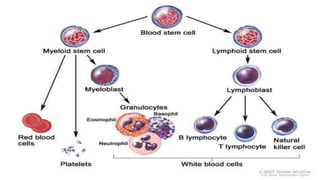
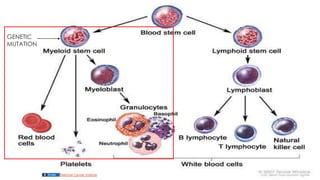
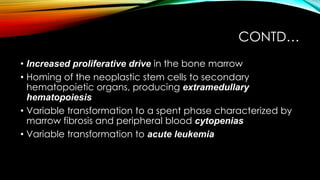
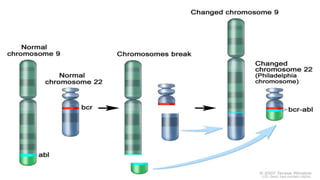
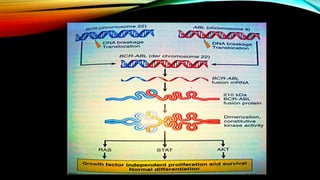
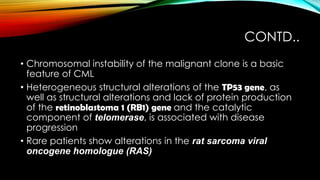
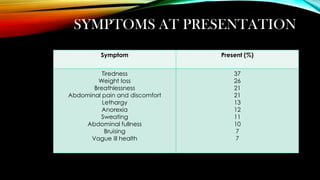
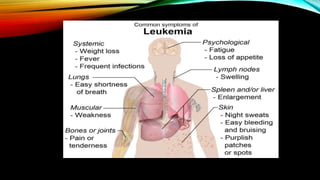
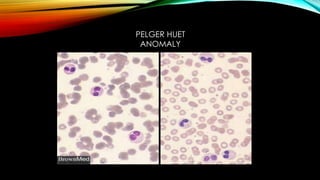
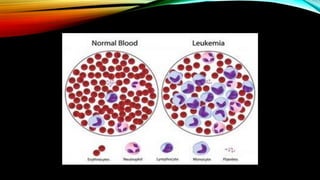
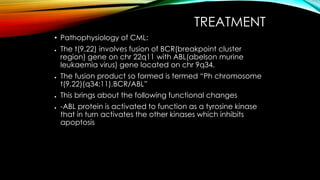
This document discusses hematopoiesis and leukemia, specifically chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). It defines CML as a clonal expansion of stem cells with a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, forming the Philadelphia chromosome. This causes a BCR-ABL fusion gene which produces a constitutively active tyrosine kinase driving proliferation. CML accounts for 14% of leukemias and presents mainly in adults aged 40-60 with increased white blood cells. The document covers classification, signs and symptoms, progression from chronic to blast phase, and treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors.











































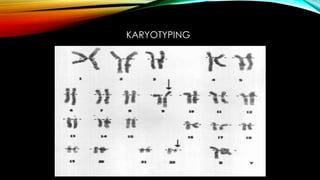
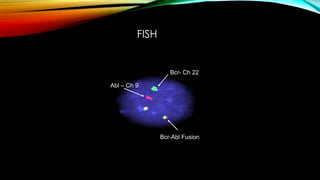












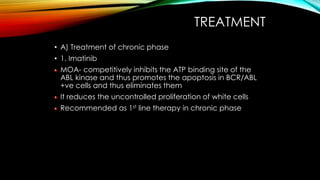
![Produces complete cytogenetic response[
disappearance of Ph chromosome ] in 76% cases at 18
months of therapy
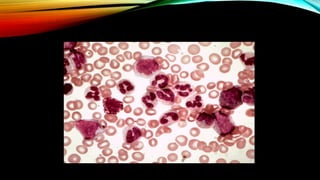
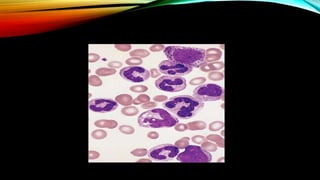
Patients are monitered by repeated bone marrow
examination until a complete cytogenetic response, and
then by 3 monthly microsatellite PCR/ by FISH
Side effects: fluid retention, nausea, muscle
cramps, diarrhoea, skin rash, myelosuppression
Resistance to imatinib results from over expression of BCRABL gene or genetic alteration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cml-131130134753-phpapp01/85/Cml-82-320.jpg)












![• Phase 1[Remission induction]→ The bulk of the tumour is
destroyed by combination chemotherapy. They require
intensive supportive care.
• Phase 2[Remission consolidation]→ This consists of a no. of
courses of chemotherapy which attacks the residual
disease.
• Phase 3[Remission maintenance]→ consisting of a
repeating cycles of drug administration. This may extend
for up to 3 years.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cml-131130134753-phpapp01/85/Cml-95-320.jpg)







