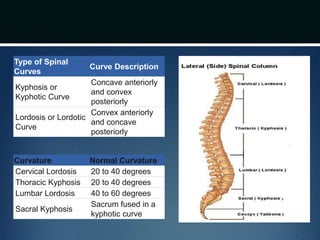
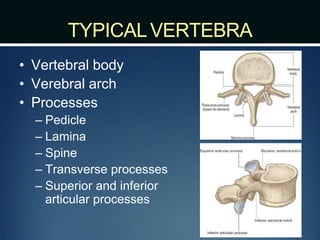
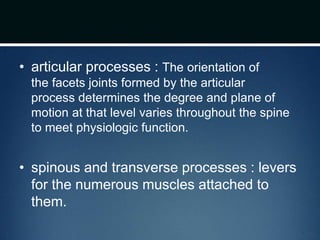
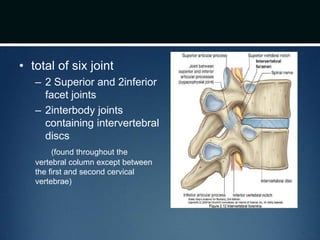
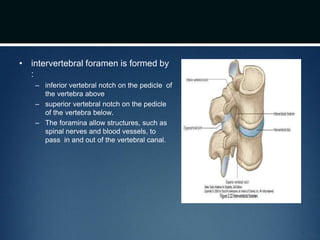
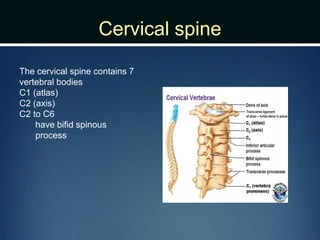
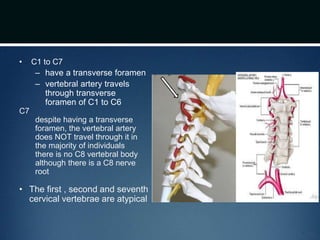
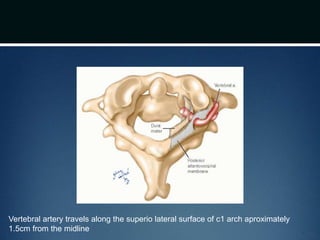
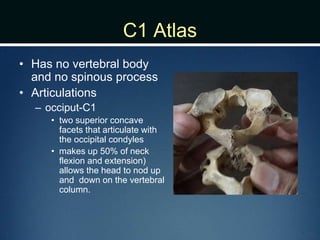
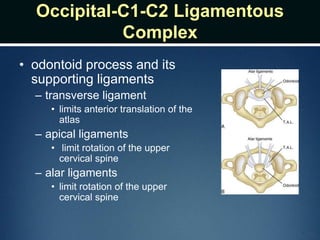
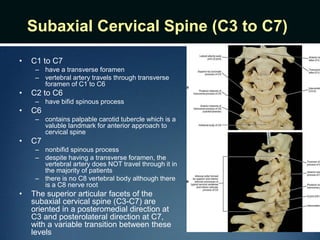
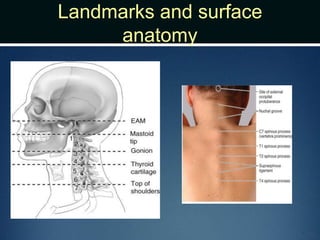
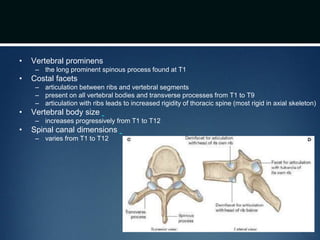
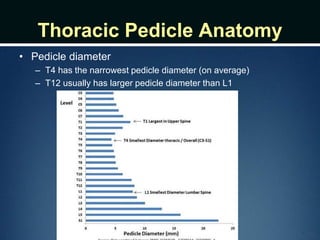
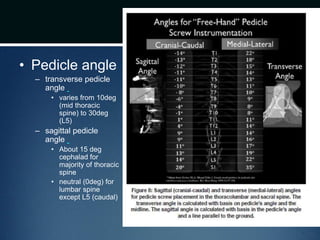
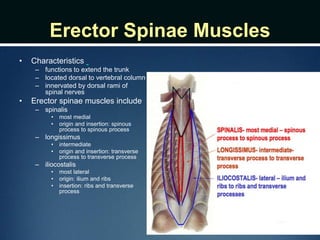
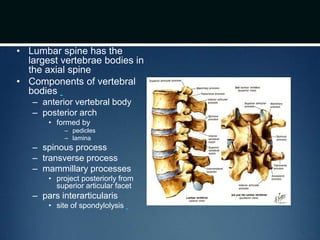
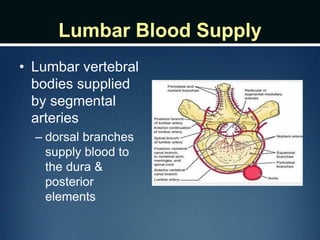
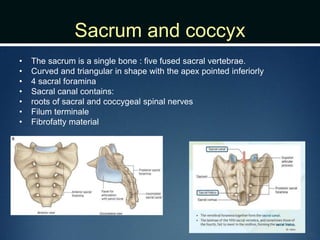
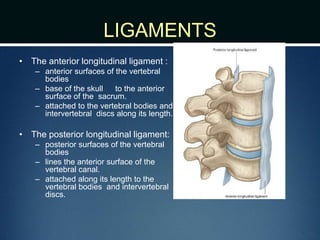
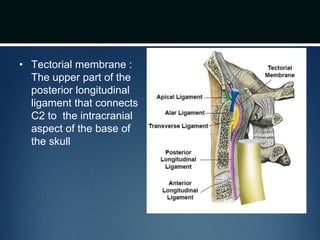
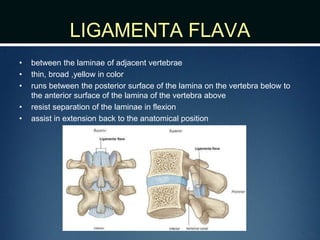
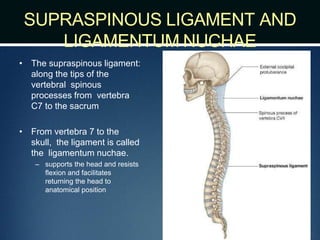
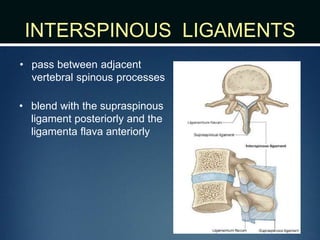
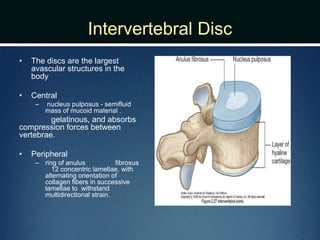
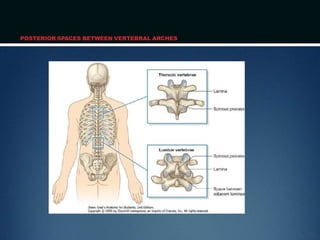
The document summarizes the anatomy of the vertebral column. It is divided into five sections - cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal. Each section contains a specific number of vertebrae that increase in size from cranial to caudal. The document describes the typical structures of a vertebra including the vertebral body, arch, processes, and joints. It then provides details on the unique anatomy of the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions including curvature, vertebral features, ligaments, and neurovascular structures.