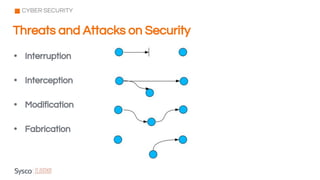
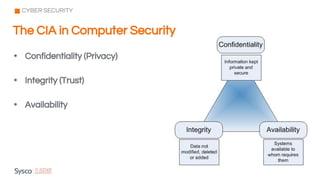
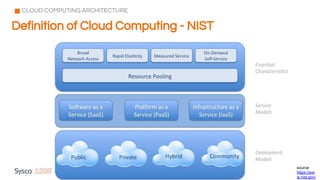
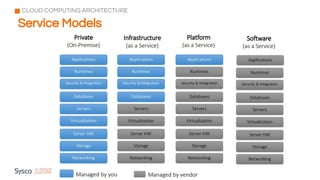
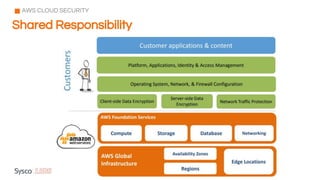
The document outlines the fundamentals of cybersecurity, cloud computing, and ethical hacking practices. It highlights various threats to cloud security, such as data breaches and account hijacking, while emphasizing the importance of regulatory standards and security measures. Additionally, it discusses the role of tools like AWS Shield and AWS WAF in protecting cloud resources and managing access control.