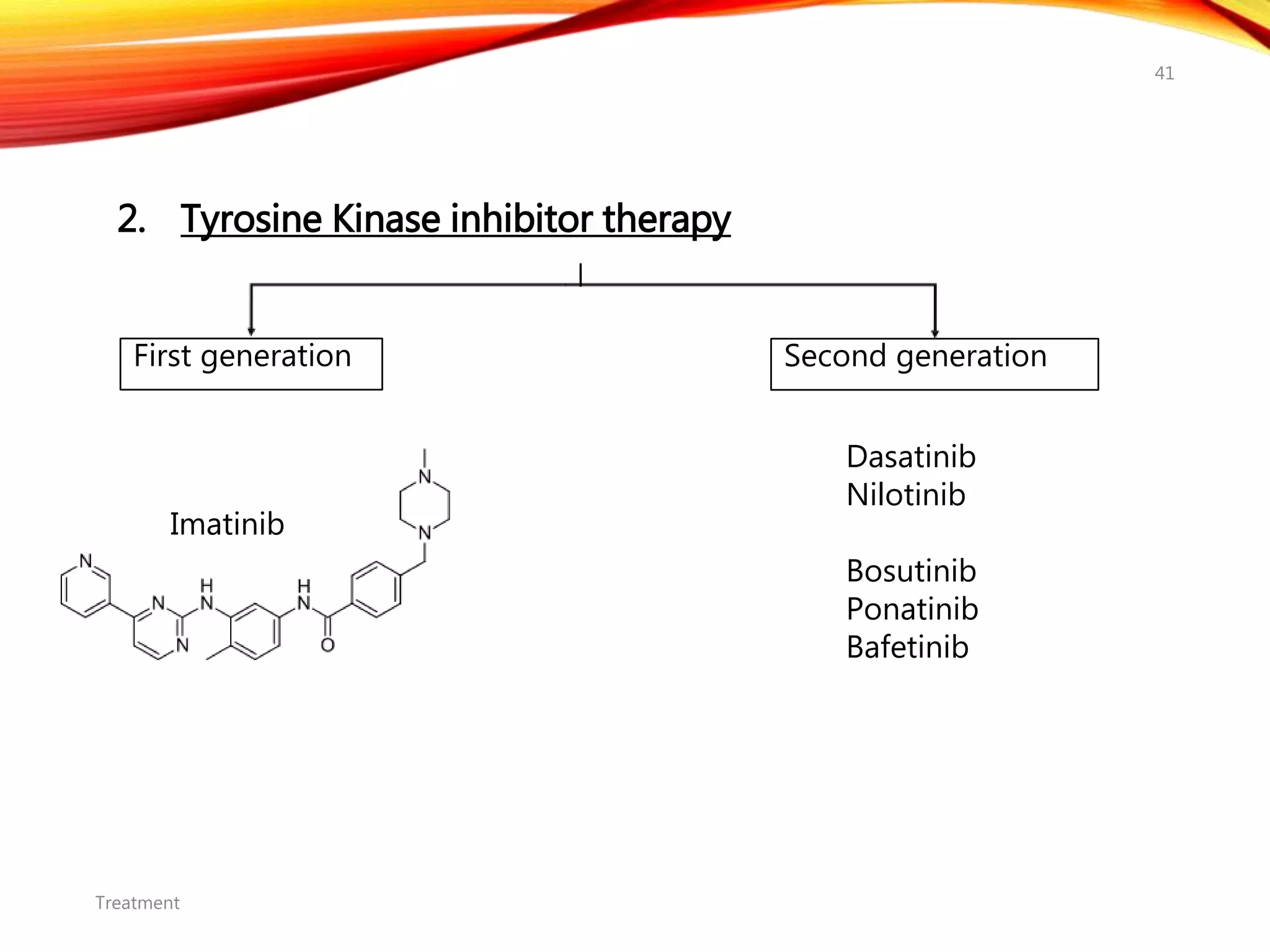
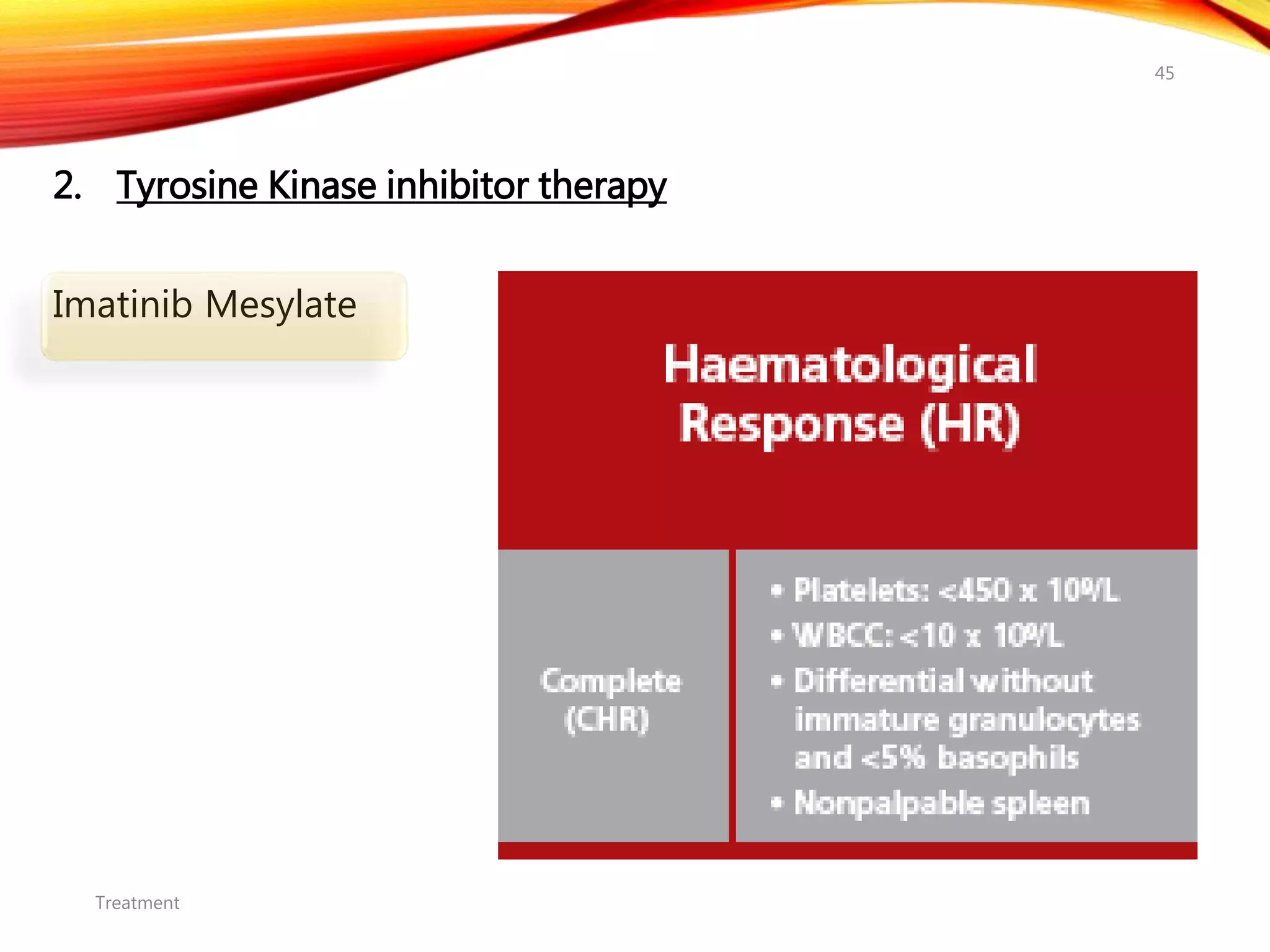
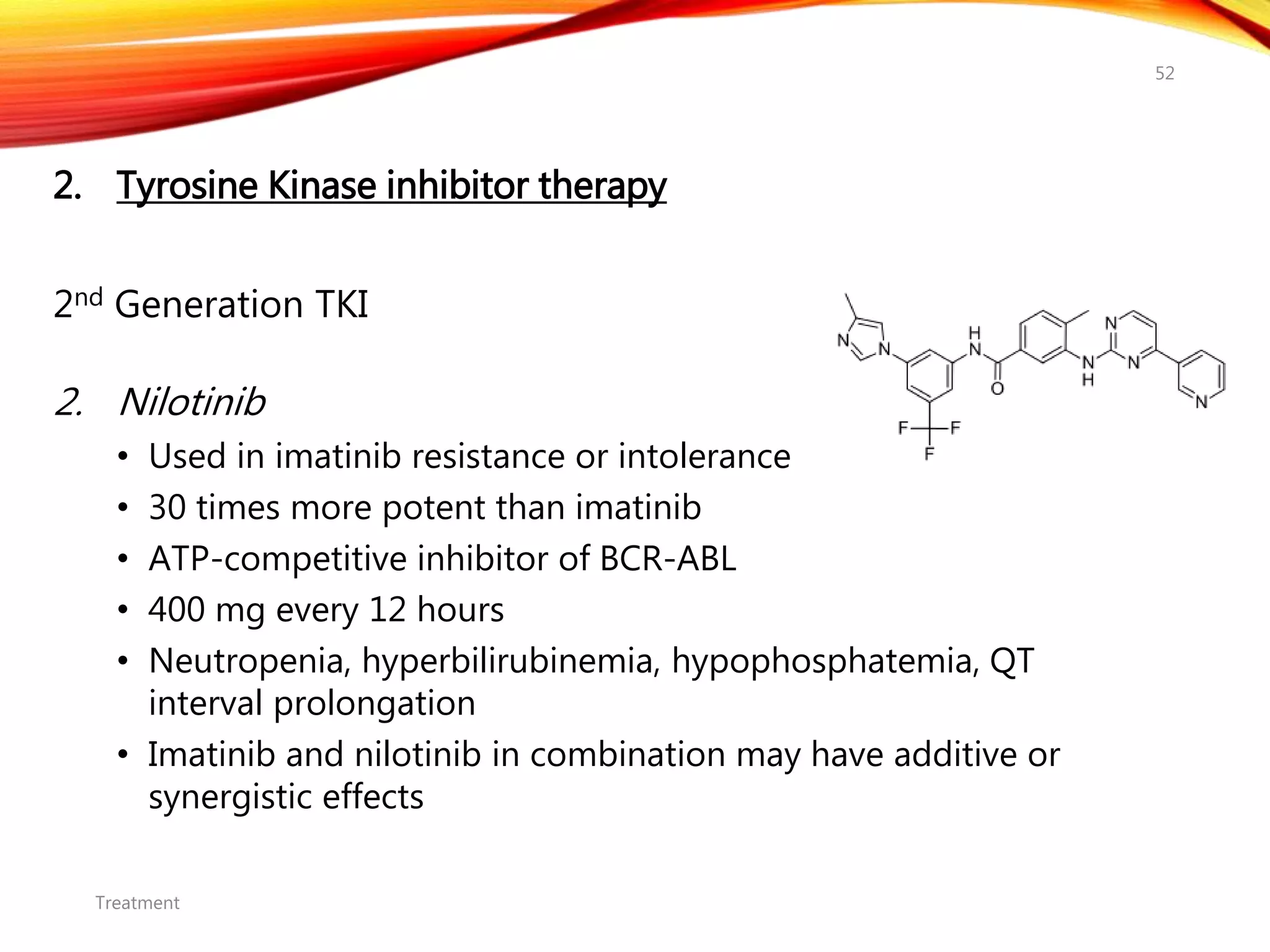
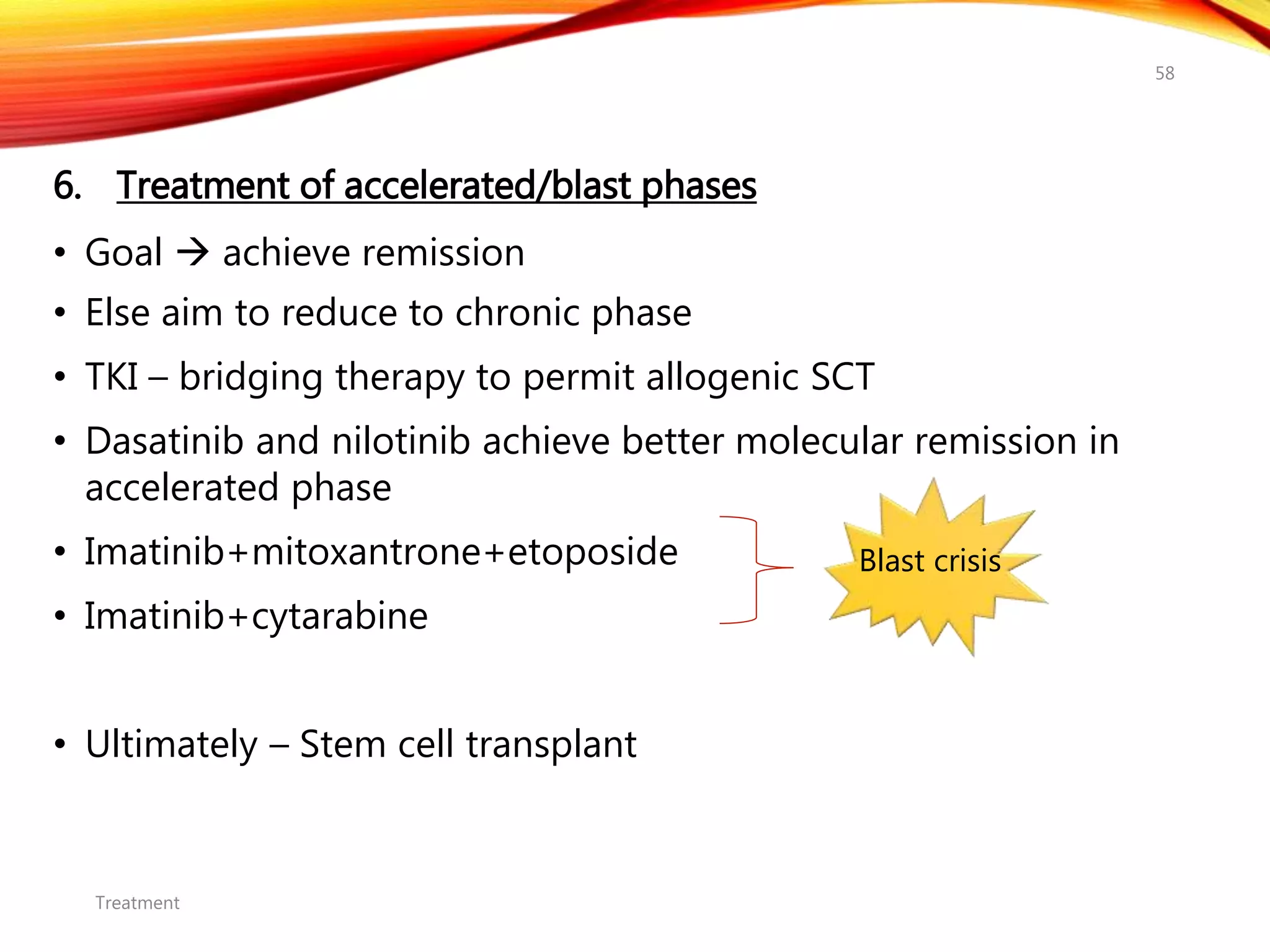
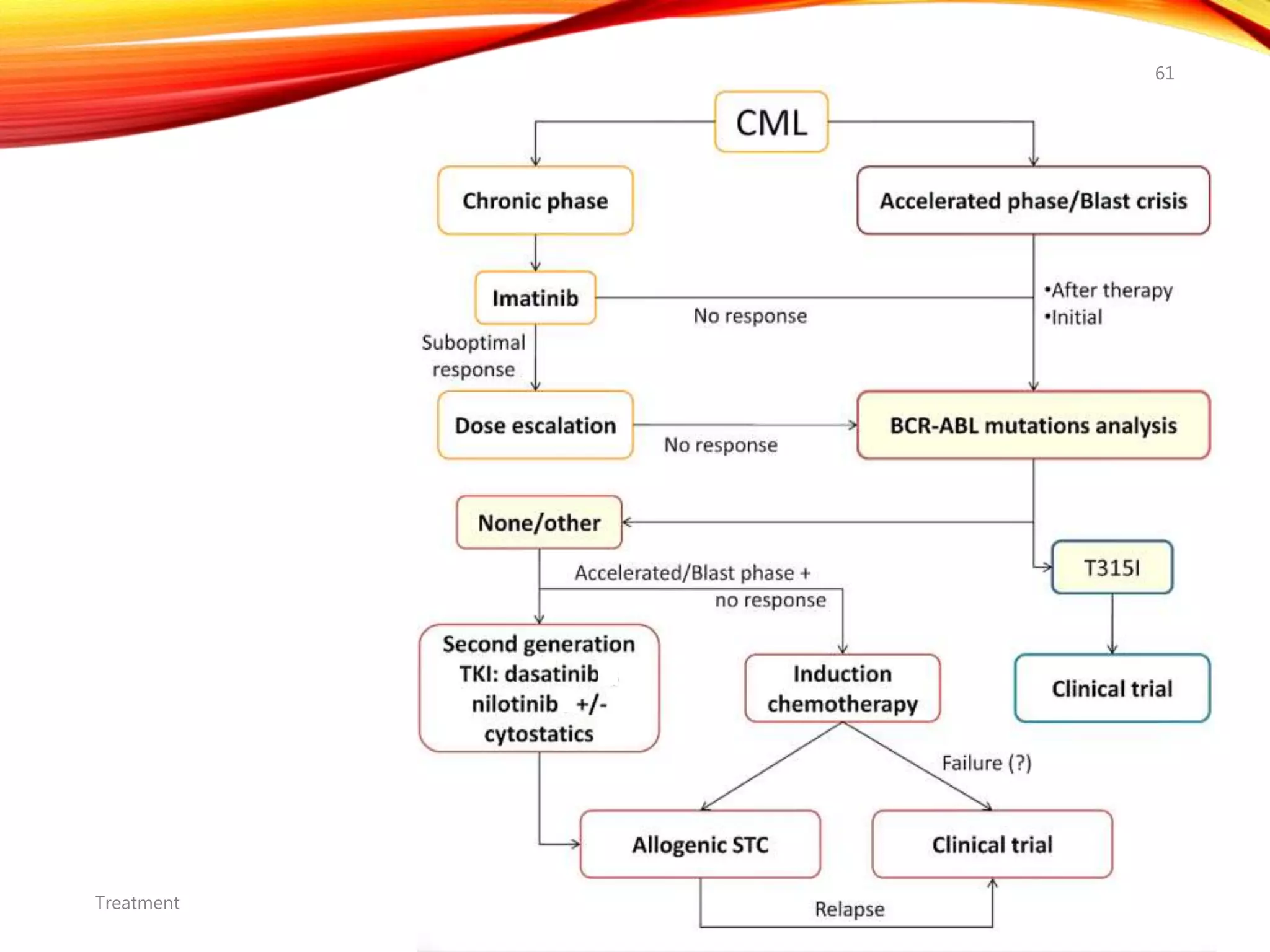
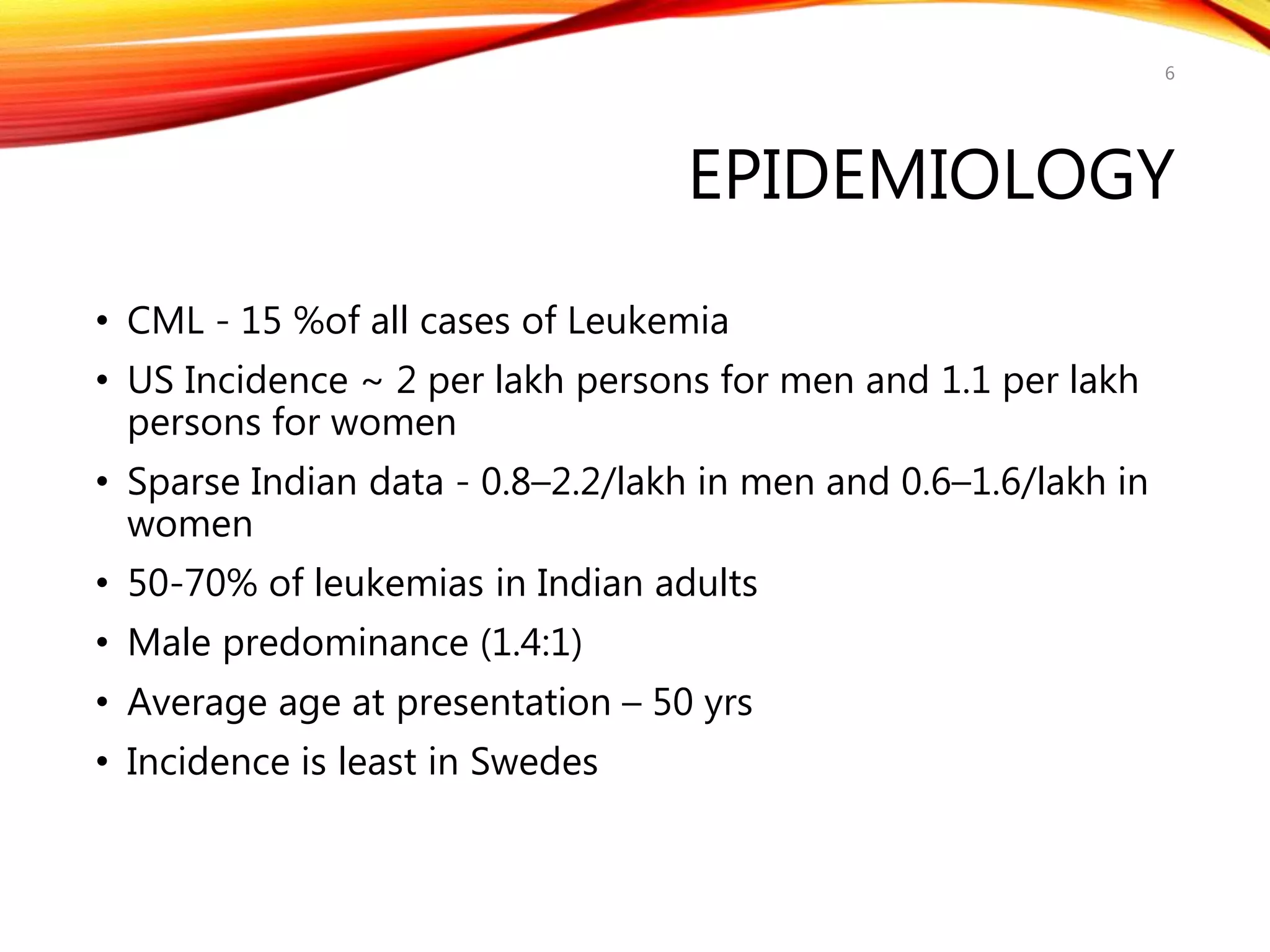
