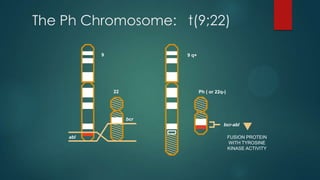
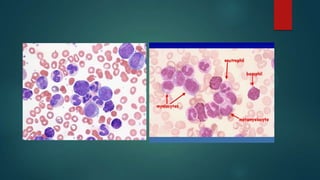
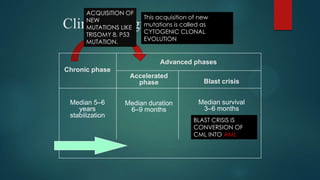
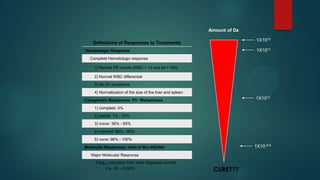
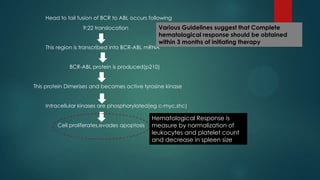
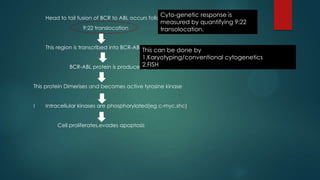
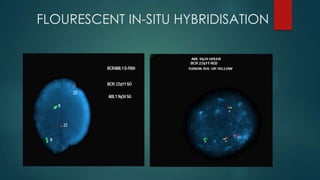
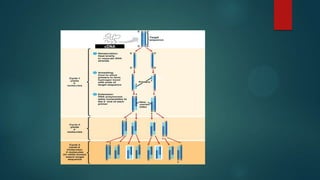
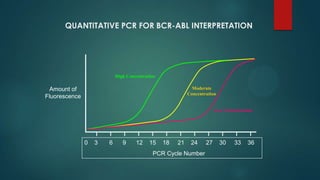
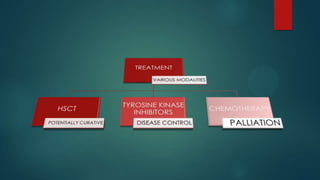
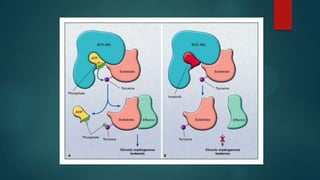
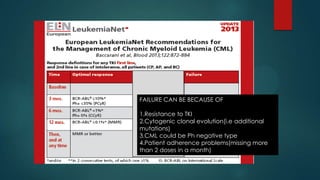
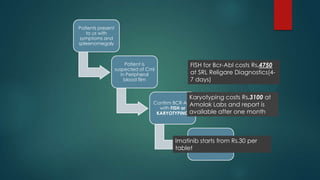
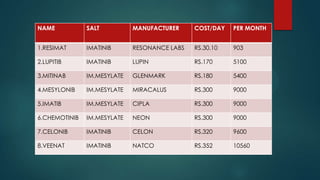
The document discusses diagnosis, management, and recent advances in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). CML results from a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, known as the Philadelphia chromosome, which produces the BCR-ABL fusion gene and oncogenic protein. Treatment involves tyrosine kinase inhibitors like imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib to inhibit BCR-ABL. Response is monitored through hematologic, cytogenetic, and molecular testing. Resistance can develop through mutations, requiring alternative TKIs or allogeneic stem cell transplant in some cases.