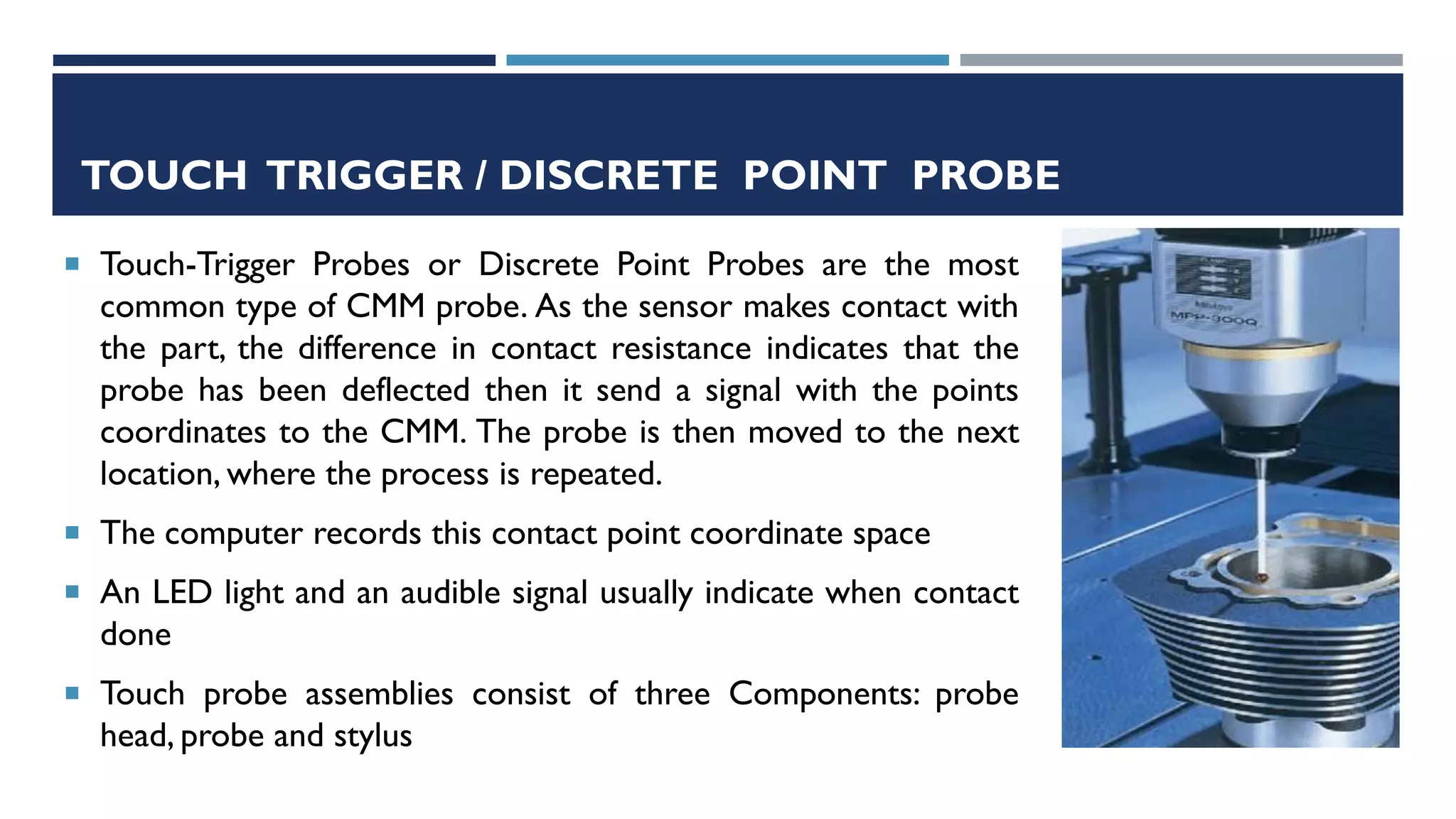
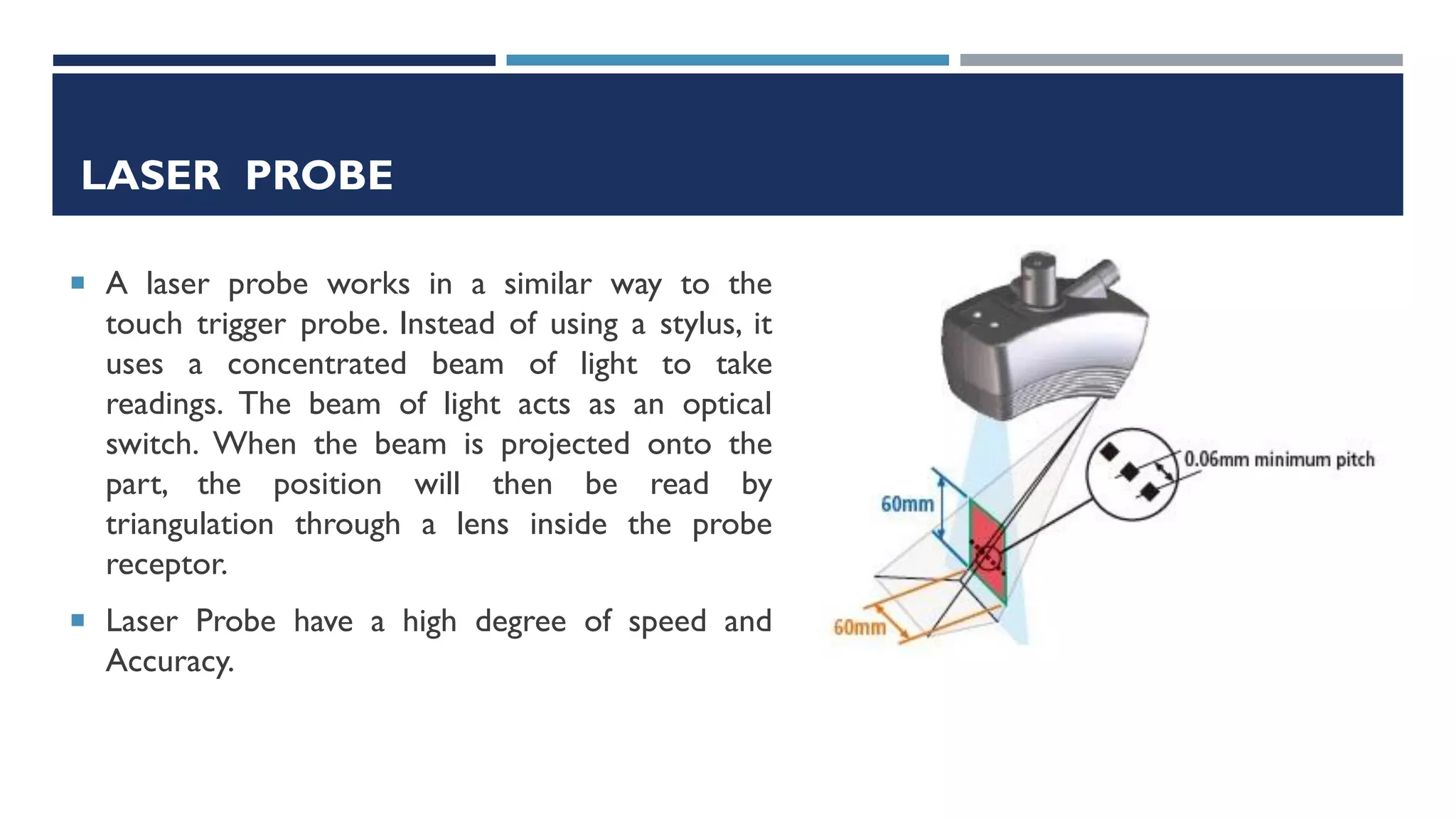
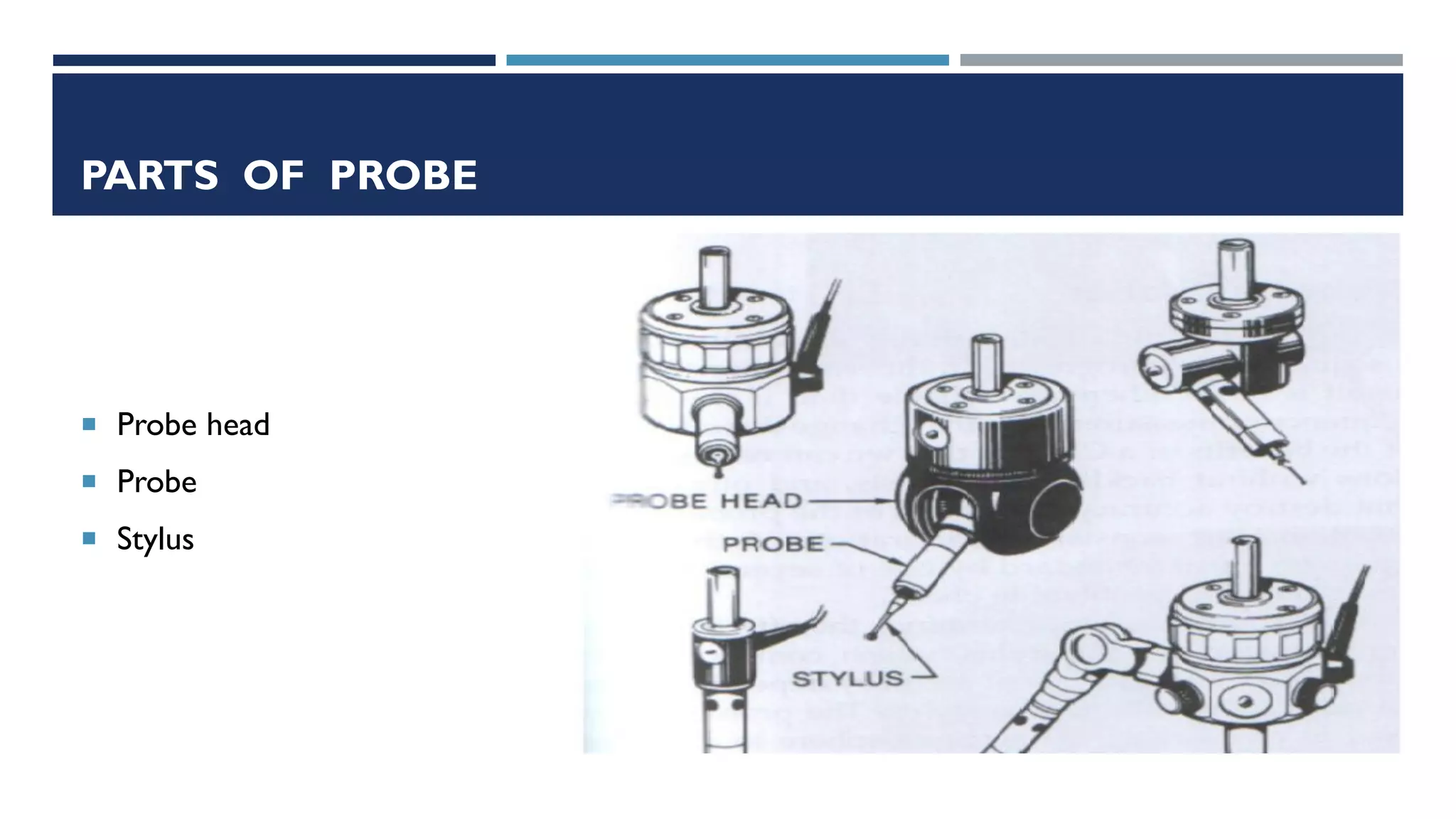
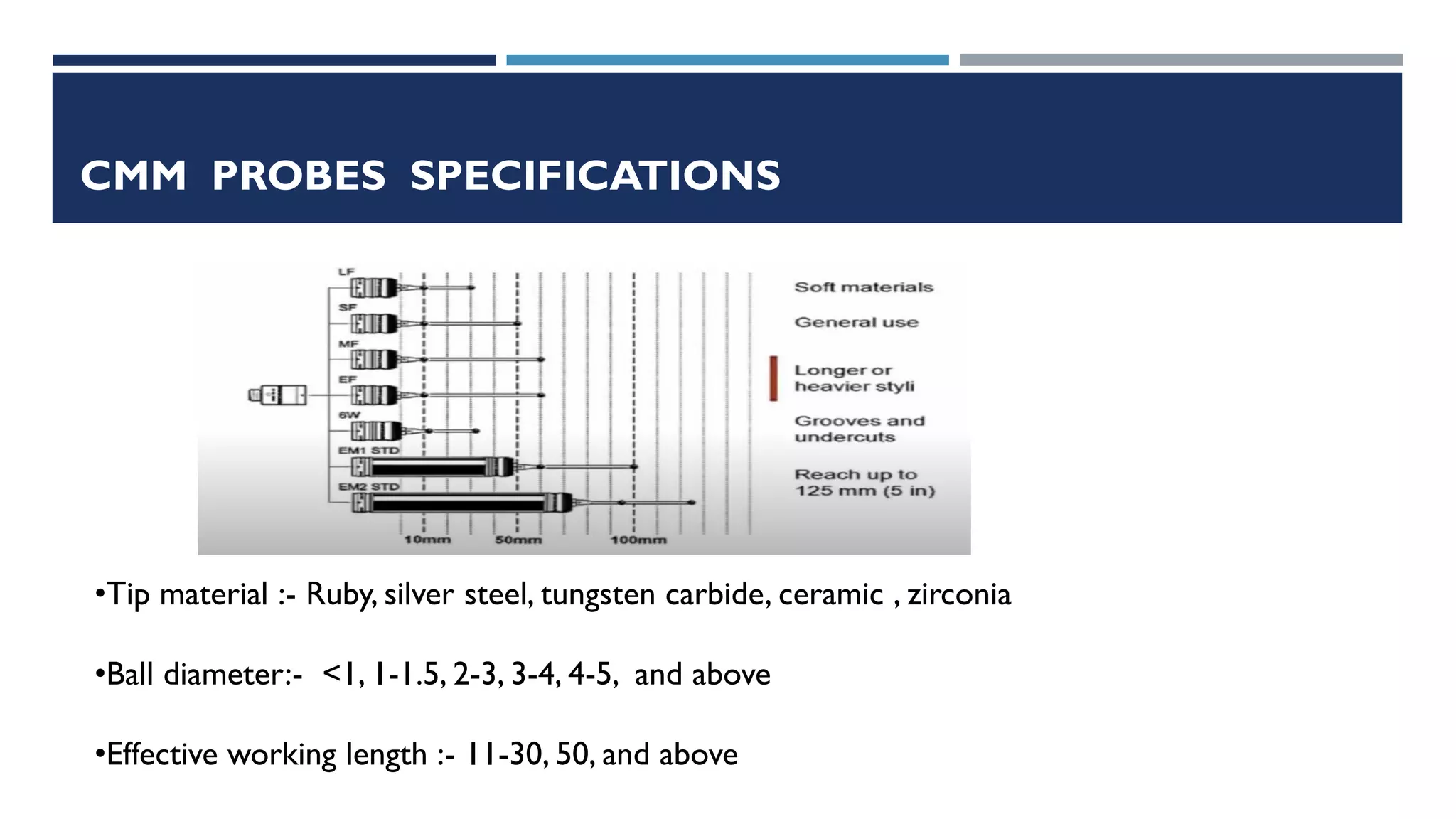
This document provides a detailed overview of coordinate measuring machine (CMM) probes, including their types, specifications, and calibration methods. It covers contact and non-contact probes, highlighting features, materials used, and advantages and disadvantages of each type. Additionally, the document addresses standardization and limitations of CMM technology, concluding with insights on the evolution of probe materials and their applications in various industries.