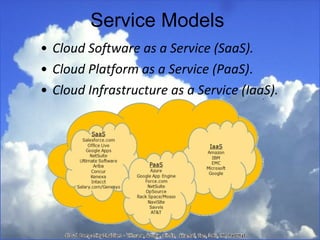
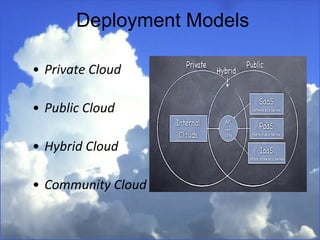
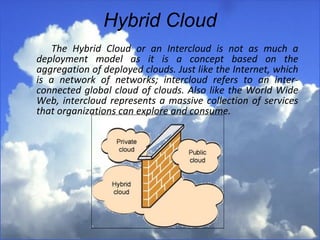
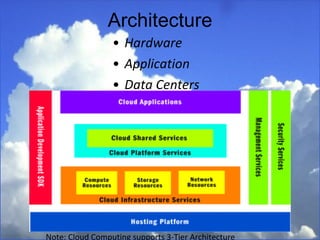
Cloud computing refers to services and applications delivered over the internet. There are three main service models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). There are also four deployment models for cloud computing: private cloud, public cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud. The document discusses the characteristics and differences between the various service and deployment models of cloud computing.