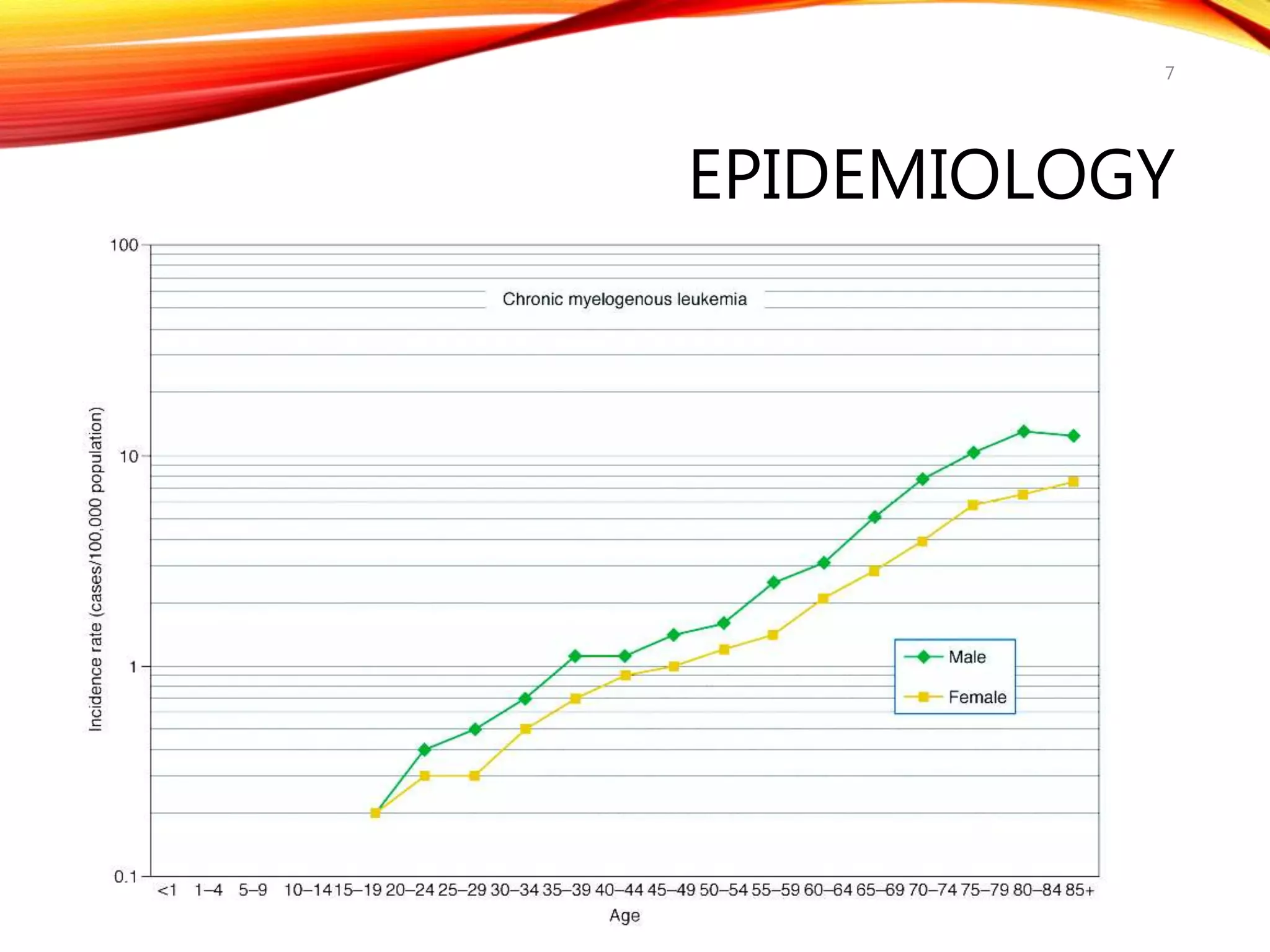
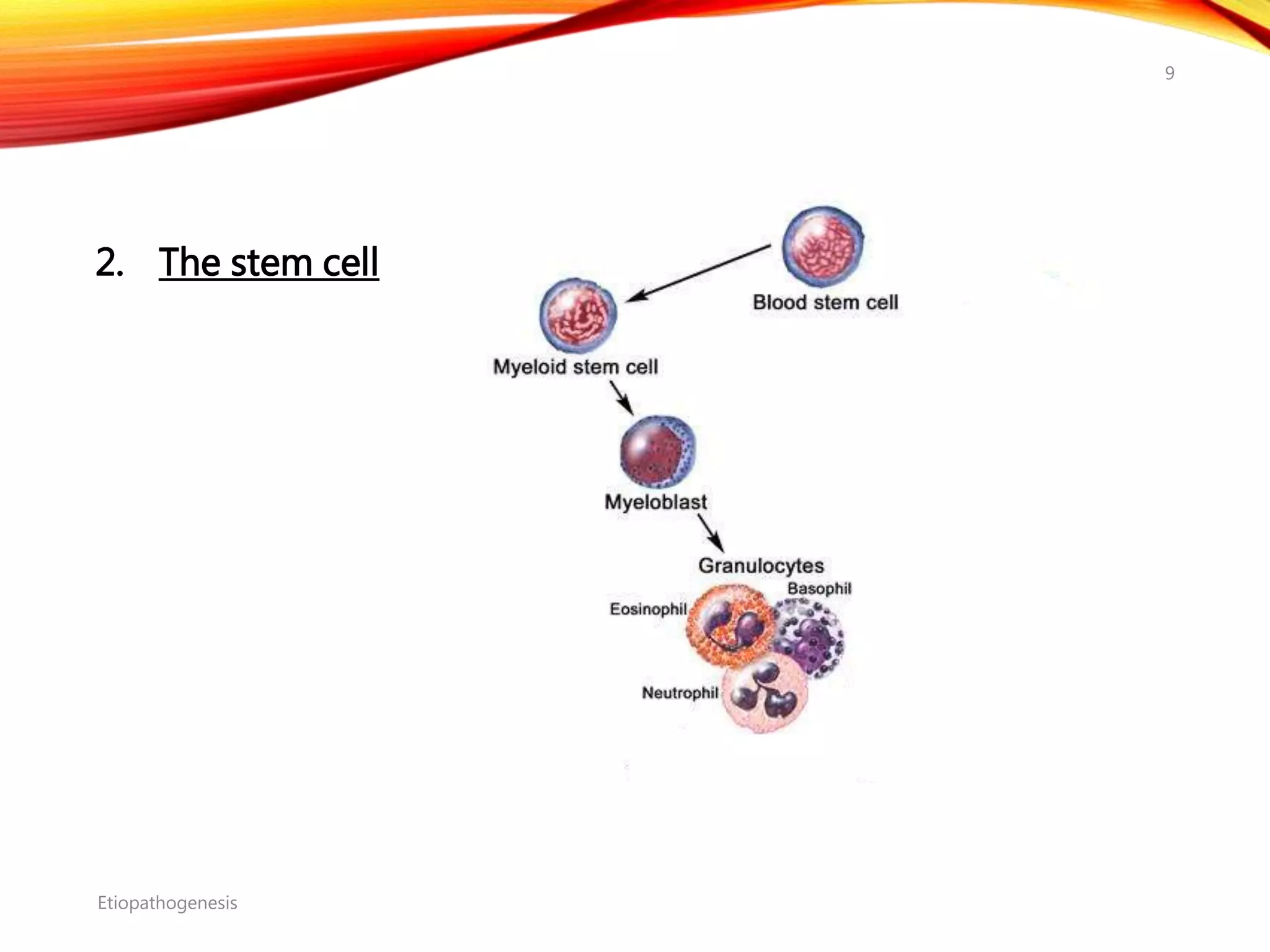
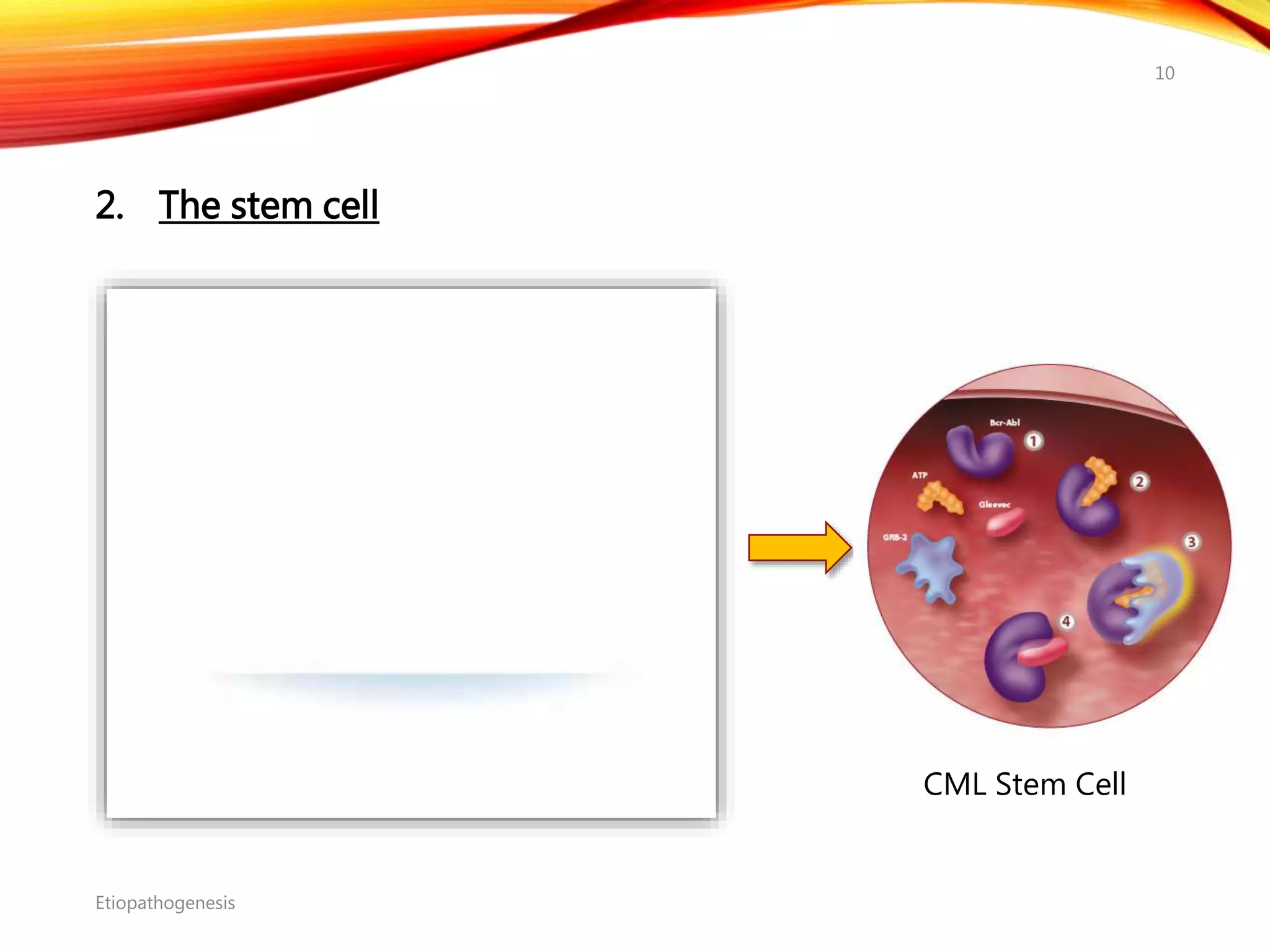
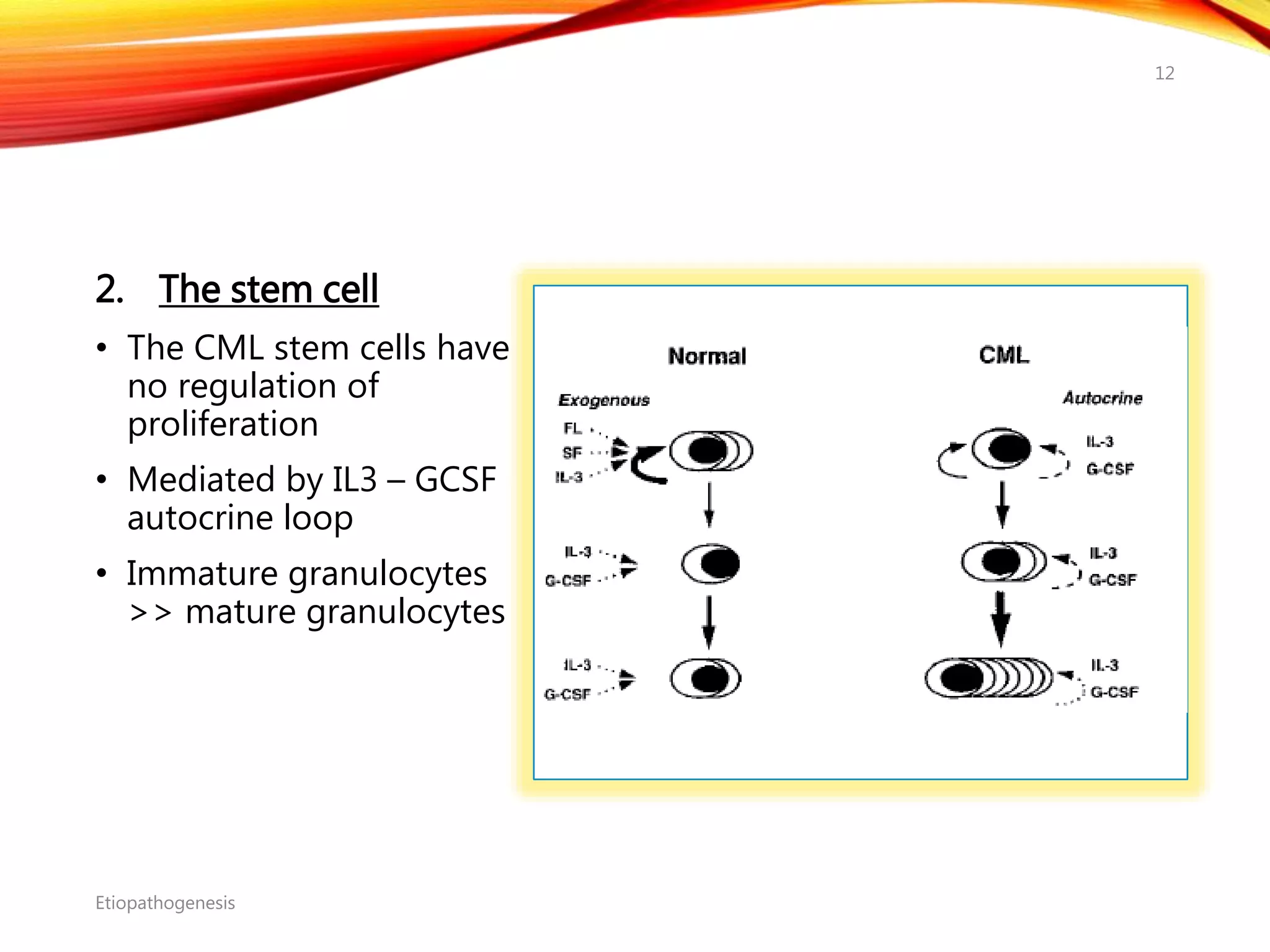
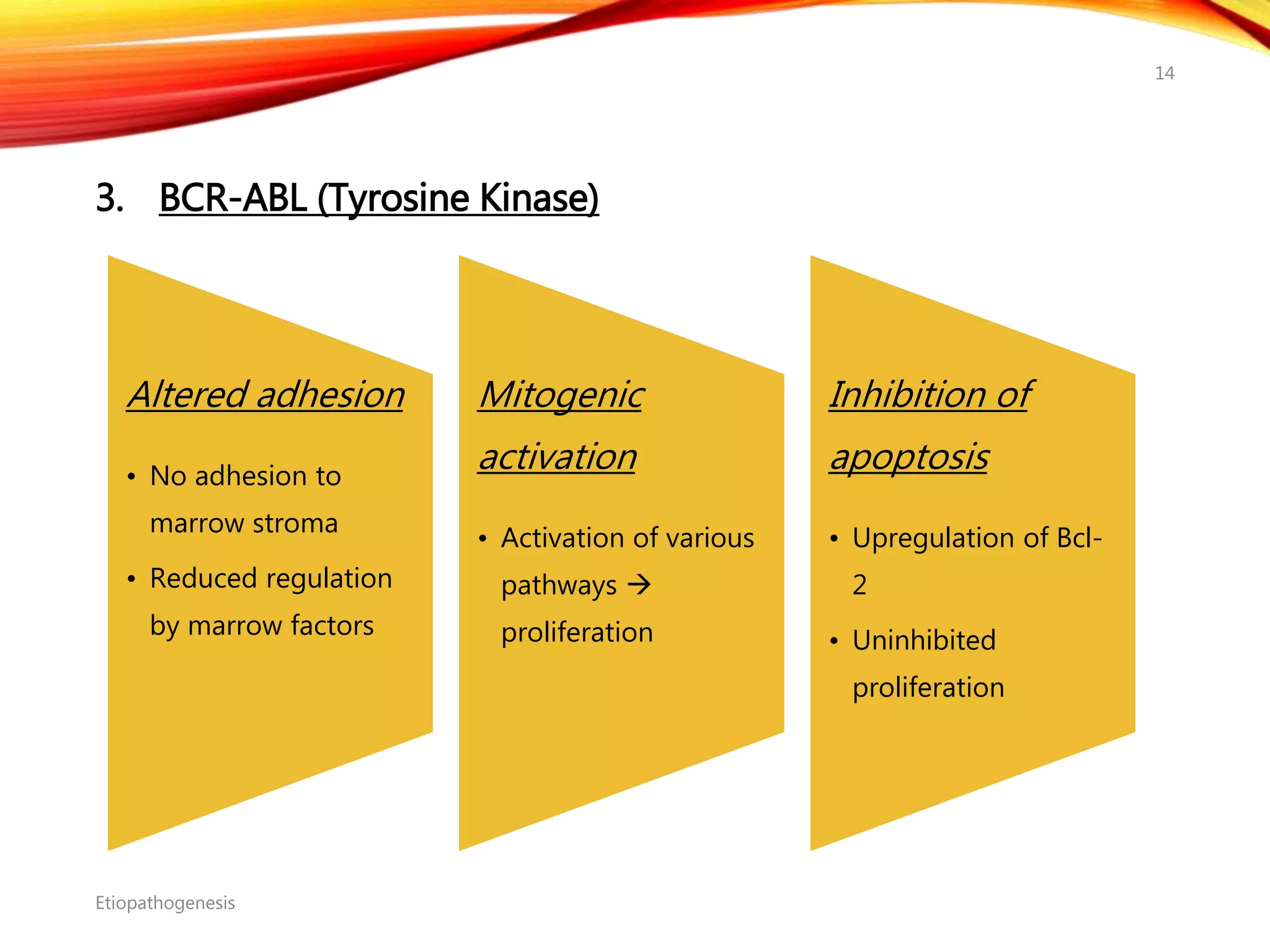
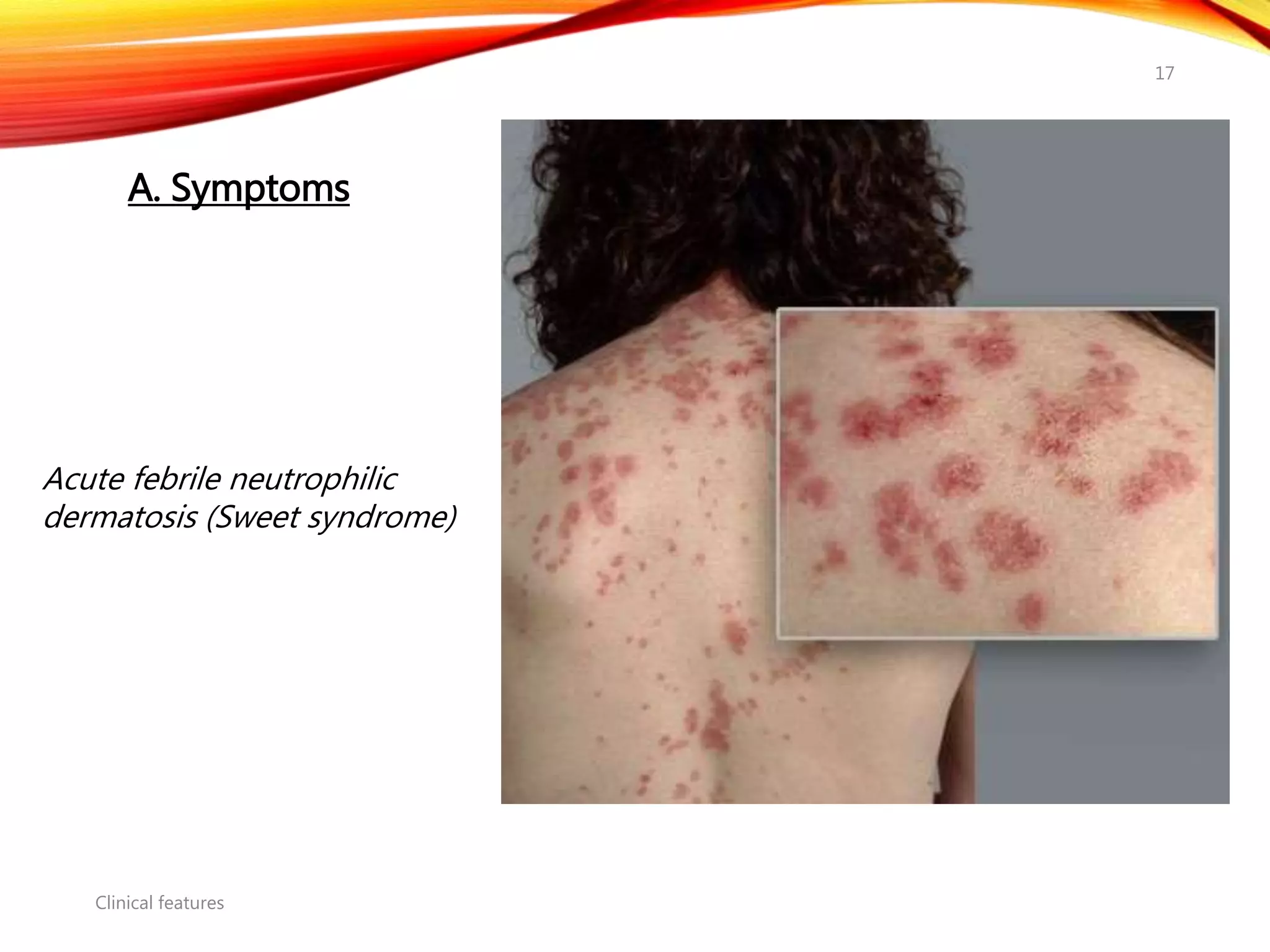
