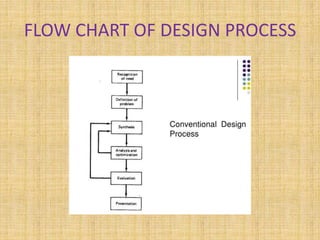
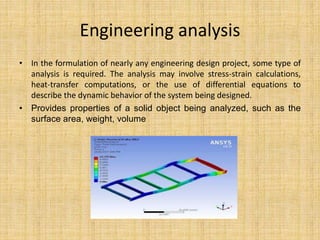
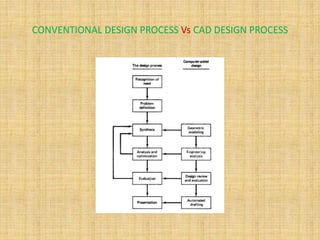
The document discusses the conventional design process and CAD design process. The conventional design process consists of 6 steps: recognition of need, problem definition, synthesis, analysis and optimization, evaluation, and presentation. The CAD design process consists of 4 steps: geometric modeling, engineering analysis, design review and evaluation, and automated drafting. The CAD design process improves engineering productivity, shortens lead times, provides better designs, and makes modifications and requests for quotations easier compared to the conventional design process.