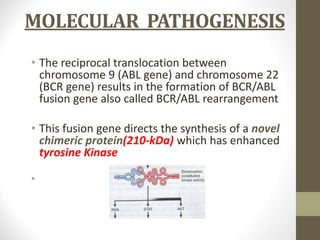
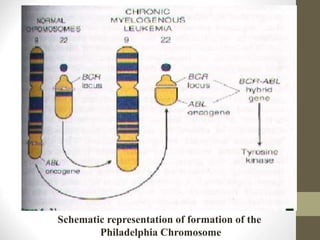
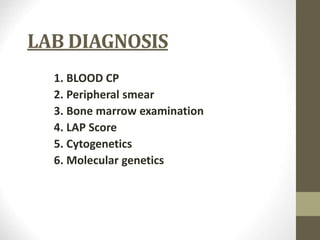
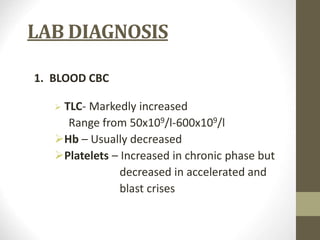
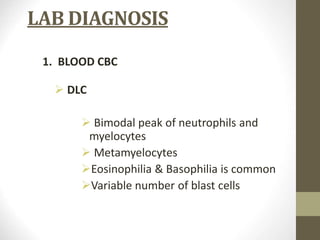
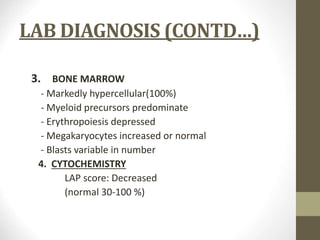
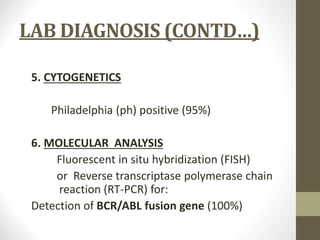
1) Chronic myeloid leukemia is a myeloproliferative neoplasm caused by the Philadelphia chromosome, a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 that results in the BCR-ABL fusion gene.
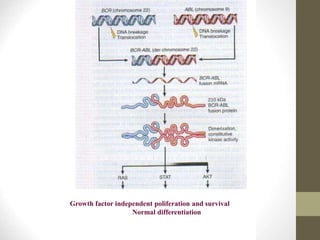
2) This fusion gene encodes a novel protein with unregulated tyrosine kinase activity that drives uncontrolled proliferation of myeloid cells.
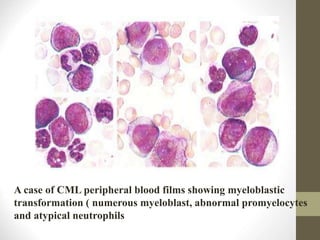
3) CML progresses through chronic, accelerated, and blast crisis phases marked by increasing myeloid blasts and worsening prognosis if untreated. Current tyrosine kinase inhibitors can achieve long-term remission.