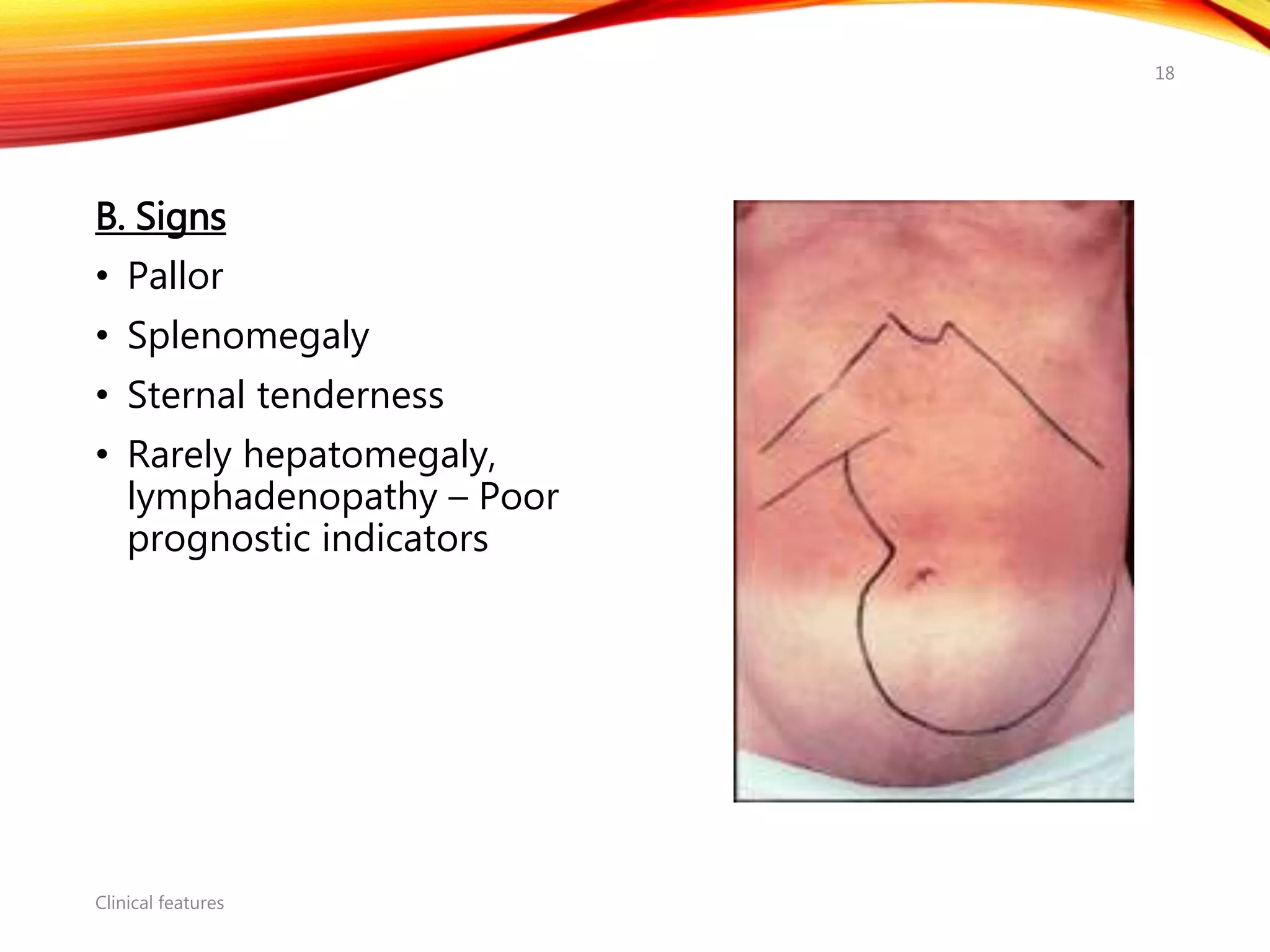
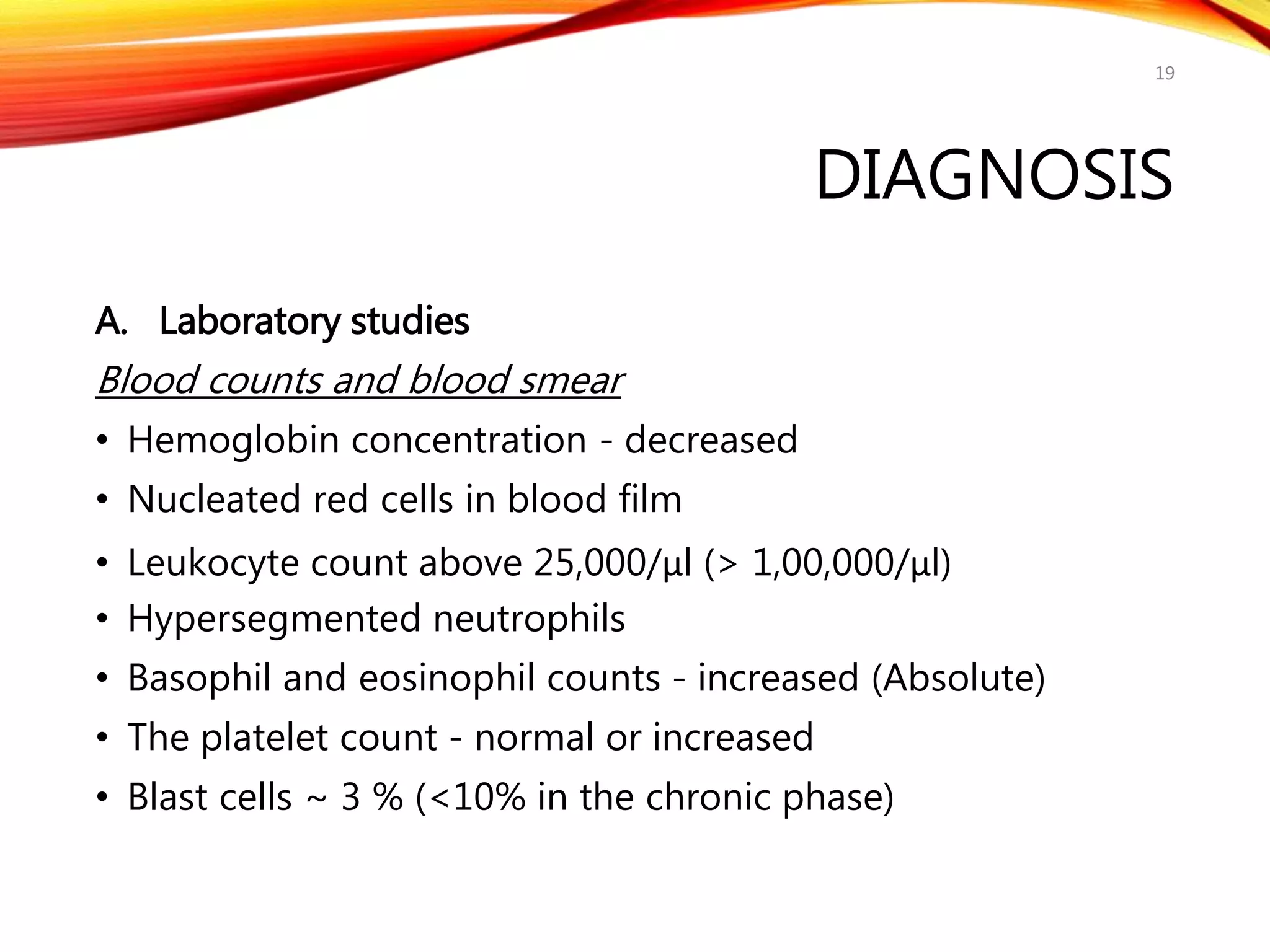
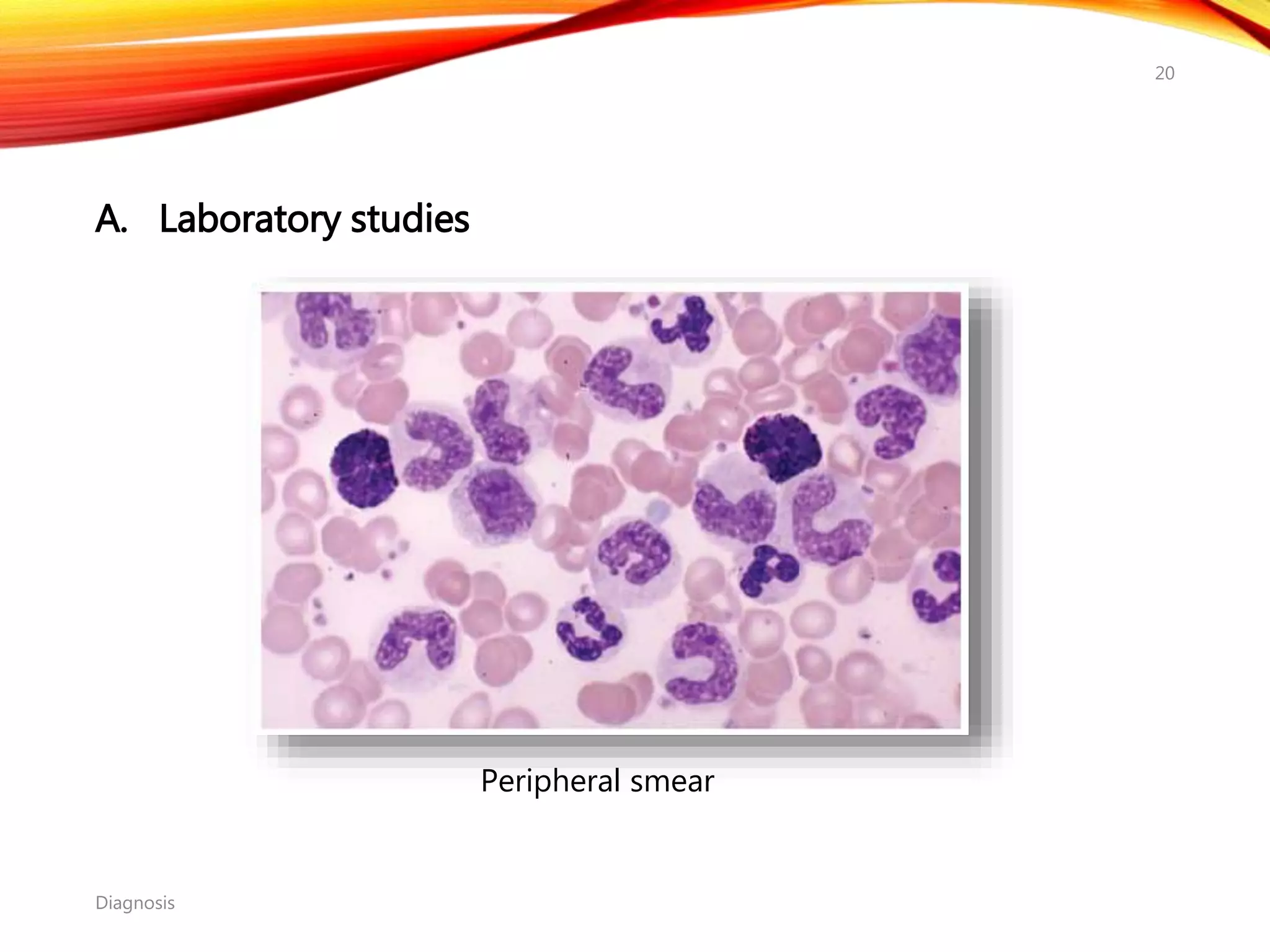
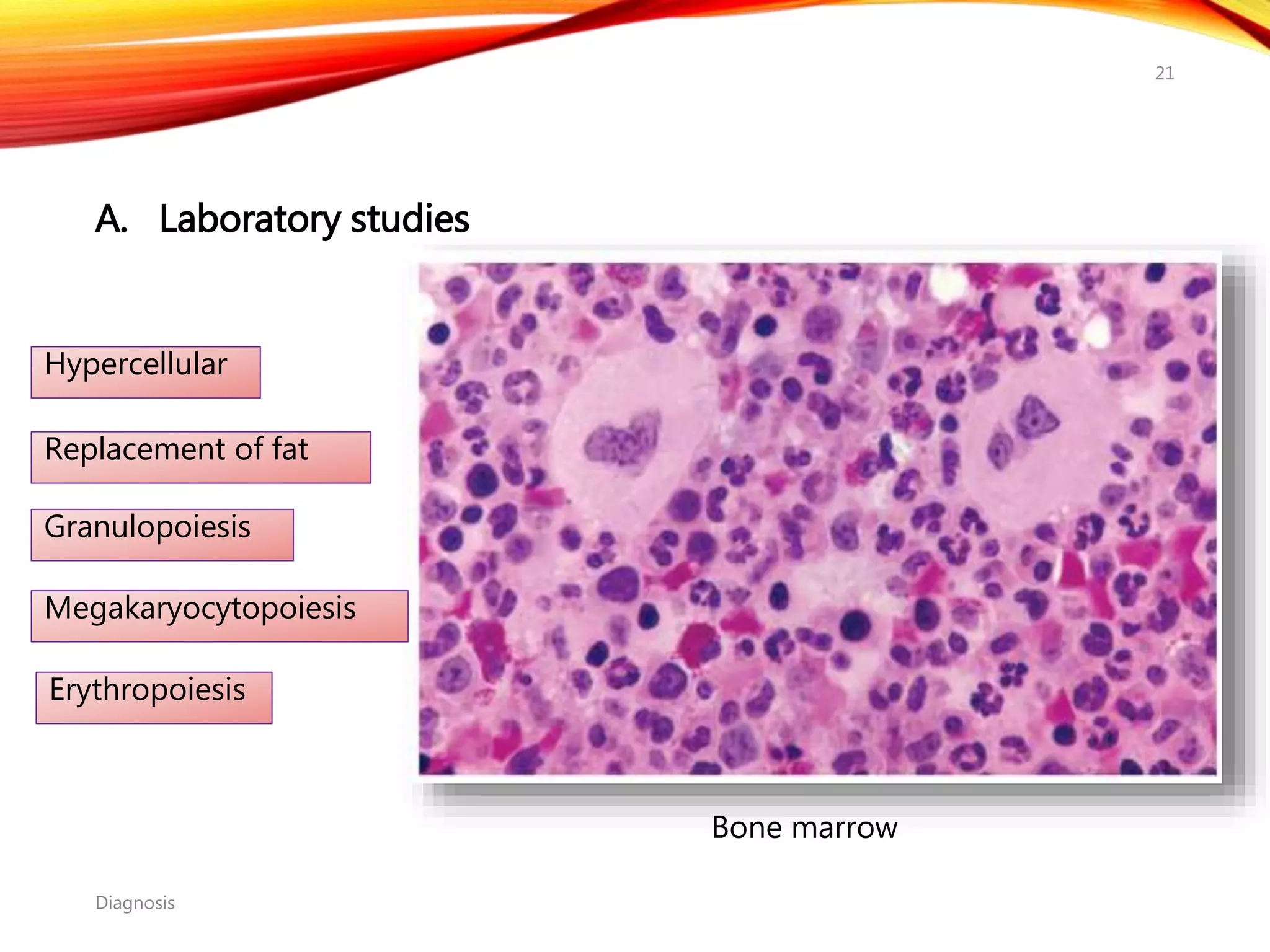
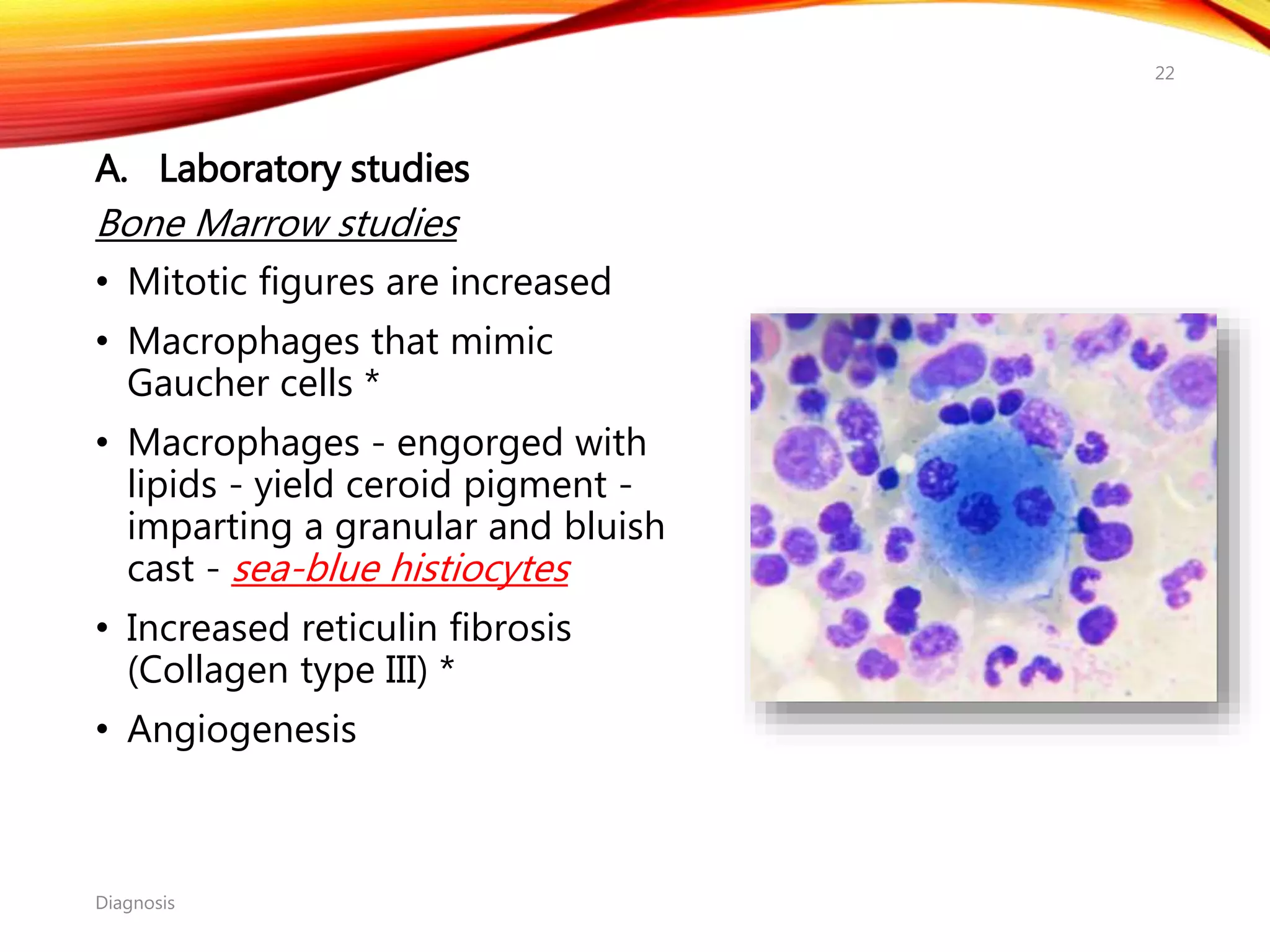
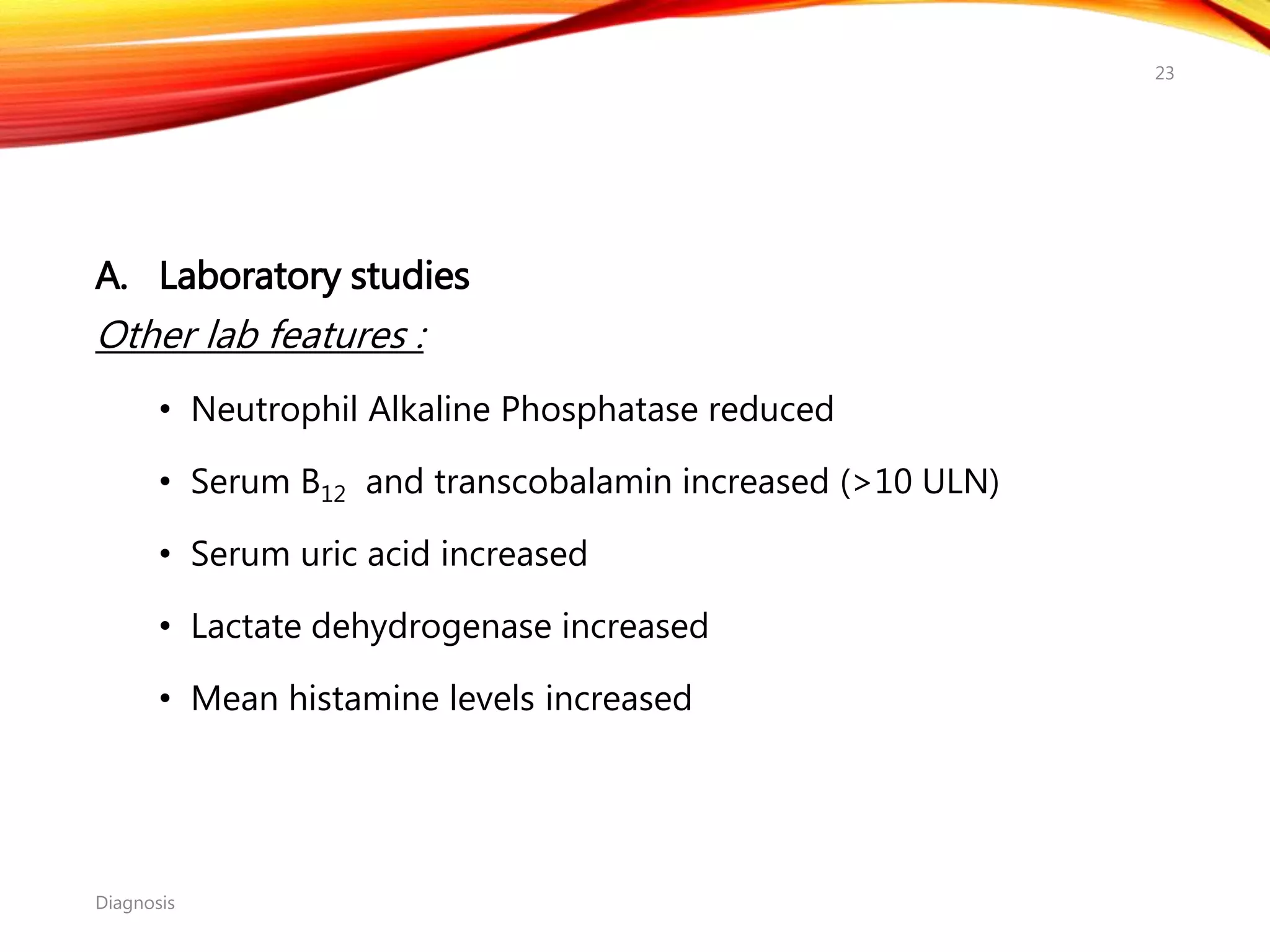
