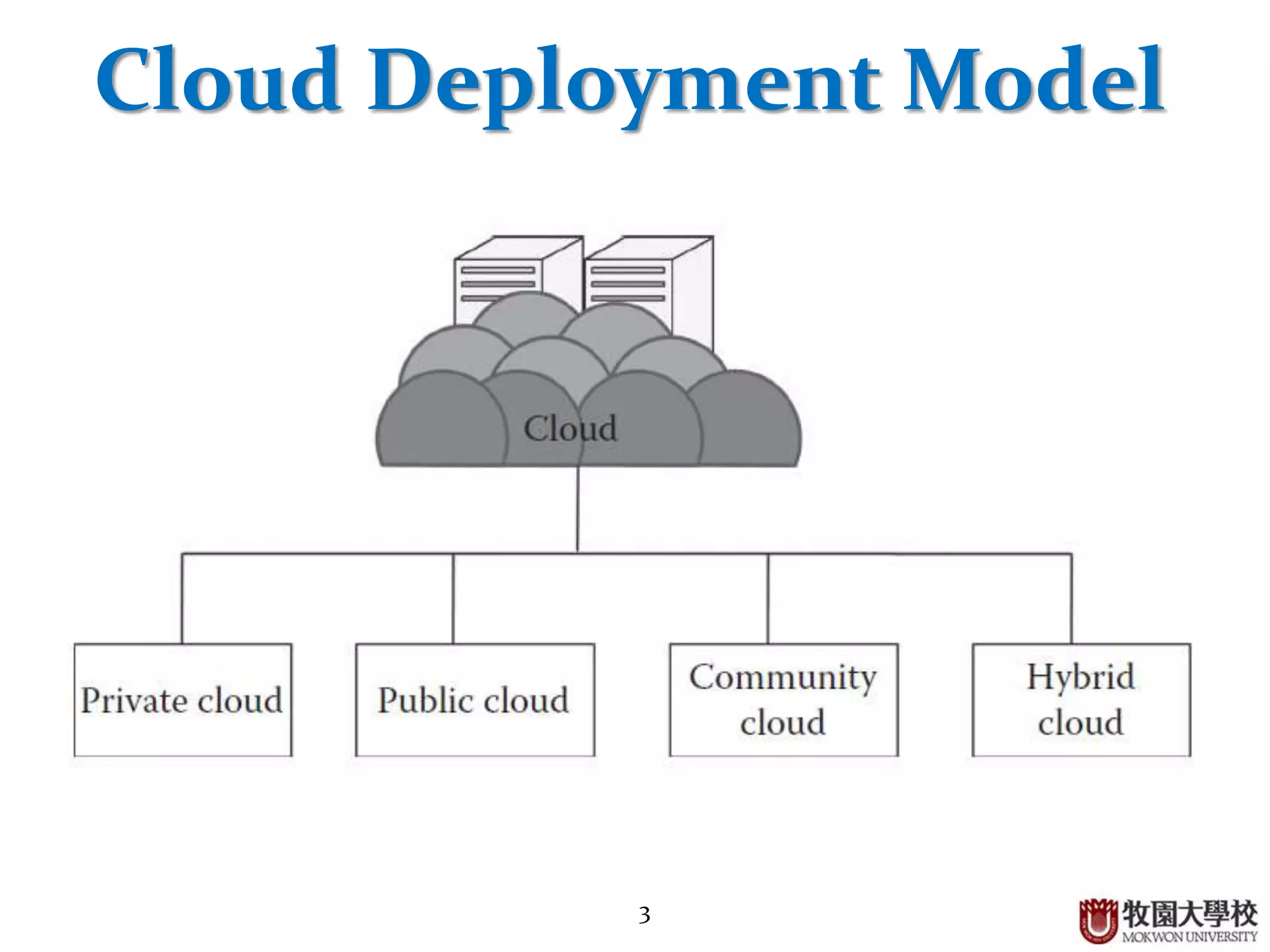
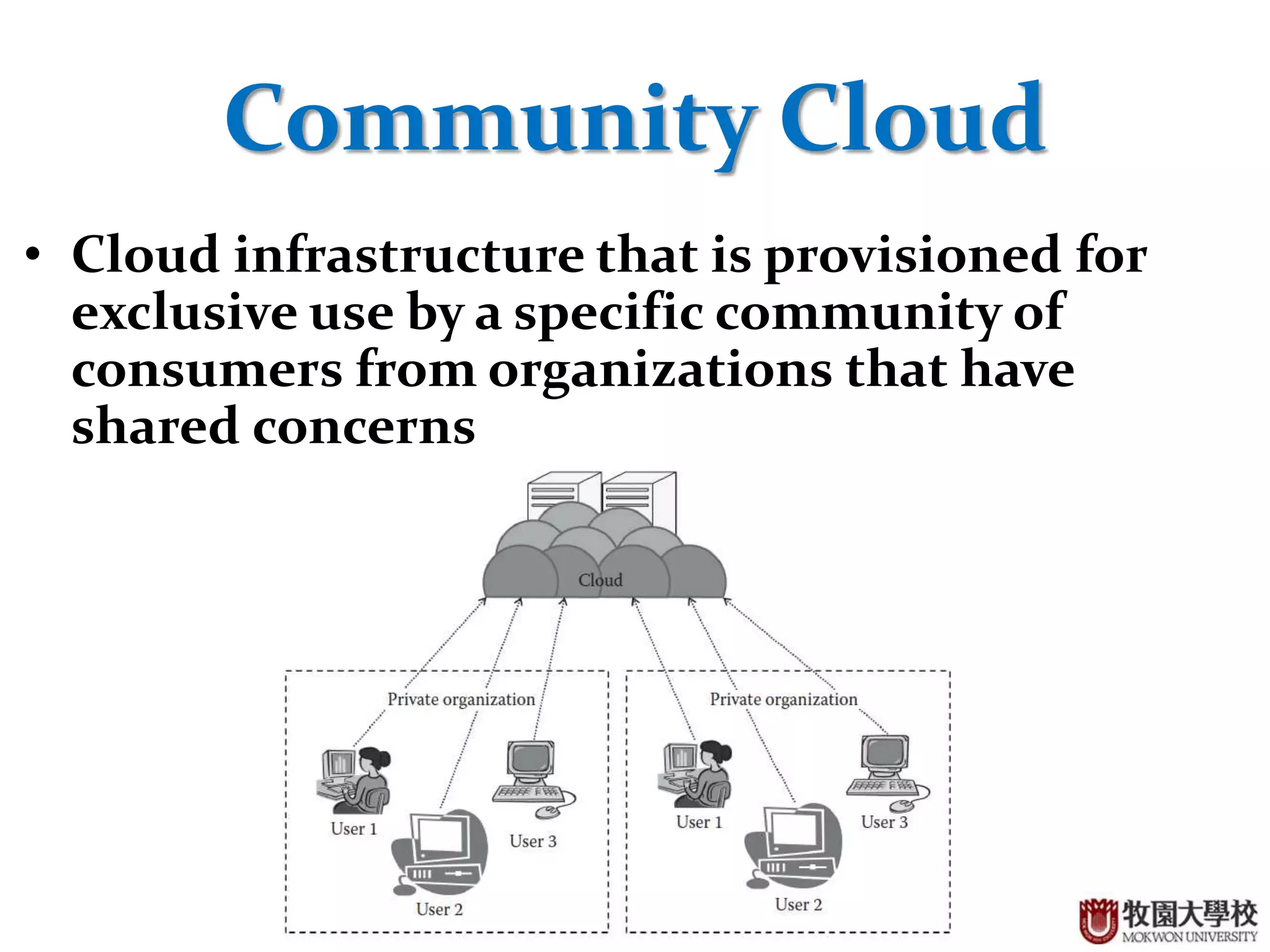
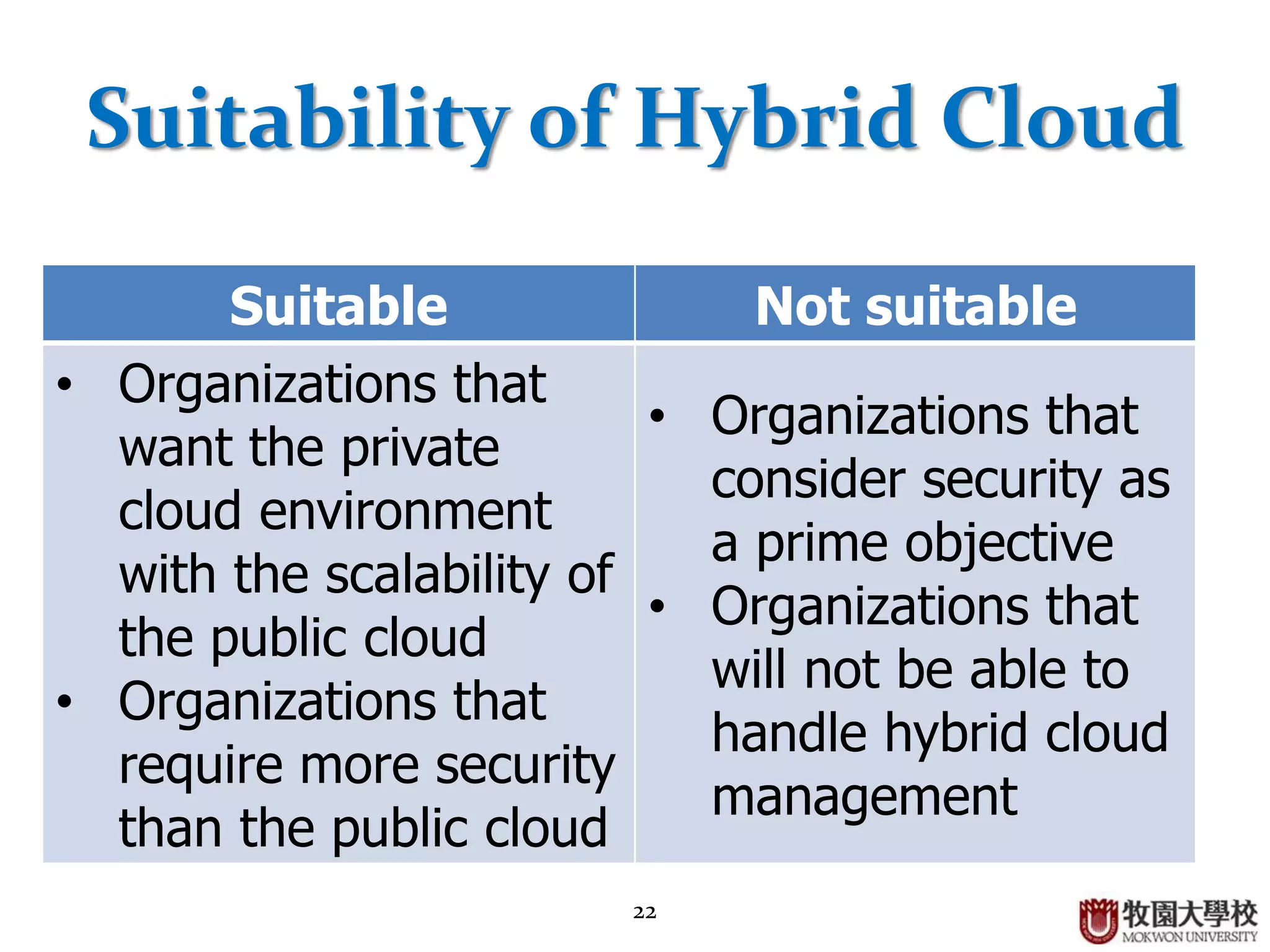
1. The document discusses