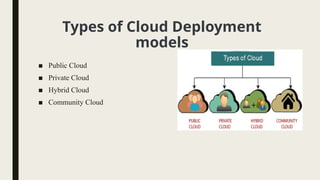
The document outlines various cloud deployment models, including public, private, hybrid, and community clouds, detailing their definitions, advantages, and disadvantages. Public clouds are cost-effective and easily accessible, while private clouds offer high security and control at the cost of accessibility. Hybrid clouds combine features of both for flexibility, and community clouds serve specific groups with shared interests, balancing collaboration and regulatory compliance needs.