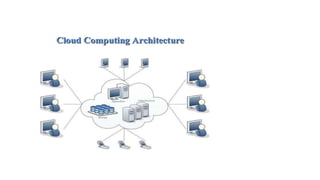
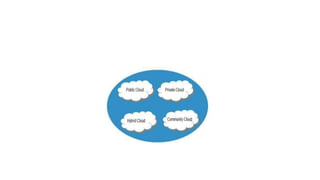
The document discusses the key characteristics, principles, deployment models, and advantages of cloud computing. Specifically, it outlines the five essential characteristics of cloud computing as on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. It also describes the basic principles of cloud computing as federation, independence, isolation, elasticity, business orientation, and trust. Finally, it summarizes the main deployment models of public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud and their respective advantages.