different cloud deployment models including private, public, community, and hybrid clouds.
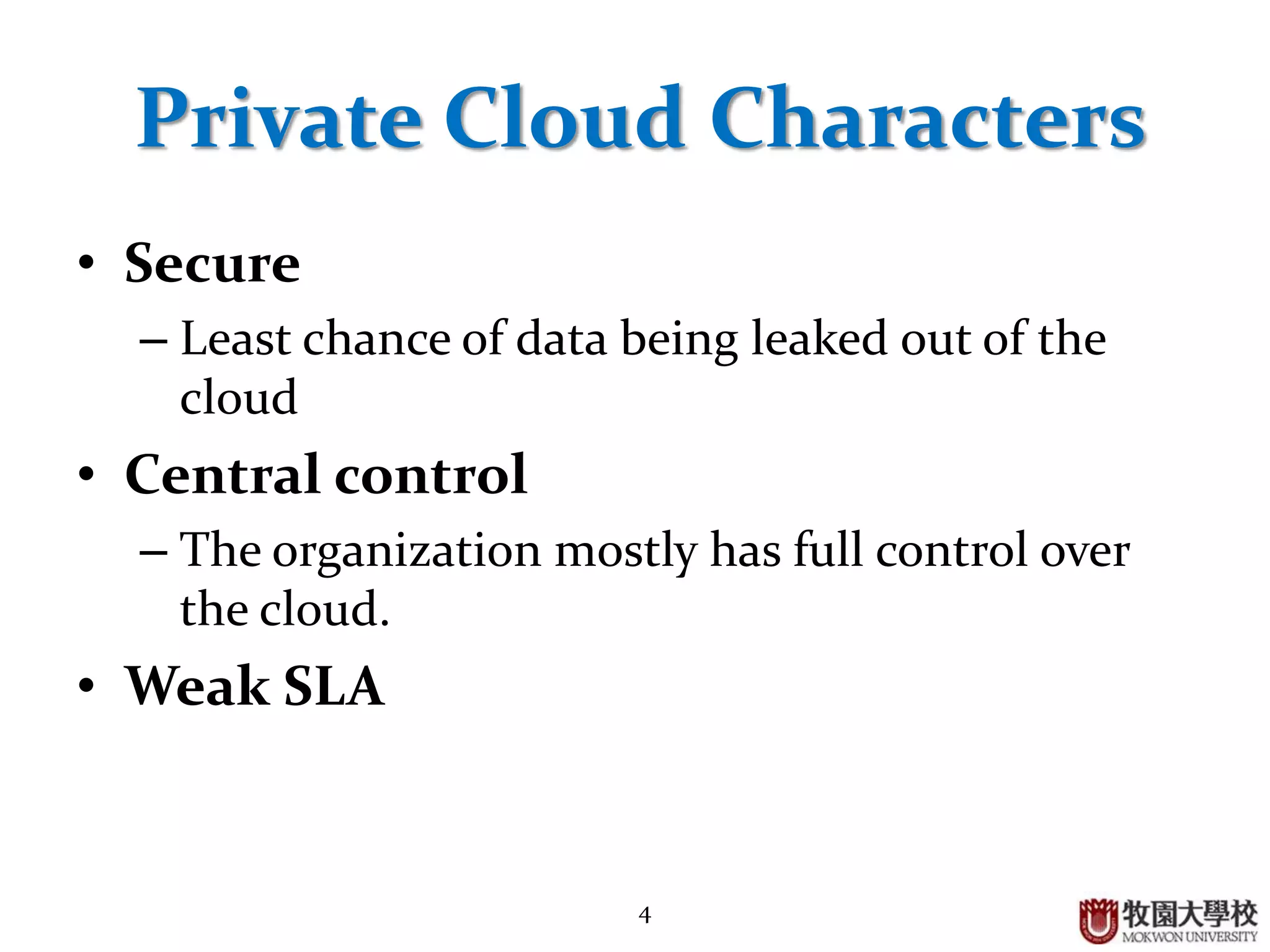
