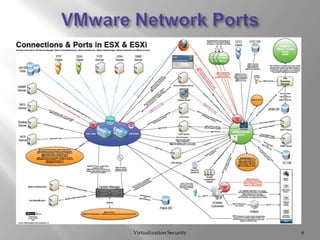
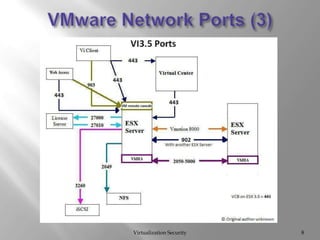
The document discusses virtualization security, highlighting vulnerabilities and risks associated with VMware systems, including a case where a former employee maliciously wiped out company data. It emphasizes the importance of hardening systems, patching, and auditing, along with compliance challenges under PCI DSS guidelines for virtual environments. Best practices for managing access controls and securing data in virtual systems are also outlined.