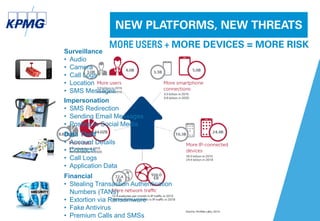
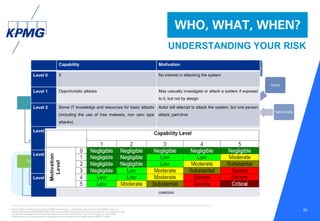
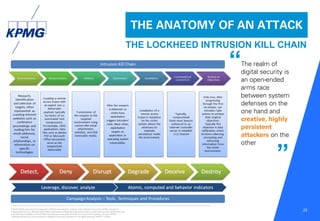
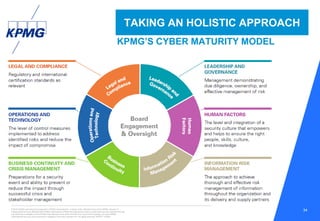
This document discusses the evolving cyber threat landscape and increasing cyber risks that organizations face. It notes that cyber attacks are becoming more frequent, sophisticated, and targeted. The document outlines several recent major cyber attacks including data breaches at Sony, Target, and Ashley Madison, as well as ransomware attacks and hacking incidents. It emphasizes that organizations need to adopt a proactive, intelligence-led approach to cyber security that includes red team exercises, assuming breaches will occur, and deploying security intelligence systems to detect threats early. The key is understanding adversaries and their tactics in order to adapt defenses accordingly.