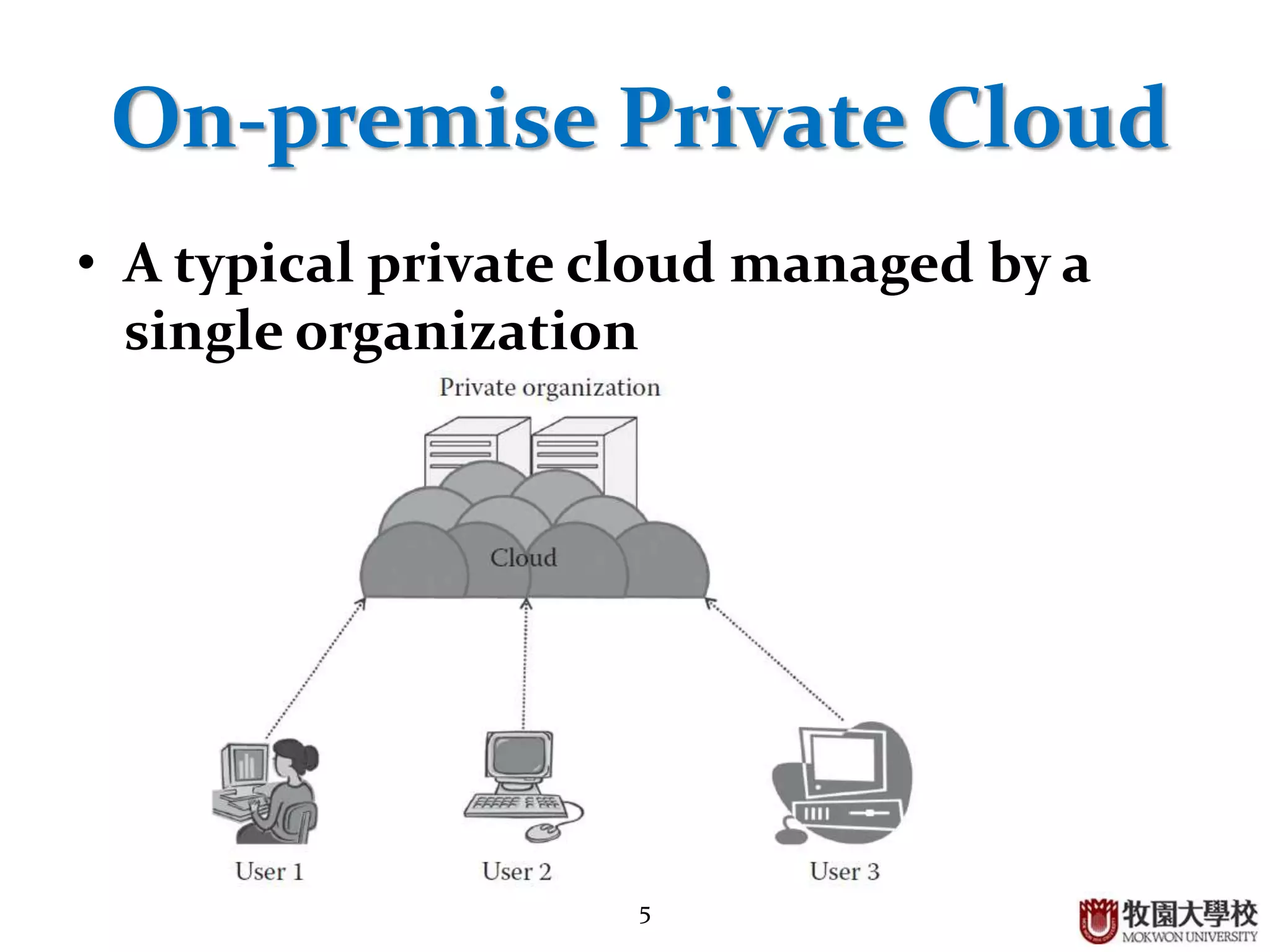
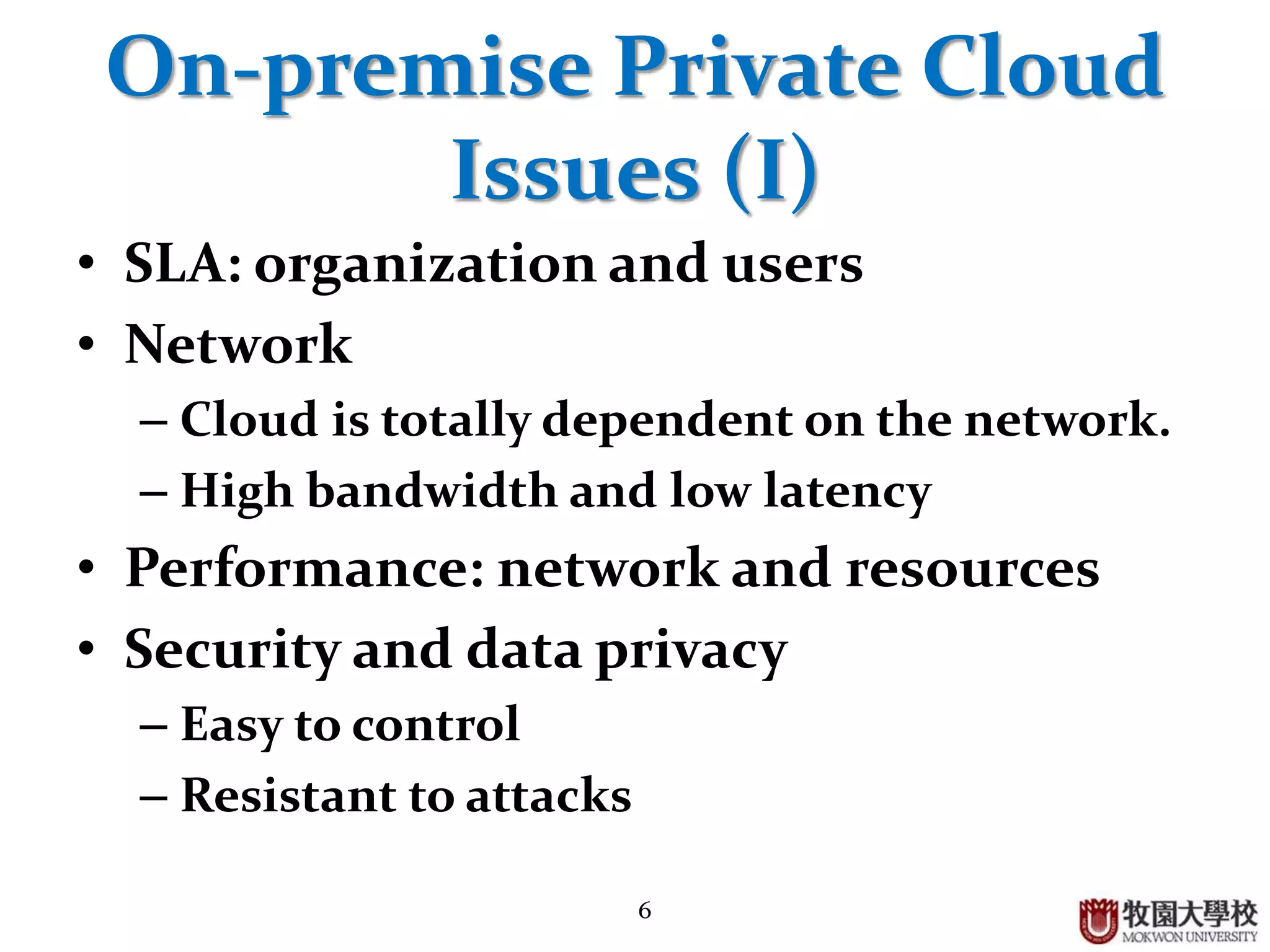
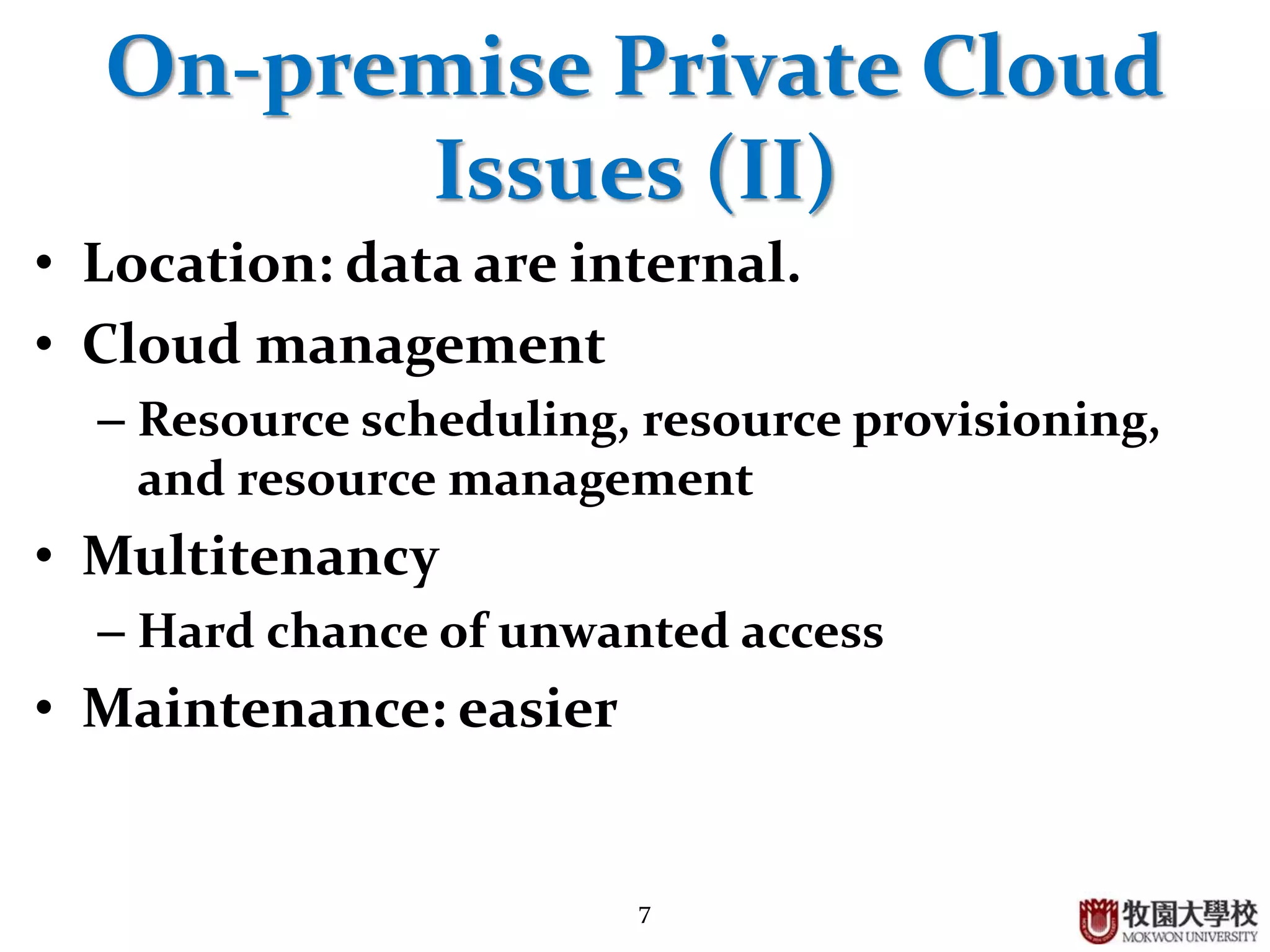
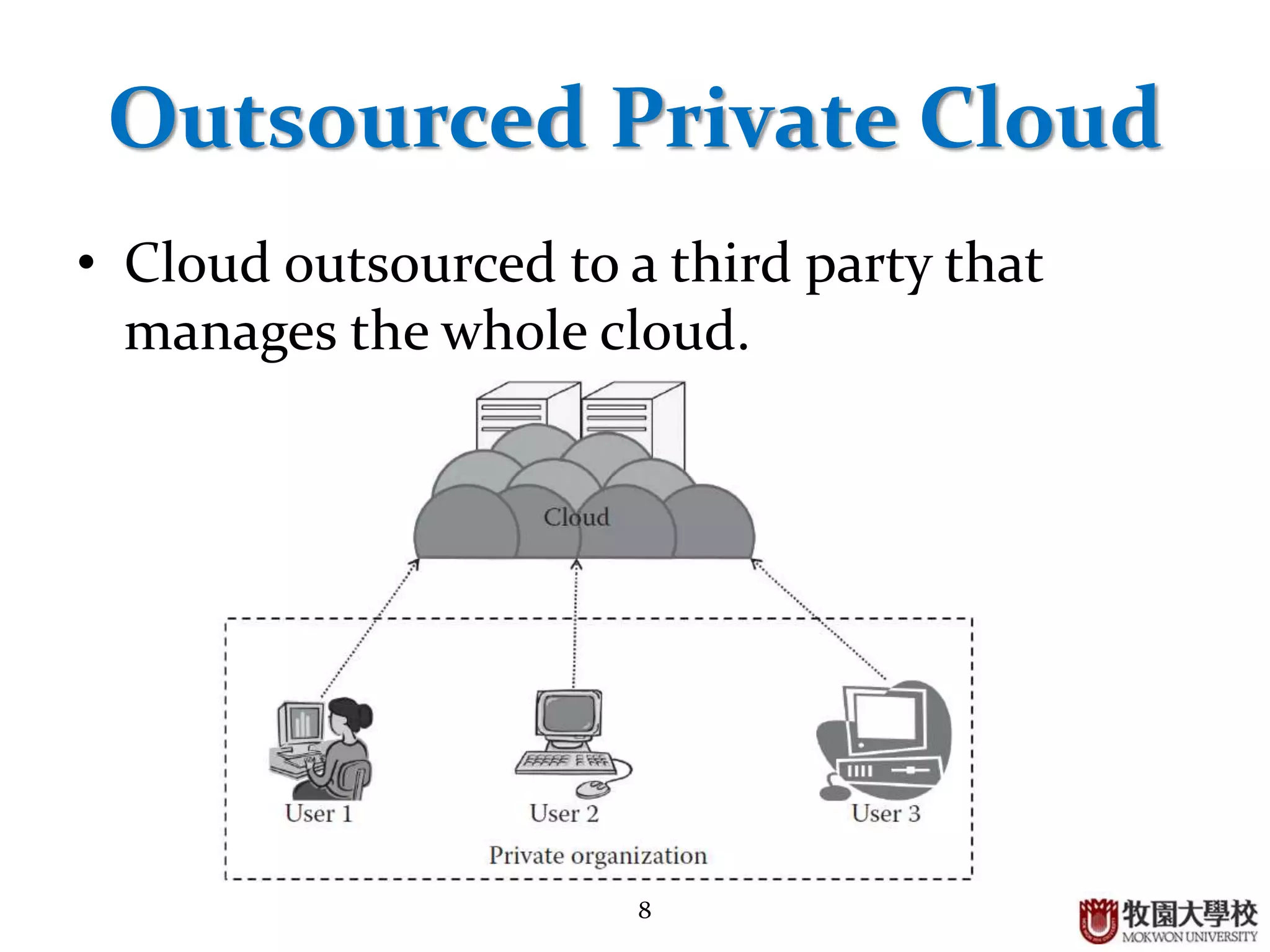
