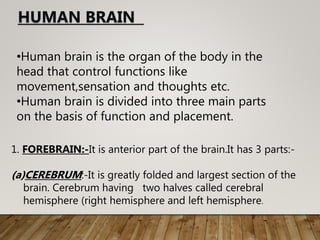
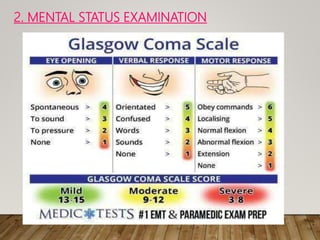
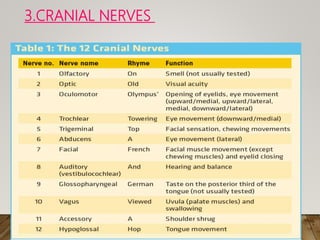
A diagnostic test is performed to aid in the diagnosis of neurological disorders. This document discusses various diagnostic tests for neurological disorders including neurological examination, CT scan, PET scan, evoked potential studies, transcranial Doppler, cerebral spinal fluid analysis, biopsy, and cerebral angiography. It also covers the nursing management aspects for these diagnostic tests such as pre-procedure, during procedure, and post-procedure care. Brain biopsy is often used as a last resort diagnostic for rapidly deteriorating neurological conditions or dementia, and this analysis found it to have a high diagnostic sensitivity to identify the underlying cause.