The document provides a comprehensive overview of cleft lip and palate, detailing its historical context, incidence rates, embryological development, classification, and associated syndromes. It further discusses the multidisciplinary management strategies, emphasizing the phases of surgical and orthodontic interventions necessary for effective treatment. Key factors influencing cleft formation, diagnosis techniques, and common complications are also highlighted.


![Aetiology --> 1] Genetic
Family history : First-degree relative affected increases
the risk to 1:25 live births.
Genetic influence ---> more significant in Cleft lip/Palate ;
Environmental factors ---> Isolated cleft palate
Role of TGF-β3 in Palatal Fusion : Expressed in MEE
Expressed by Medial Edge Epithelial cells
Homozygous null TGF-β3 --> Cleft Secondary Palate
Defect in Wnt9b Signaling
Insufficient Growth of Maxillary prominces
Mutation in FOXE1 gene
Expressed at point of Fusion b/w Maxillary & Nasal Process](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleftlipandpalate-190910135205/75/Cleft-Lip-and-Palate-14-2048.jpg)
![2] Environmental factors
Maternal smoking or Tobacco exposure
Viral infections • Poor nutrition
Maternal Epilepsy
Teratogens like:
Rubella virus, Cortisone/ steroids, Mercaptopurine,
Methotrexate, Valium, Dilantin, diazepam, phenytoin
3] Predisposing Factors
• High maternal age • Diabetes • Toxemia
• Reduced blood supply • Folic acid deficiency
• Racial – mongoloids • Radiations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleftlipandpalate-190910135205/75/Cleft-Lip-and-Palate-15-2048.jpg)




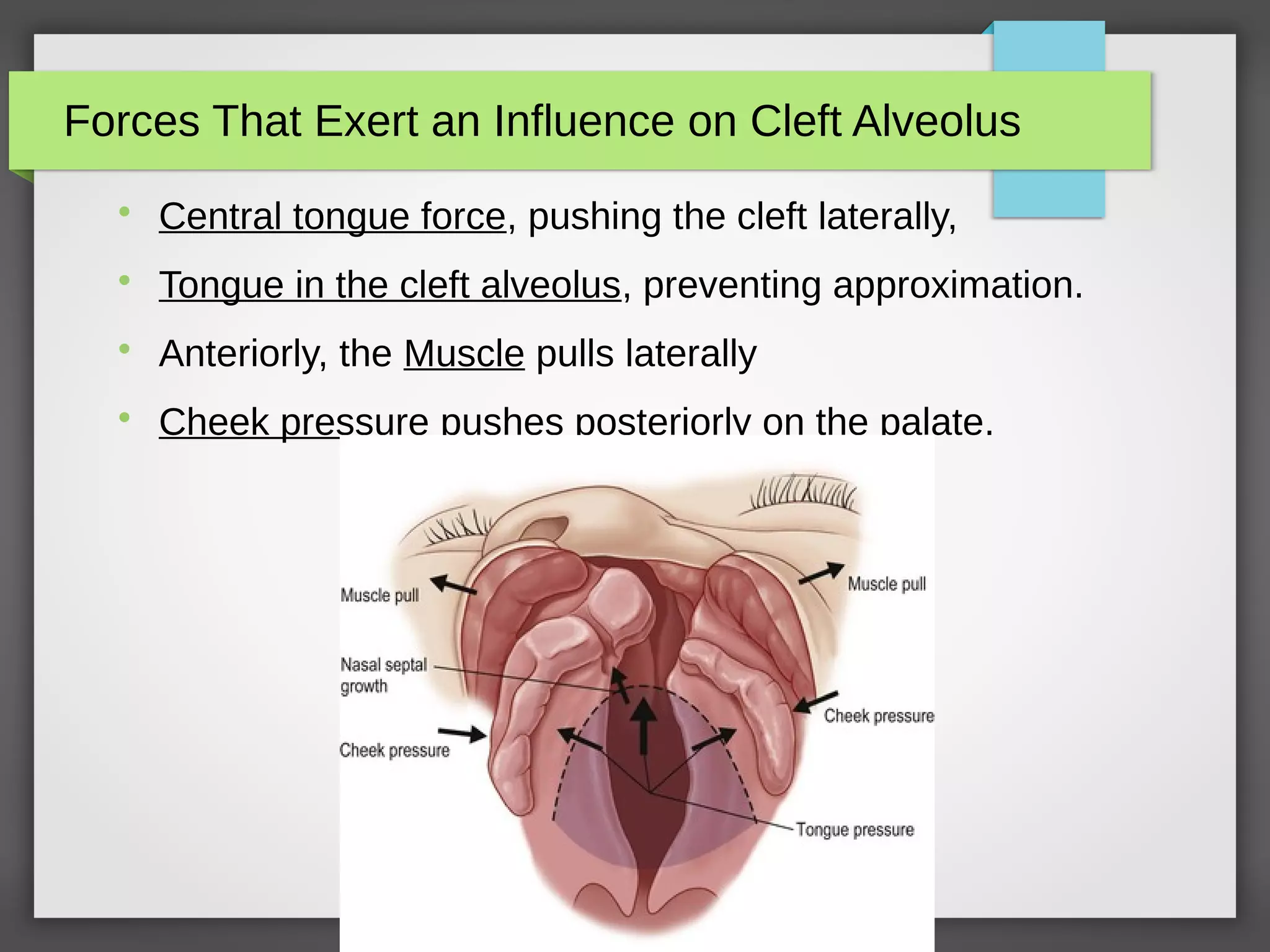
![Facial Growth in Cleft Lip & Palate
Prenatal Growth
Various forces which influence the facial growth in utero are:
A] Over maxillary segment on non-cleft side:
Pull of lip and cheek muscles
Tongue pressure
Relatively unstrained nasal septum growth
B] Over maxillary segment on cleft side:
Instrinsic Deficiency
Pressure from alar base due to stretching of the nostrils.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleftlipandpalate-190910135205/75/Cleft-Lip-and-Palate-29-2048.jpg)
![Facial Growth in Cleft Lip & Palate
Due to above mentioned forces, deficiency produced in cleft lip and
palate babies are:
A] Incomplete unilateral cleft lip and palate:
Severe deviation of midline away from cleft.
