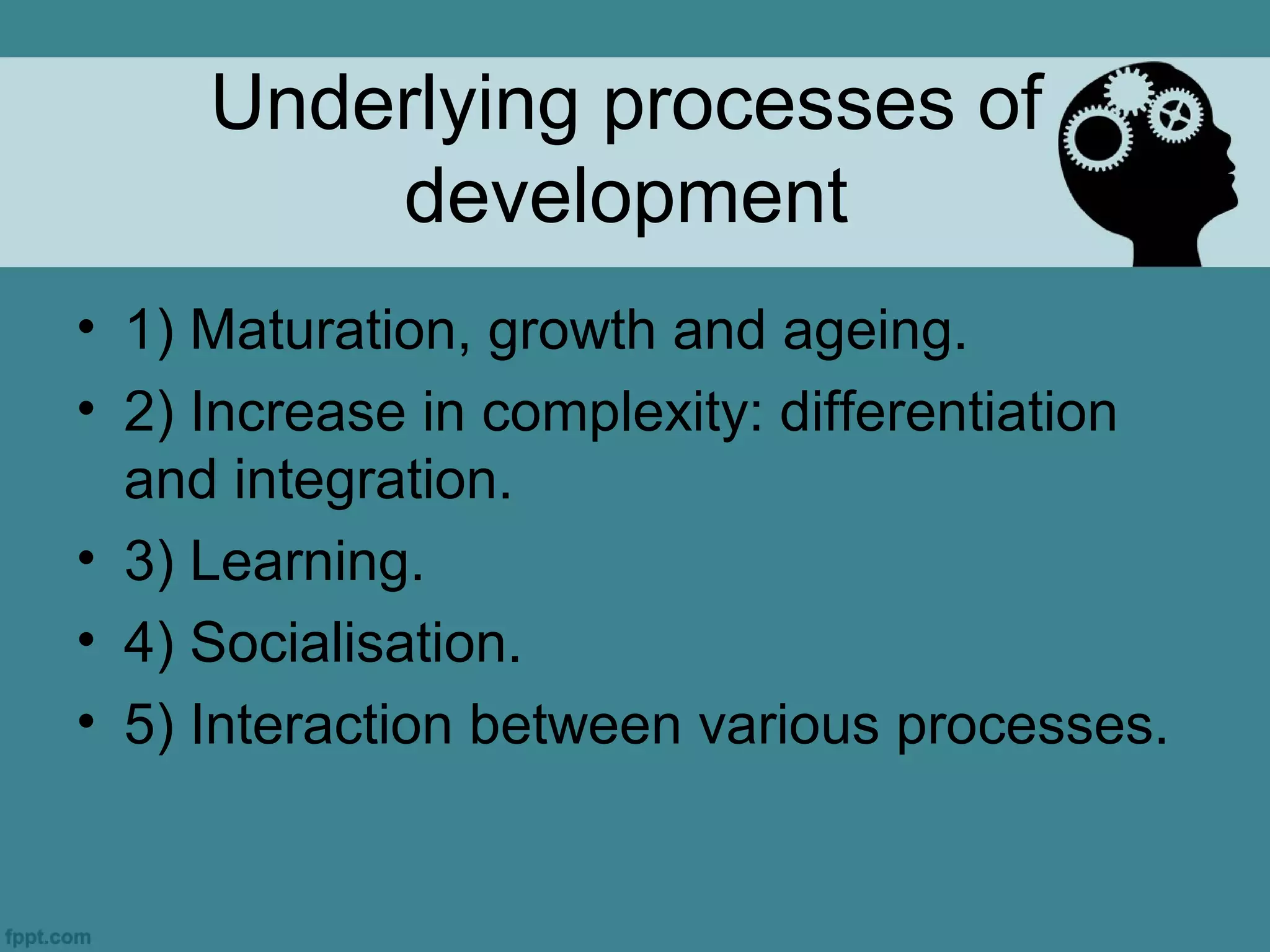
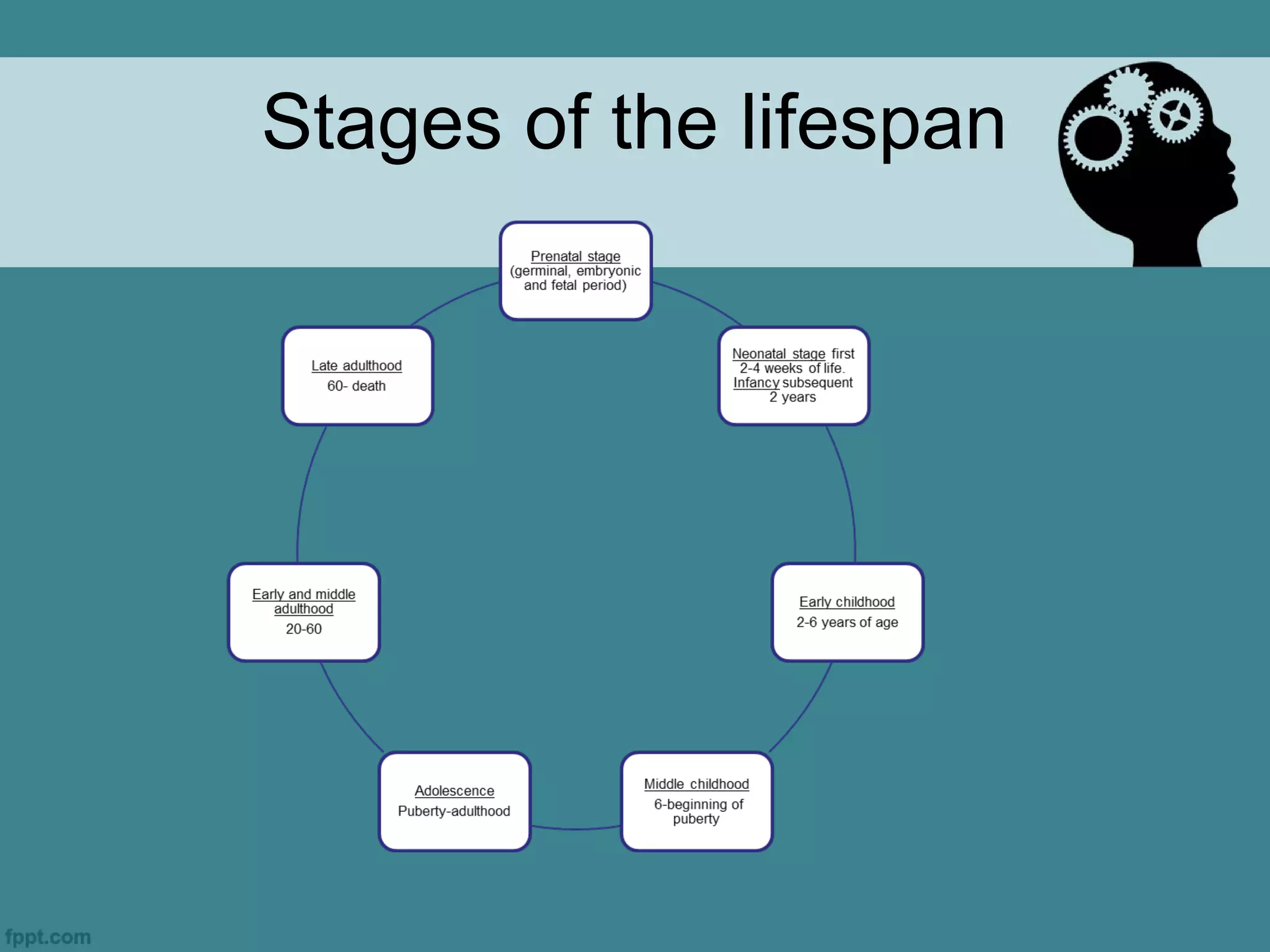
Developmental psychology studies human growth from conception to death, focusing on psychological processes, stages of development, and their implications for understanding health care. It examines factors such as maturation, learning, and socialization, which influence developmental trends and complexities throughout the lifespan. Key concepts include critical and optimal periods for development, as well as the interplay between environmental and genetic determinants.