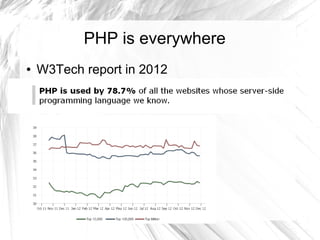
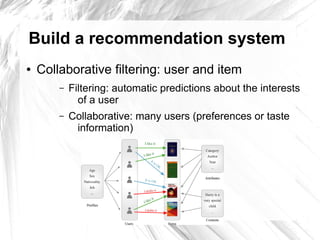
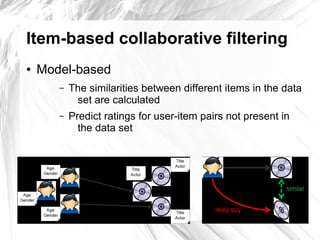
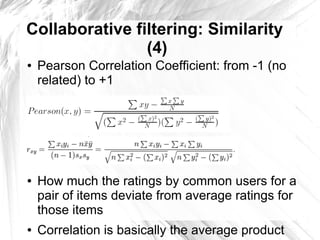
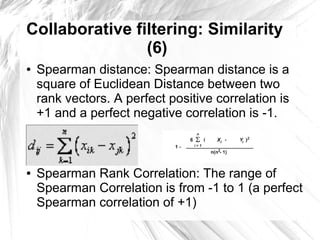
This document provides an introduction to item-based collaborative filtering for building recommendation engines. It discusses how recommendation systems can help provide engaging content for websites. Item-based collaborative filtering models calculate similarities between items based on user ratings and preferences, then uses those similarities to recommend other items users may like. The key steps are collecting user-item interaction data, calculating inter-item similarities, and using those similarities to compute and rank recommendations for users.