Smaller maxillary segment shows retro-positioning or growth
inhibition and collapse.
Nose is deviated towards normal side.
B] In bilateral cleft lip and palate cases
Premaxilla tilts forward and/or shifts to one side due to tongue
pressure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleftlipandpalate-190910135205/75/Cleft-Lip-and-Palate-30-2048.jpg)






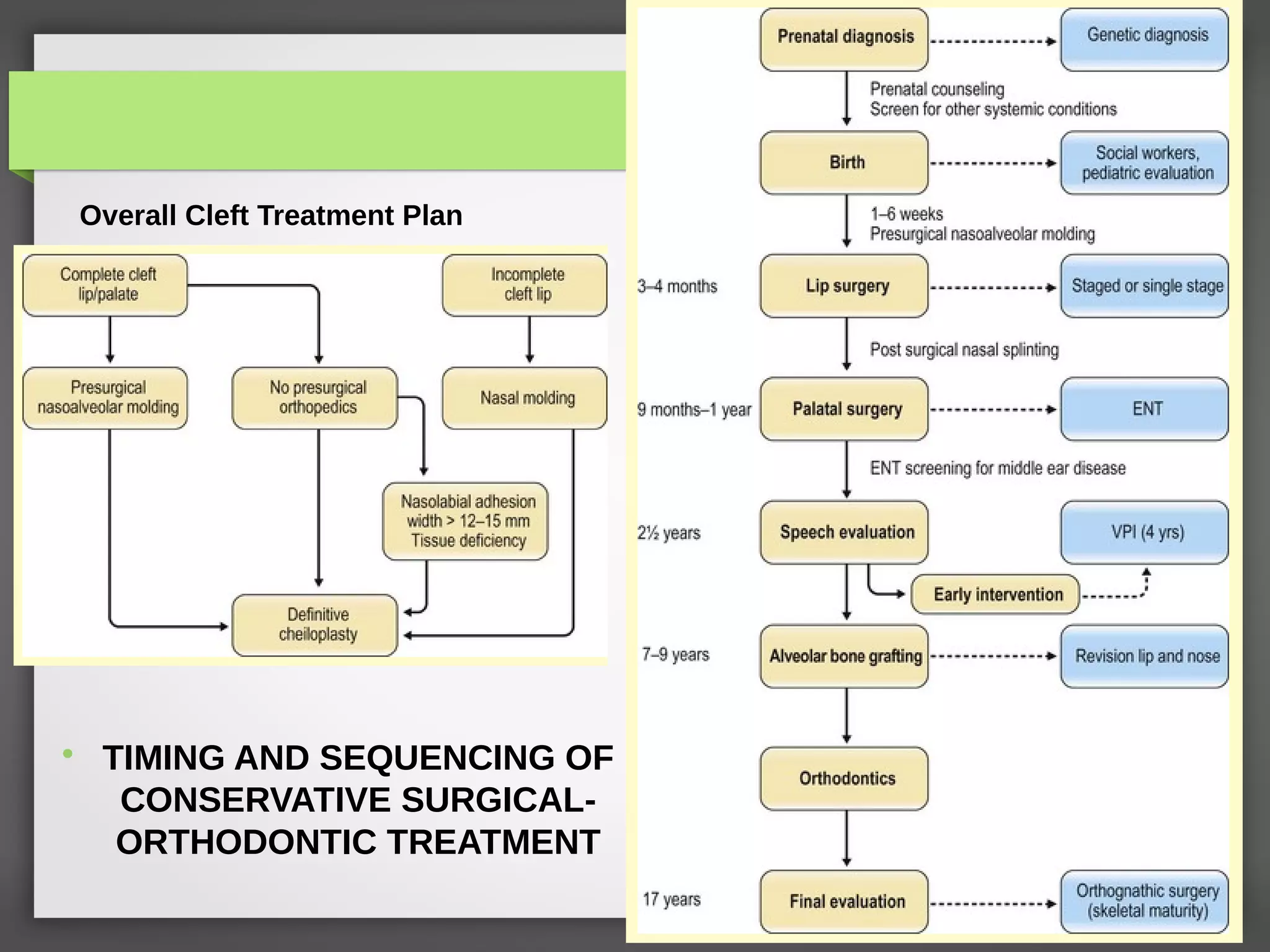

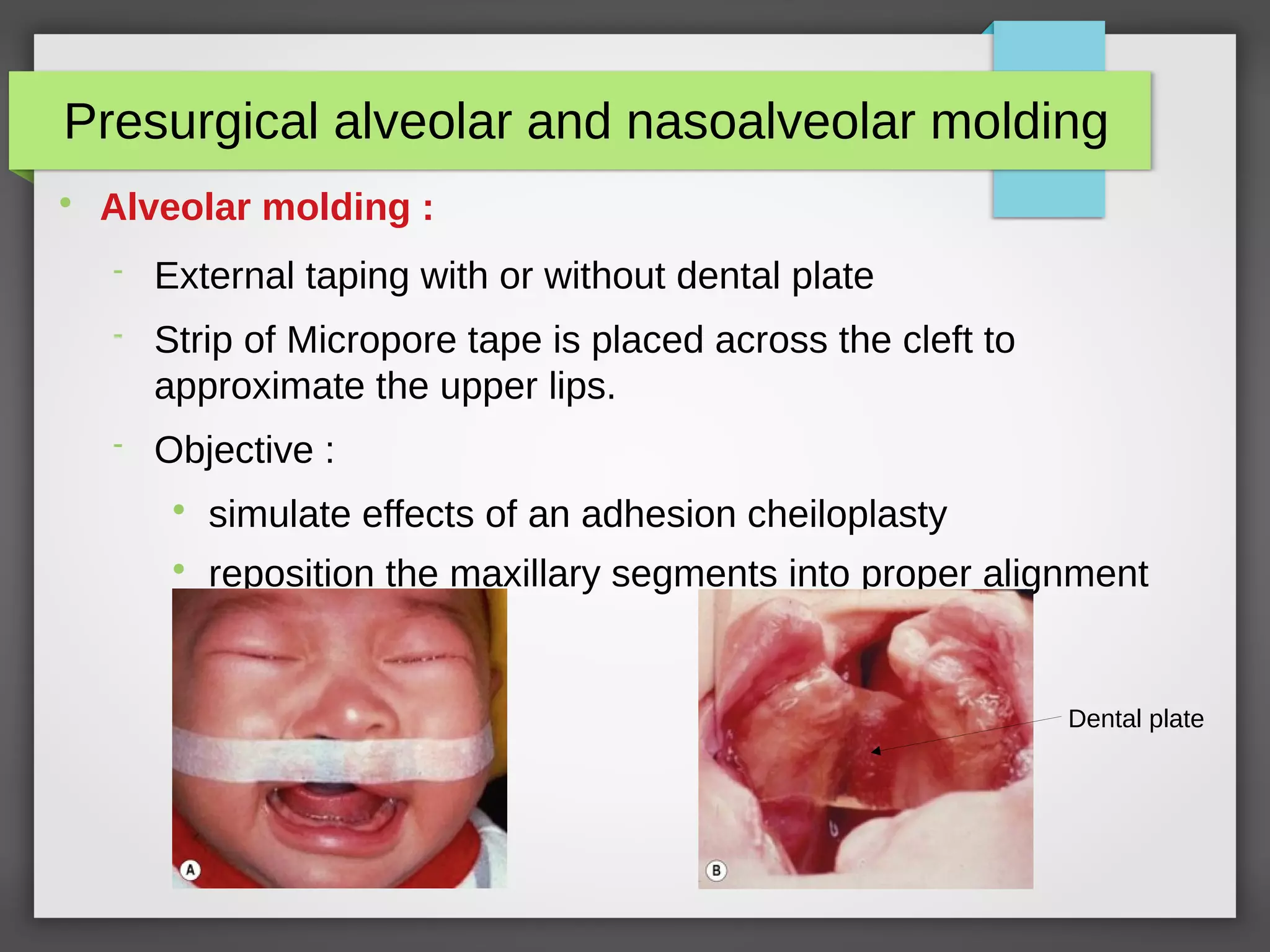
![Stages of Management
Stage I treatment Includes:
1] Fabrication of a passive obturator
2] Pre surgical orthopedics
3] Surgical management of cleft lip
4] Surgical management of cleft palate
Passive maxillary obturator:
Intraoral prosthetic device
Fills the palatal clefts
Provides false roofing against which child can suckle
Reduces the feeding difficulties like insufficient suction, choking,
excessive air intake](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cleftlipandpalate-190910135205/75/Cleft-Lip-and-Palate-43-2048.jpg)