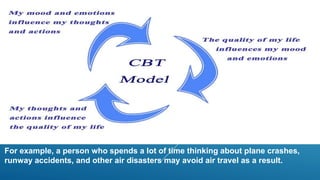
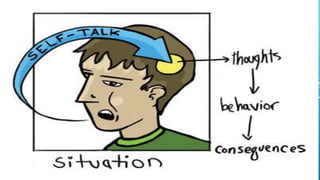
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that helps people identify and change destructive thought patterns. The document outlines the definition, aims, objectives, types (cognitive therapy, dialectical behavior therapy, multimodal therapy, rational emotive behavior therapy), indications, impact and role of nurses in CBT. The impact includes making people aware of negative thoughts, engaging in healthier thinking patterns, being an effective short-term treatment, helping overcome behaviors without medication, and being affordable.
![PRACTICE TEACHING ON
COGNITIVE BEHAVIOUR THERAPY
PRESENTED BY
TAMBOLI AMIT S.
FIRST YEAR
MSC[PSYCHIATRIC]NURSING
MIMH PUNE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbtppt-210521104245/75/Cbt-ppt-1-2048.jpg)