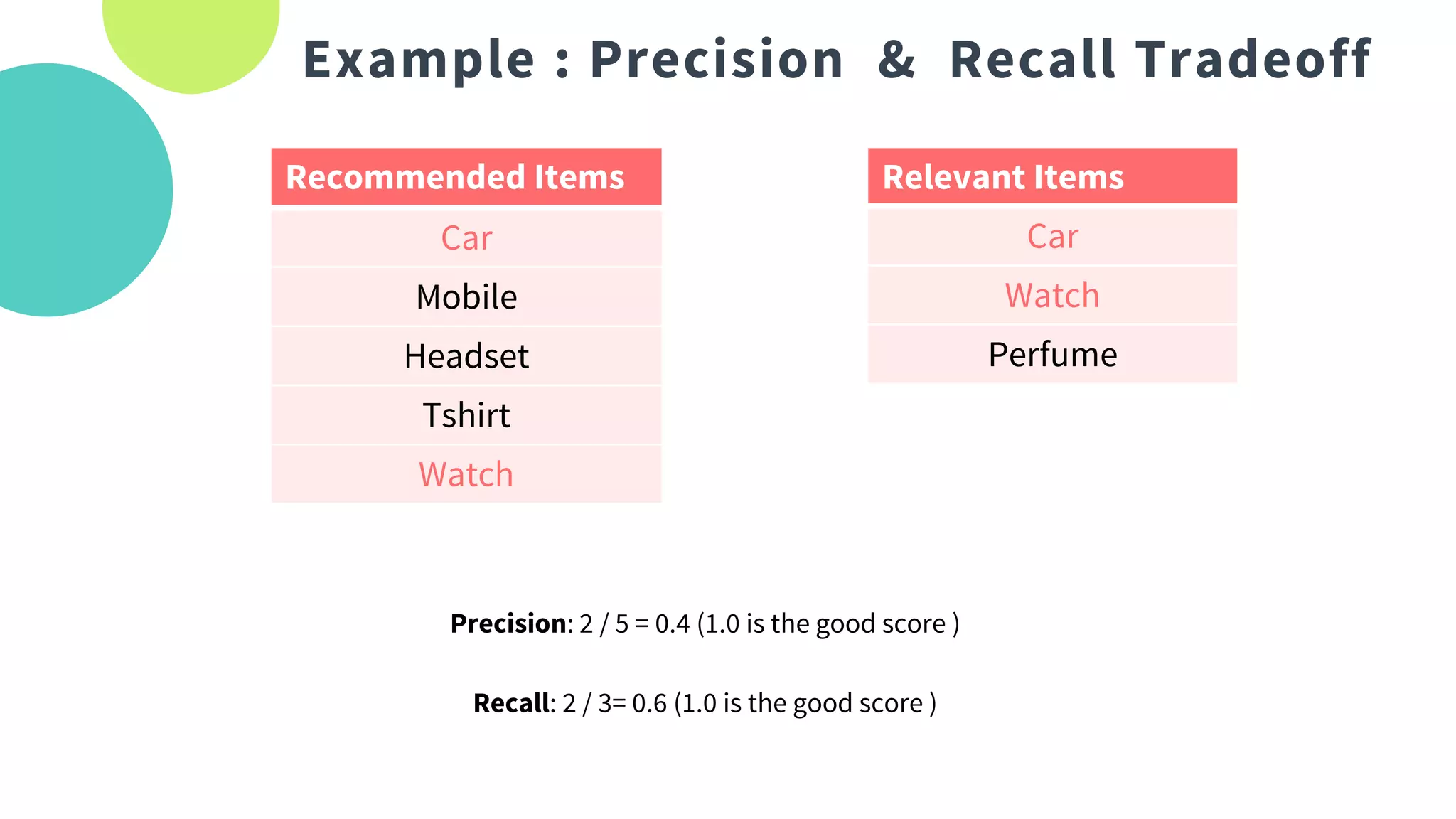
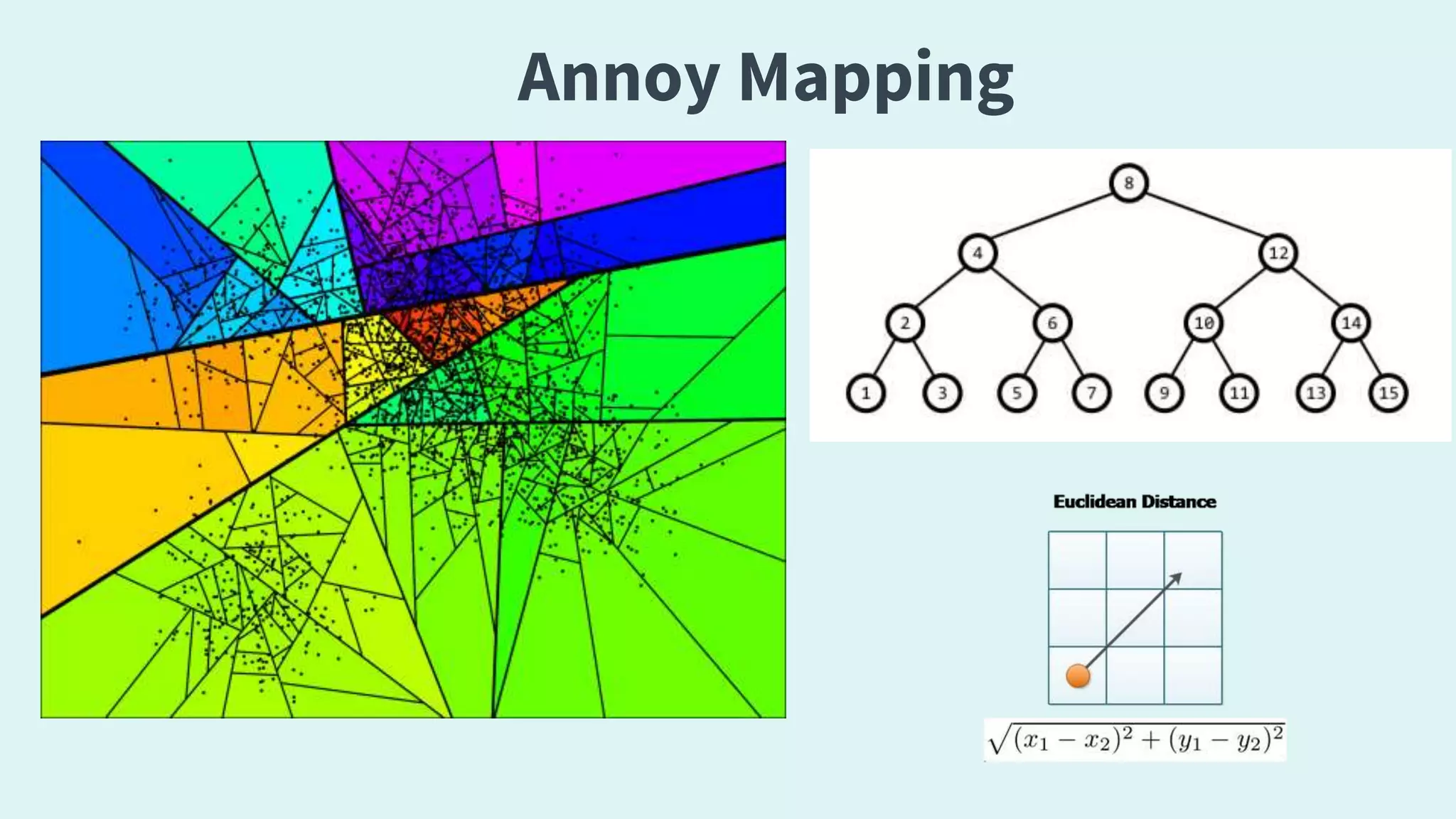
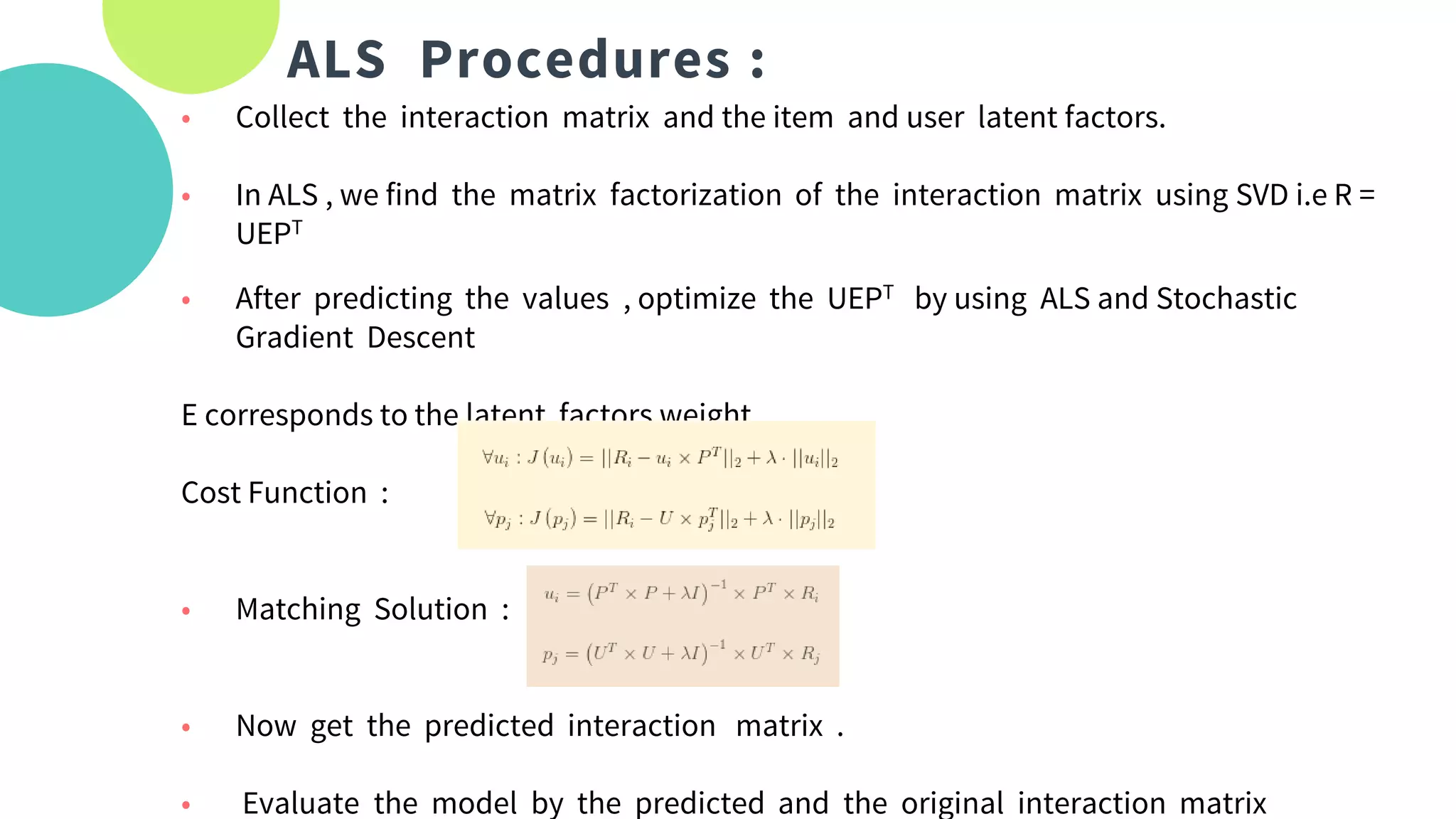
The document provides an overview of recommendation systems, which automate item suggestions to users based on their interactions. It discusses various methodologies such as content-based filtering, collaborative filtering, and hybrid systems, along with evaluation metrics like precision and recall. Additionally, it highlights tools and libraries like LightFM, FAISS, and NMSLIB for implementation and addresses challenges such as the cold start problem.