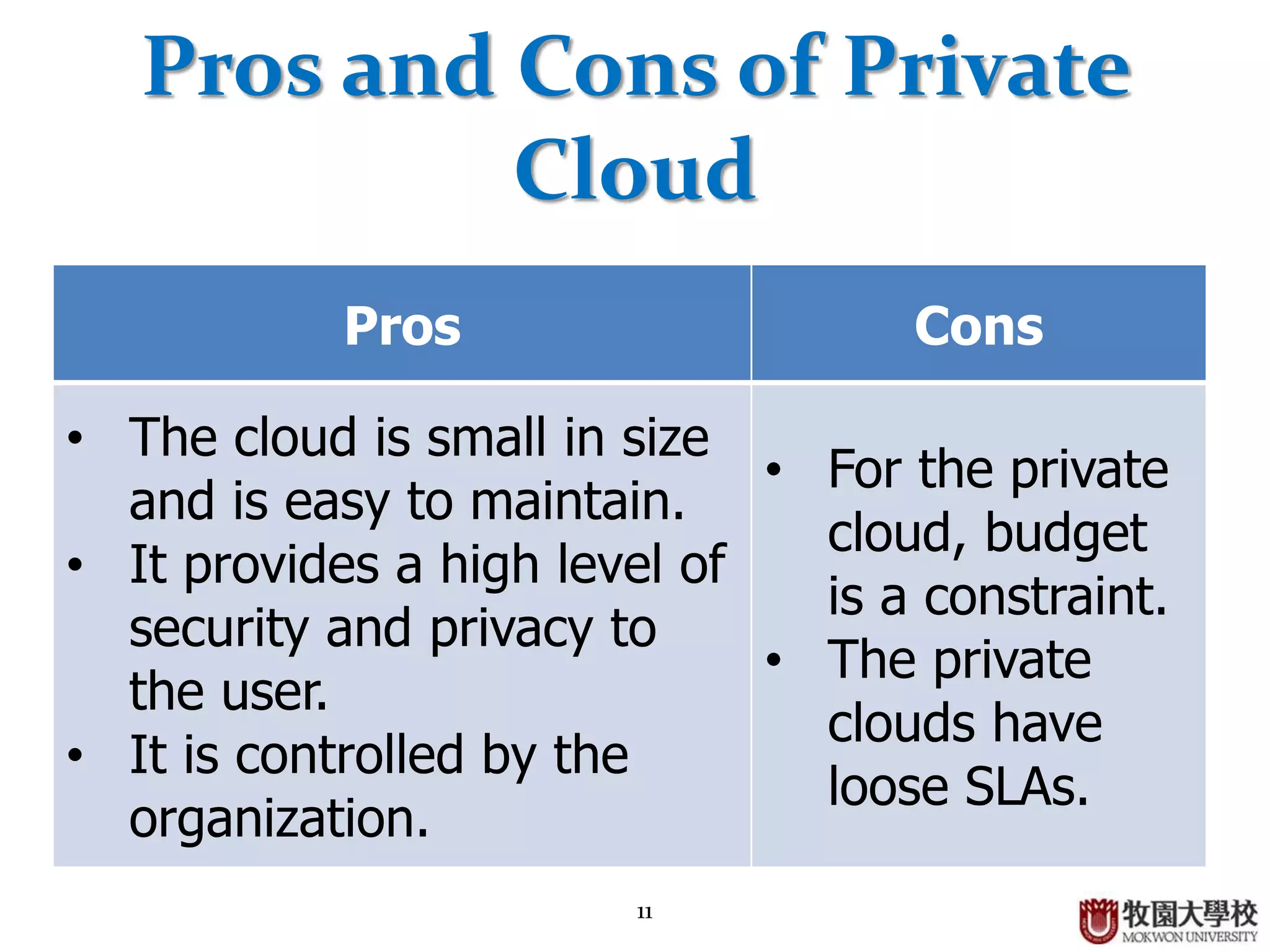
2. Private clouds can be either on-premise or outsourced to a third party, and provide a high level of