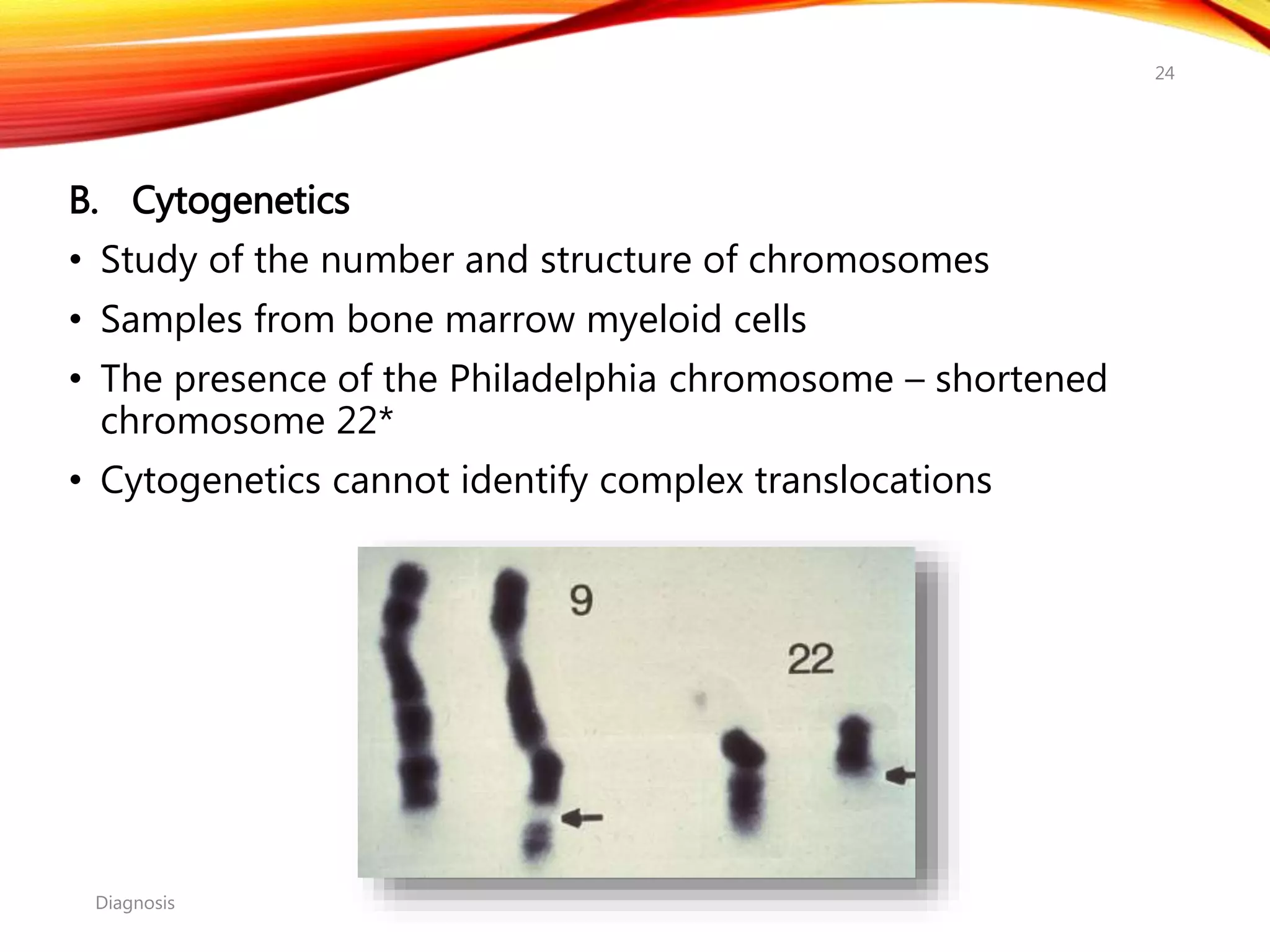
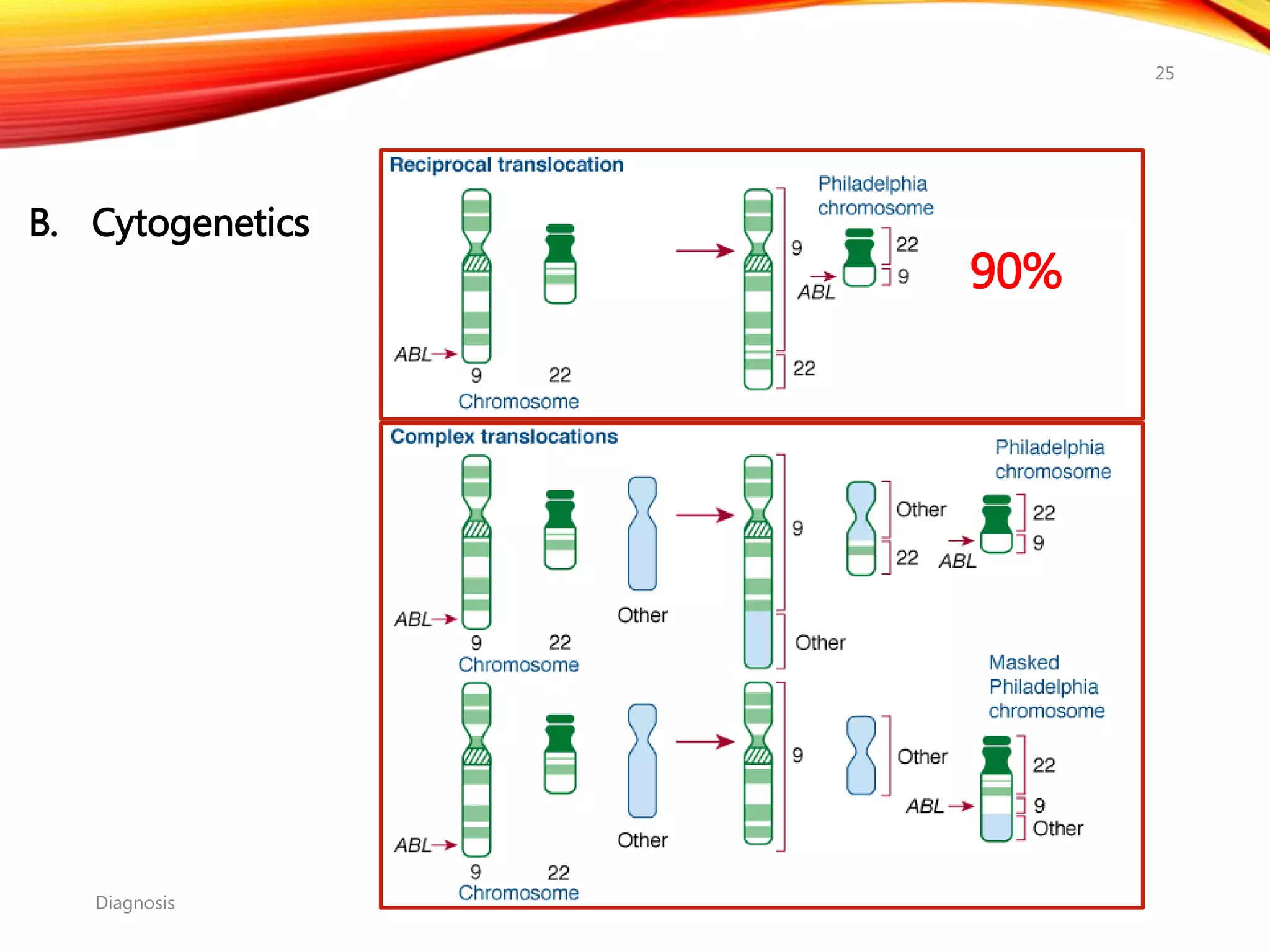
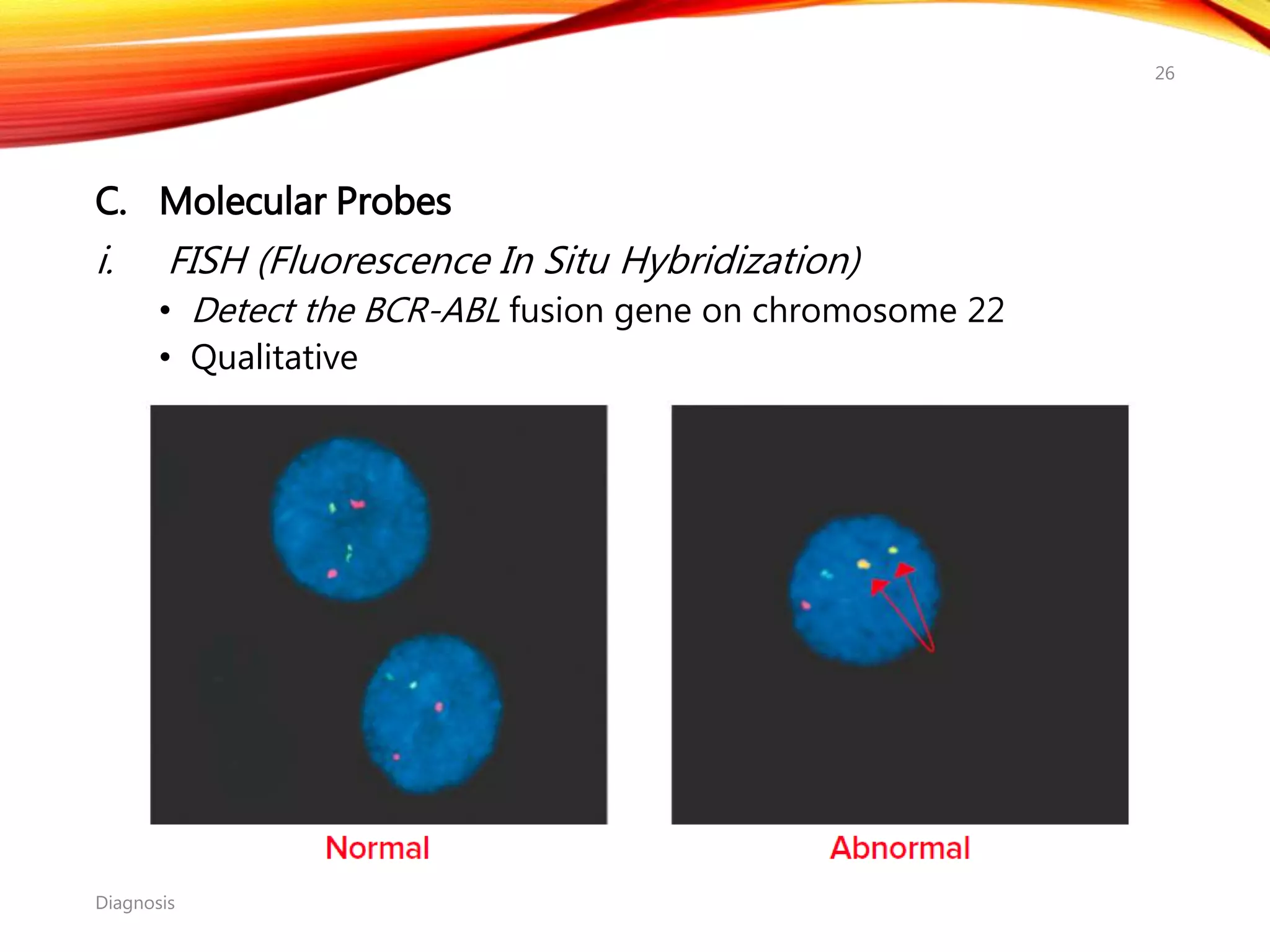
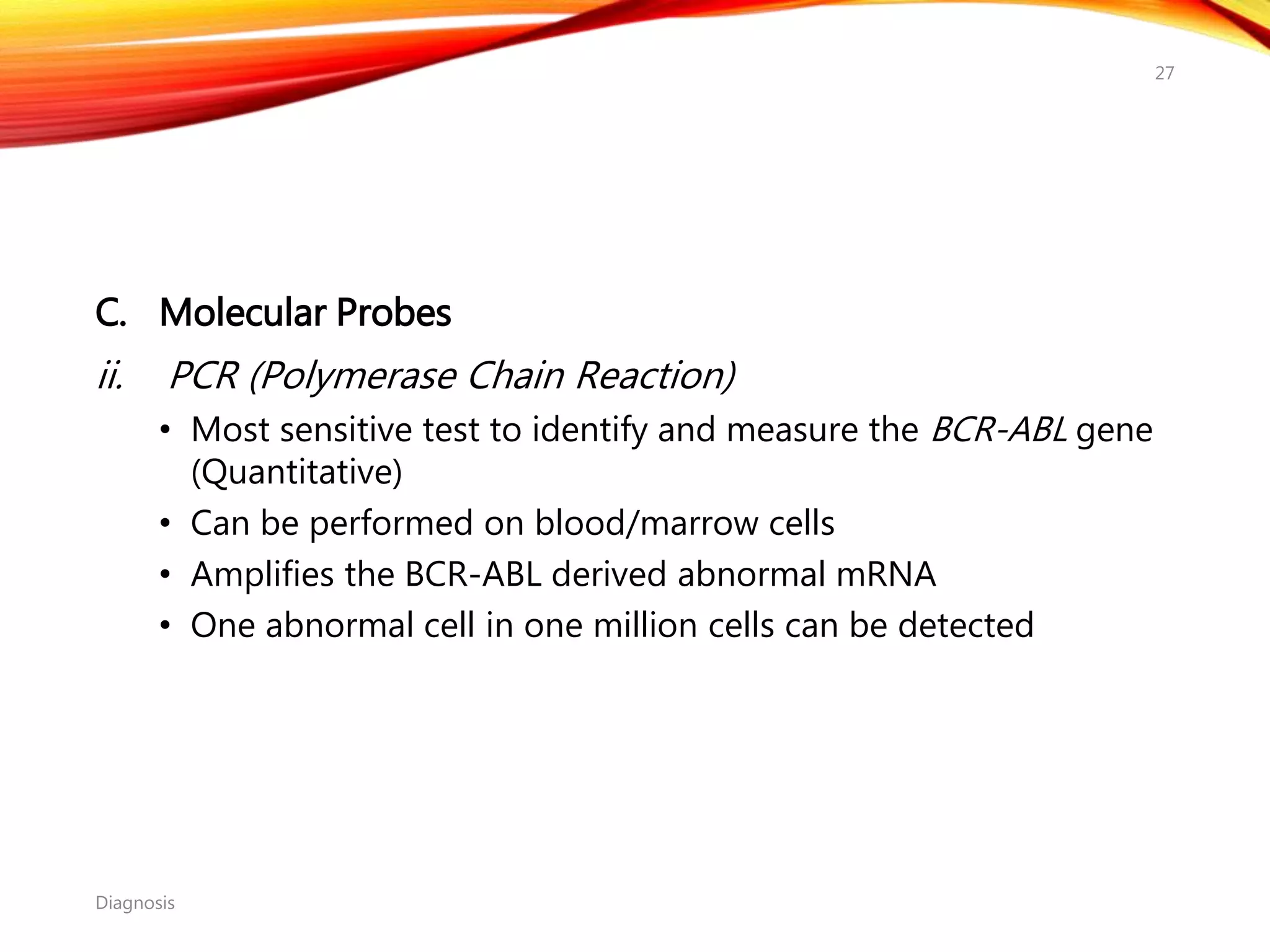
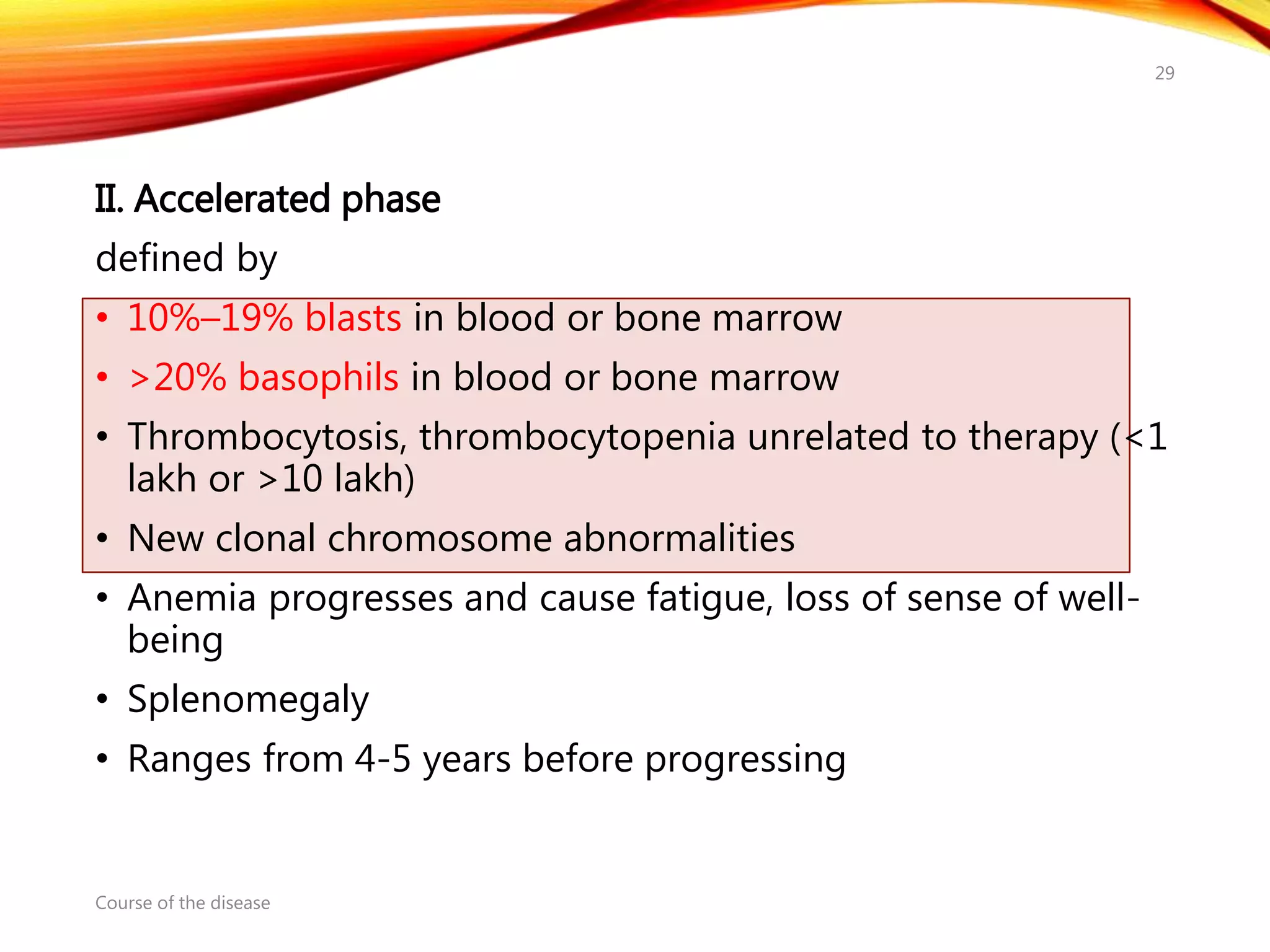
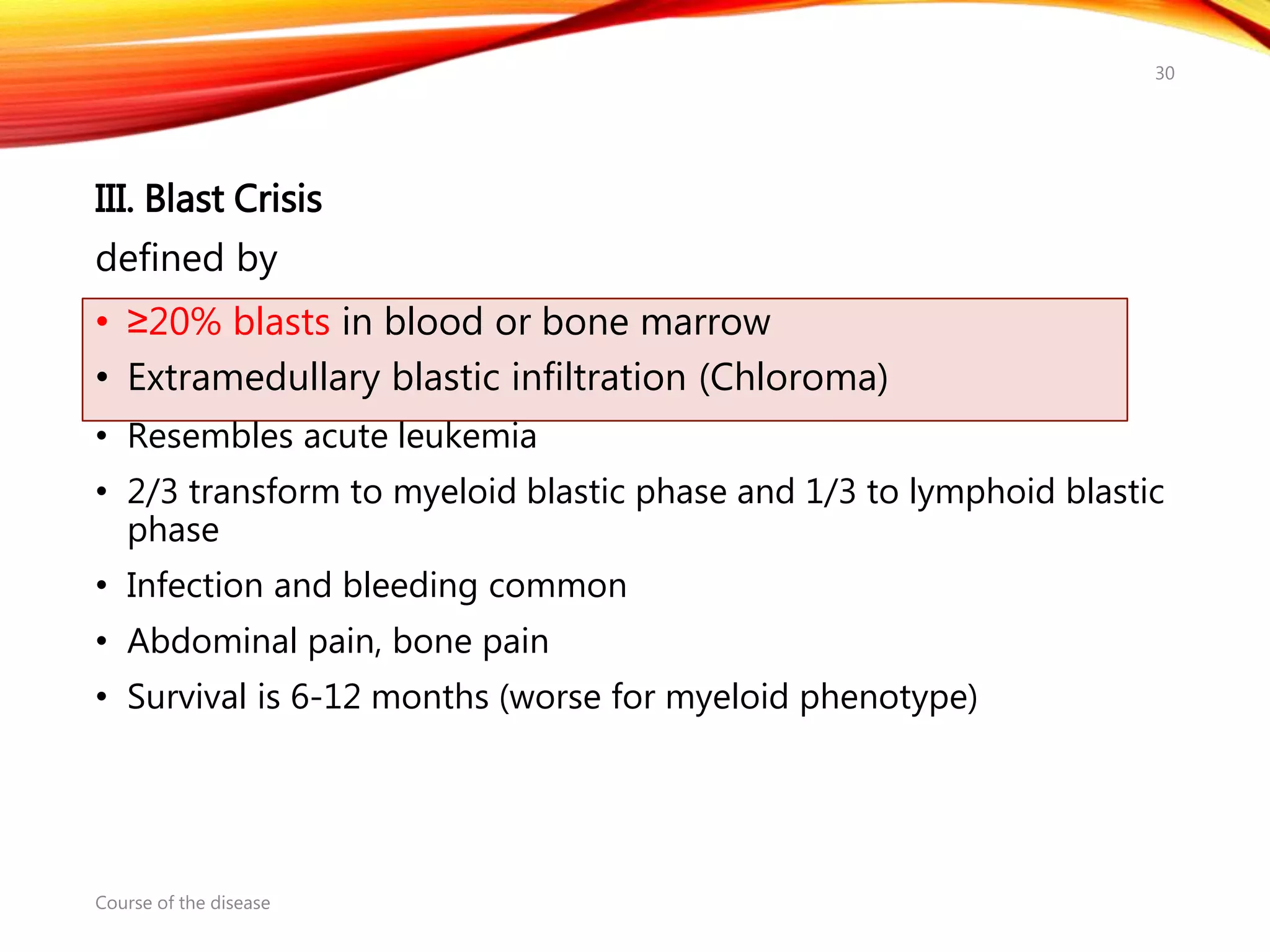
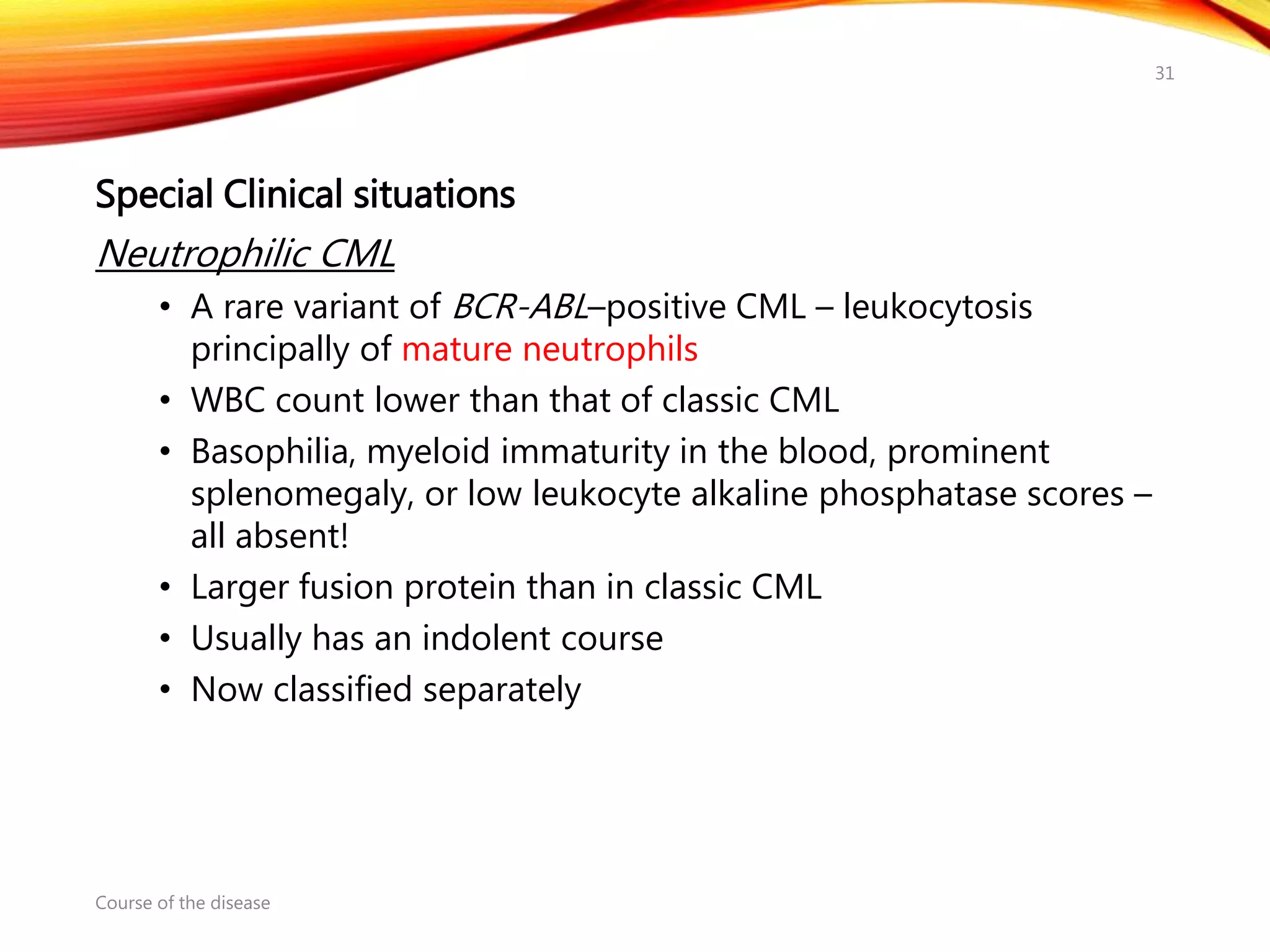
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a pluripotential stem cell disease characterized by anemia, extreme granulocytosis, and a genetic defect known as the Philadelphia chromosome. The treatment landscape for CML has evolved significantly with the introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors like imatinib, which have improved patient outcomes, although the disease remains incurable. CML progresses through three phases: chronic, accelerated, and blast crisis, with various risk assessment tools available to guide treatment strategies.















![3. The European Treatment and Outcome Study
(EUTOS) risk score
• Low risk - <87
• High risk - >87
• Also proposed a formula for predicting probability of
no CCyR at 18 months
• Presently used – ‘Imatinib era’
Risk assessment
38
(7 x basophil [%]) + (4 x spleen size)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cmlslideshare-140717103011-phpapp02/75/Chronic-Myelogenous-Leukemia-38-2048.jpg)