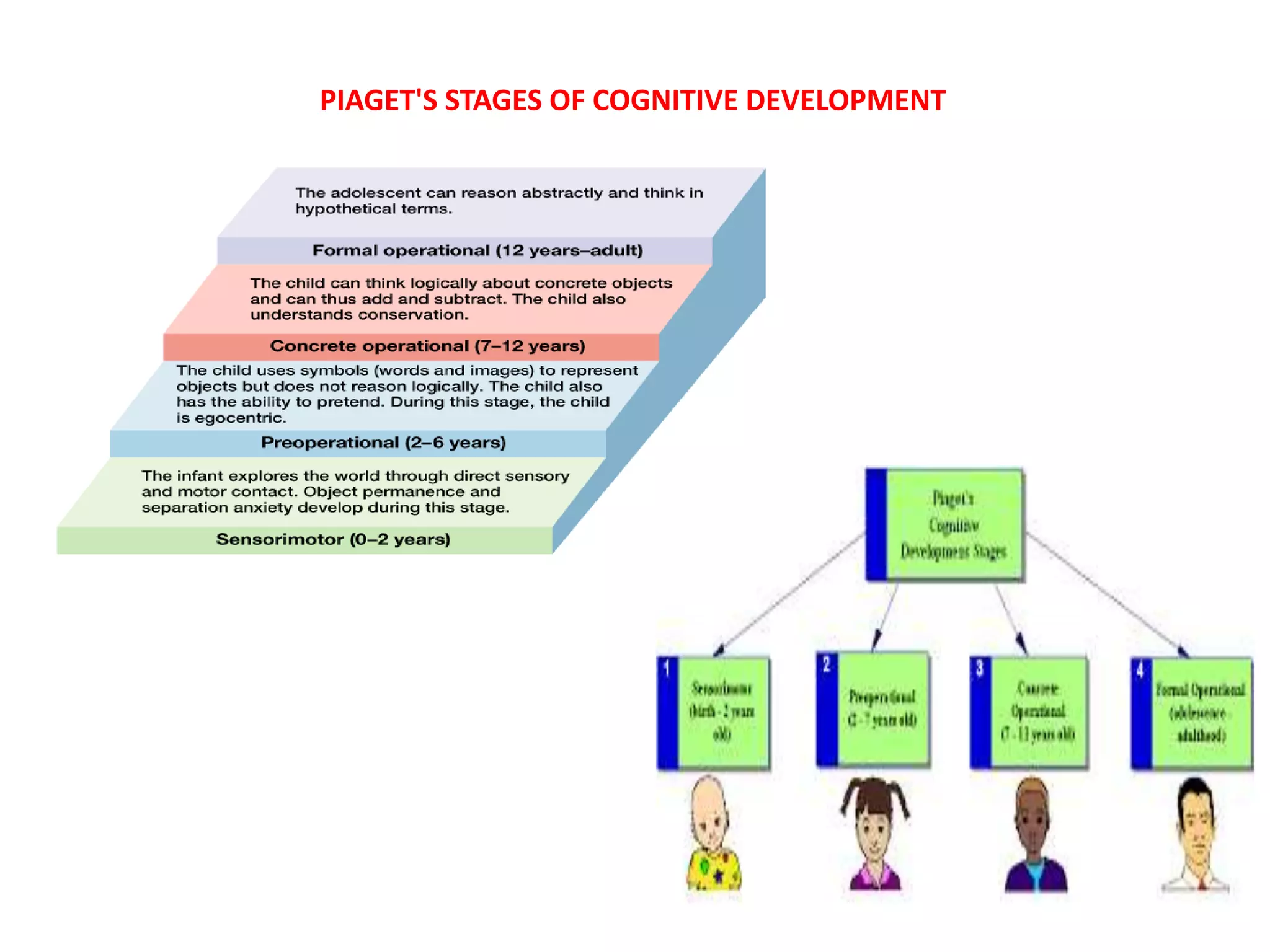
1. Jean Piaget developed four stages of cognitive development based on his observations of children: the sensorimotor stage from birth to age 2, the preoperational stage from ages 2 to 7, the concrete operational stage from ages 7 to 11, and the formal operational stage from ages 11 to adulthood.
2. Each stage is characterized by different types of thinking. In the sensorimotor stage, infants think through manipulating objects using their senses. In the preoperational stage, children use symbols and engage in pretend play. During the concrete operational stage, thinking becomes more logical and focused. In the formal operational stage, abstract thinking develops.
3. Piaget's theory emphasizes that children are active