security but have constraints around budget and SLAs.
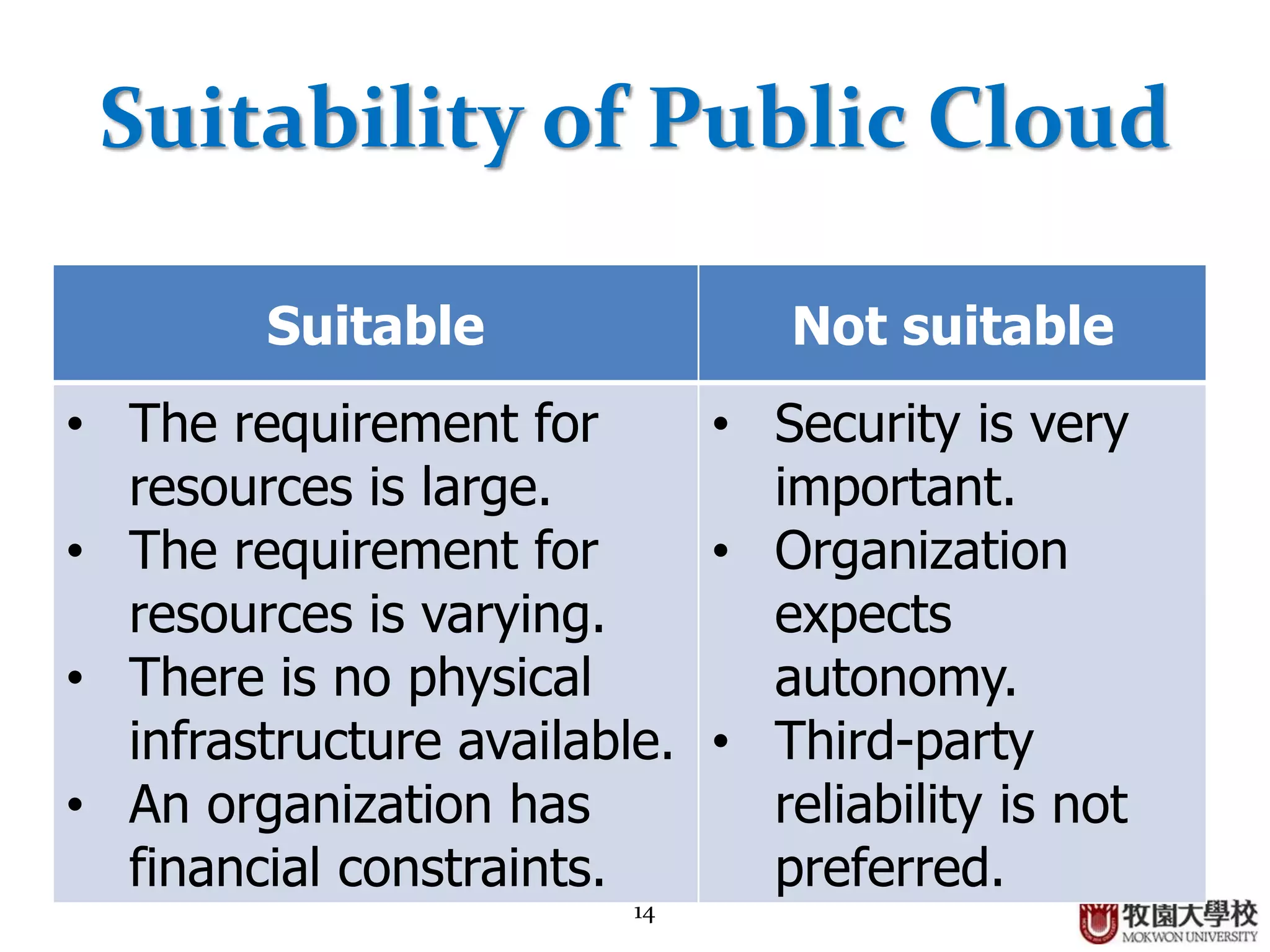
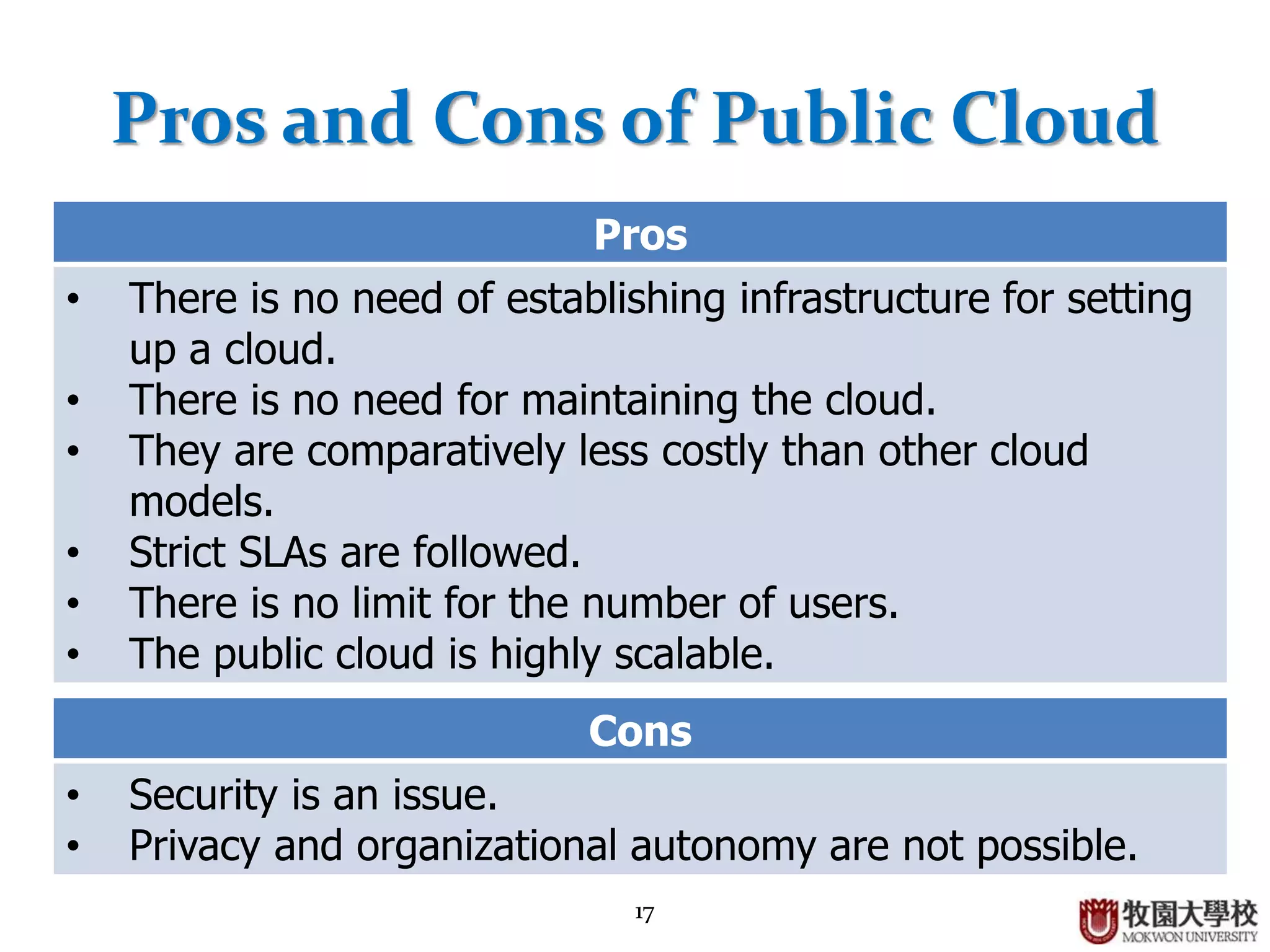
3. Public clouds are highly scalable and affordable but have challenges around security, data privacy, and organizational autonomy.
![Cloud Deployment
Model
Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University
Some of slides are referred to and all credits should go to:
[1] K. Chandrasekaran, Essentials of Cloud Conputing, CRC Press, 2015.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-180228122029/75/Cloud-Deployment-Model-1-2048.jpg)