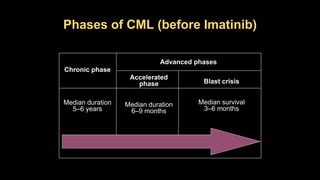
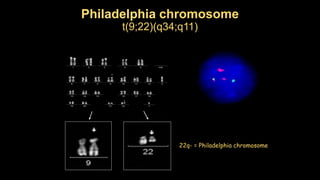
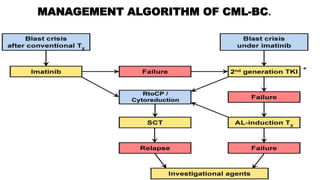
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a type of leukemia caused by the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene which results in uncontrolled proliferation of white blood cells. CML progresses through three phases: chronic phase, accelerated phase, and blast crisis. The chronic phase can last 5-6 years before progressing to more advanced phases. CML is diagnosed through blood tests and bone marrow biopsy to detect the Philadelphia chromosome and BCR-ABL1 fusion. Targeted therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as imatinib have significantly improved outcomes by inhibiting the BCR-ABL1 fusion protein. Resistance can still develop through additional genetic mutations.