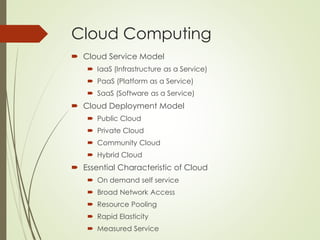
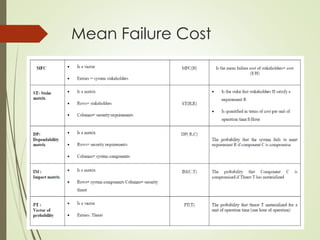
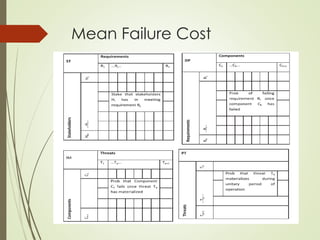
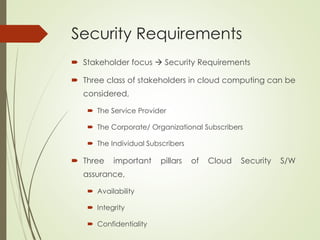
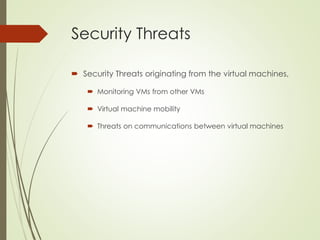
This document proposes a cyber security model for cloud computing environments. It discusses key cloud concepts like service and deployment models. It then covers cyber security threats in cloud computing, including those originating from the host, between the customer and datacenter, and from virtual machines. The document also presents a mean failure cost approach to measure security and quantify risks through stakeholder, dependency, and impact matrices. Finally, it argues the model can support cloud business decisions by pricing security upgrades and assessing enhancement cost effectiveness.