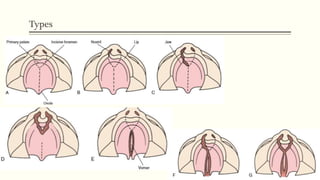
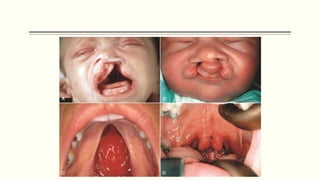
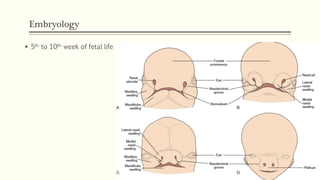
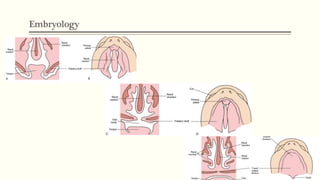
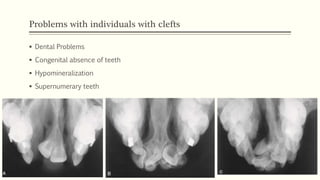
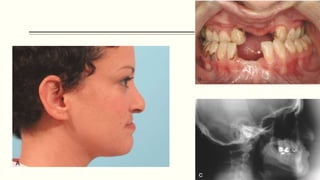
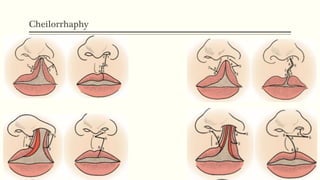
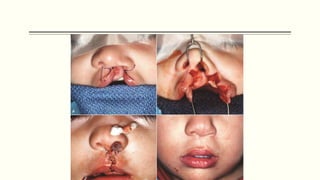
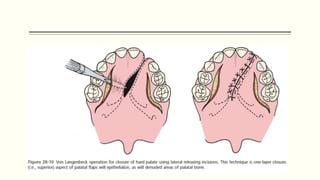
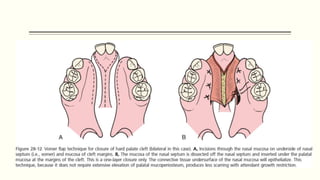
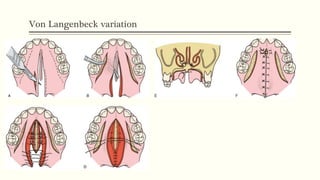
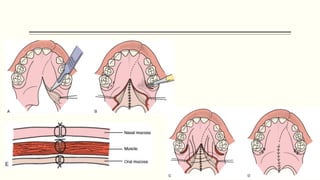
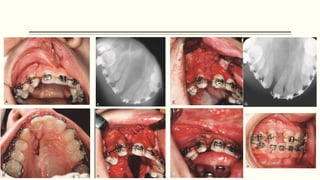
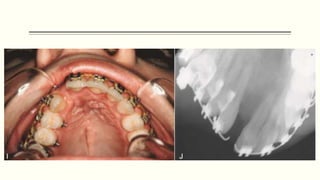
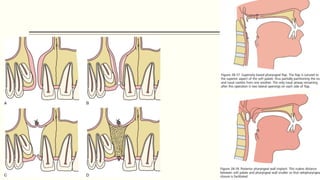
This document discusses cleft lip and palate, including the embryology, causes, problems individuals may experience, and treatment approaches. It notes that clefts occur due to failure of fusion during embryonic development. Individuals with clefts often experience dental issues, malocclusion, speech difficulties, and ear problems. Treatment is multi-disciplinary and involves surgical procedures like cheilorrhaphy to repair the lip and palatorrhaphy to repair the hard and soft palate, as well as alveolar bone grafts and dental treatments throughout development. The goal is to correct anatomical issues and produce normal function and appearance.