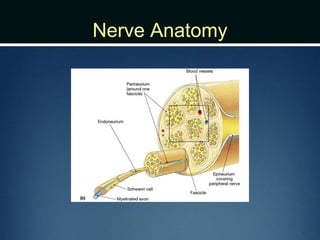
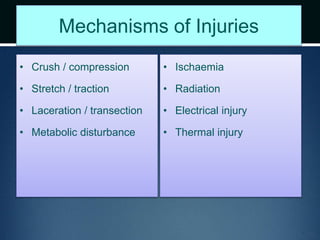
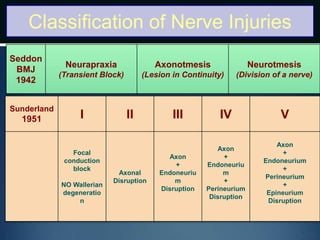
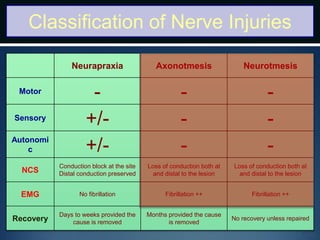
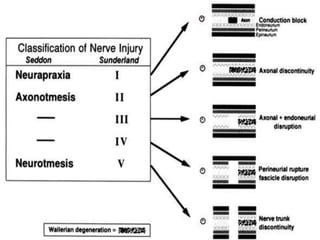
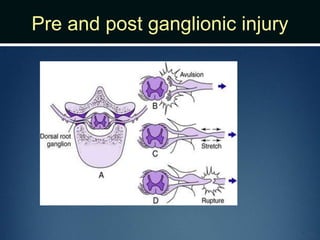
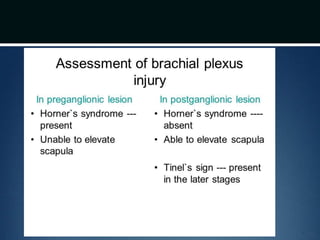
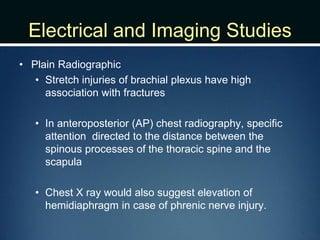
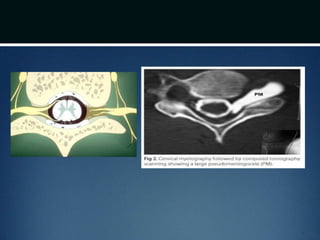
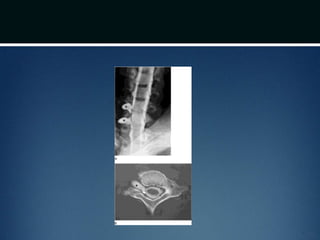
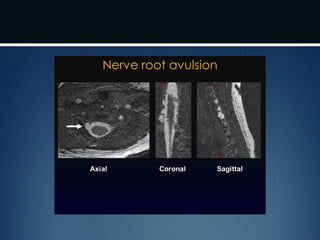
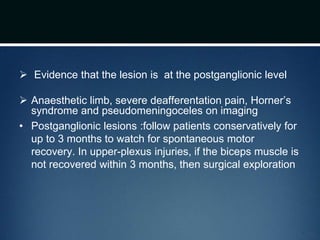
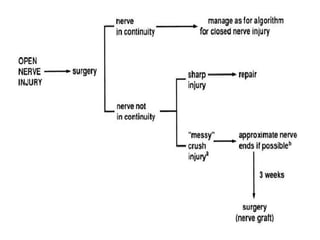
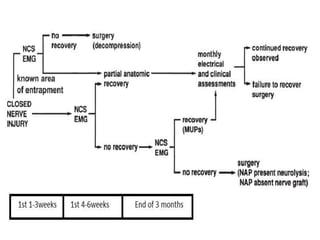
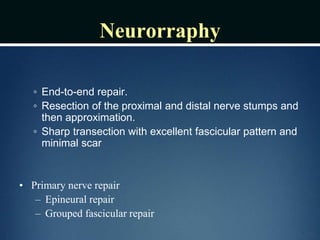
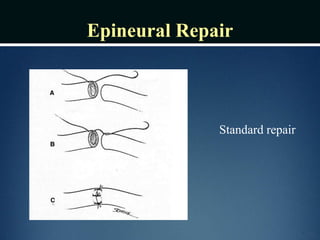
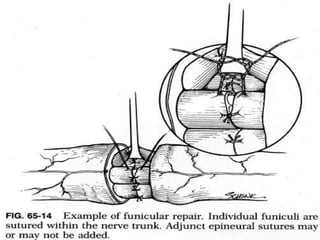
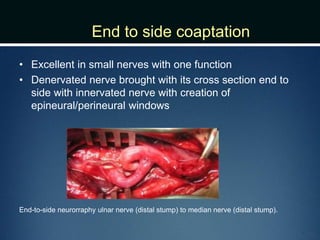
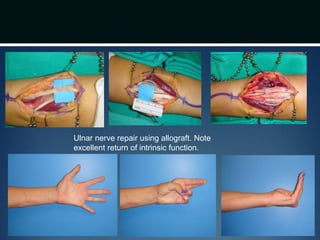
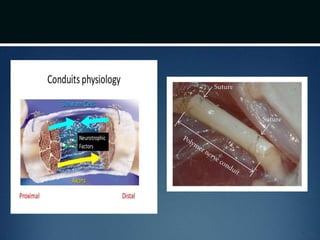
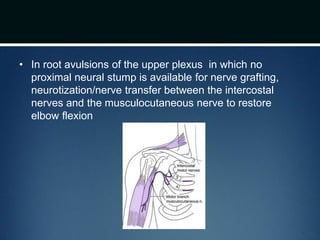
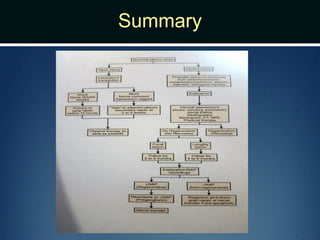
Nerve injuries can occur through various mechanisms and be classified based on severity. Electrodiagnostic studies and imaging help evaluate the degree of injury. For severe injuries, exploration may be needed for neurolysis, neurorrhaphy, grafting, or nerve transfers to restore function. The timing and type of surgical intervention depends on the severity, location, and symptoms in each individual case.