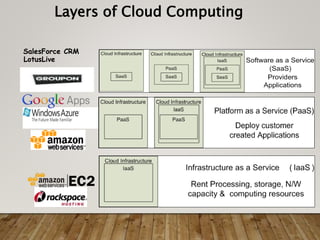
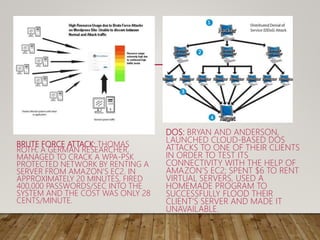
Cloud computing delivers computing resources over a network and includes three service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Security threats to cloud computing include hackers abusing cloud resources to conduct denial of service attacks and brute force attacks at low cost. Data breaches are also a risk as sensitive data stored in the cloud has been targeted by online theft. Malware injection attacks and wrapping attacks that change the execution of web applications are additional security risks. Countermeasures include access management, data protection techniques, and implementing security policies and technologies.