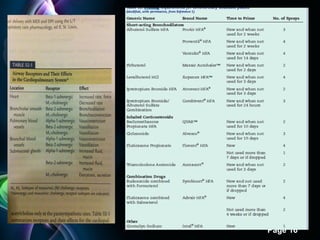
The document outlines the differences between compounds and mixtures in respiratory medications, explaining how compatibility is important for administering multiple drugs without adverse effects. It categorizes respiratory medications, including antihistamines, antitussives, bronchodilators, decongestants, and expectorants, and discusses their physiological effects. Additionally, it highlights the necessity for studies on the physical and chemical compatibility of medications for nebulization and presents case examples related to their use.