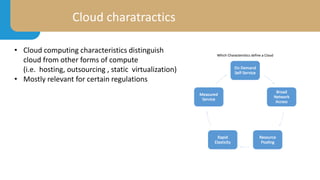
This document provides an overview of building secure cloud architecture. It discusses cloud characteristics and services models like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. It also covers the shared responsibility model between providers and customers. Additional topics include compliance requirements, privacy basics, architecting for availability, network separation, application protection, identity and access management, monitoring tools, log management, and containers security. The document aims to educate readers on best practices for securely designing cloud infrastructure and applications.