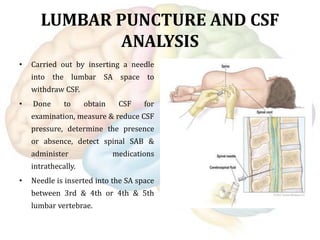
The document discusses various diagnostic measures used to evaluate the central nervous system including lumbar puncture and CSF analysis, CT scan, MRI, EEG, myelography, evoked potentials, and more. Lumbar puncture involves inserting a needle into the spinal canal to withdraw CSF for examination. CT scans provide cross-sectional brain images while MRI uses magnetic fields to identify abnormalities. EEG records brain electrical activity and evoked potentials assess nerve conduction velocities.