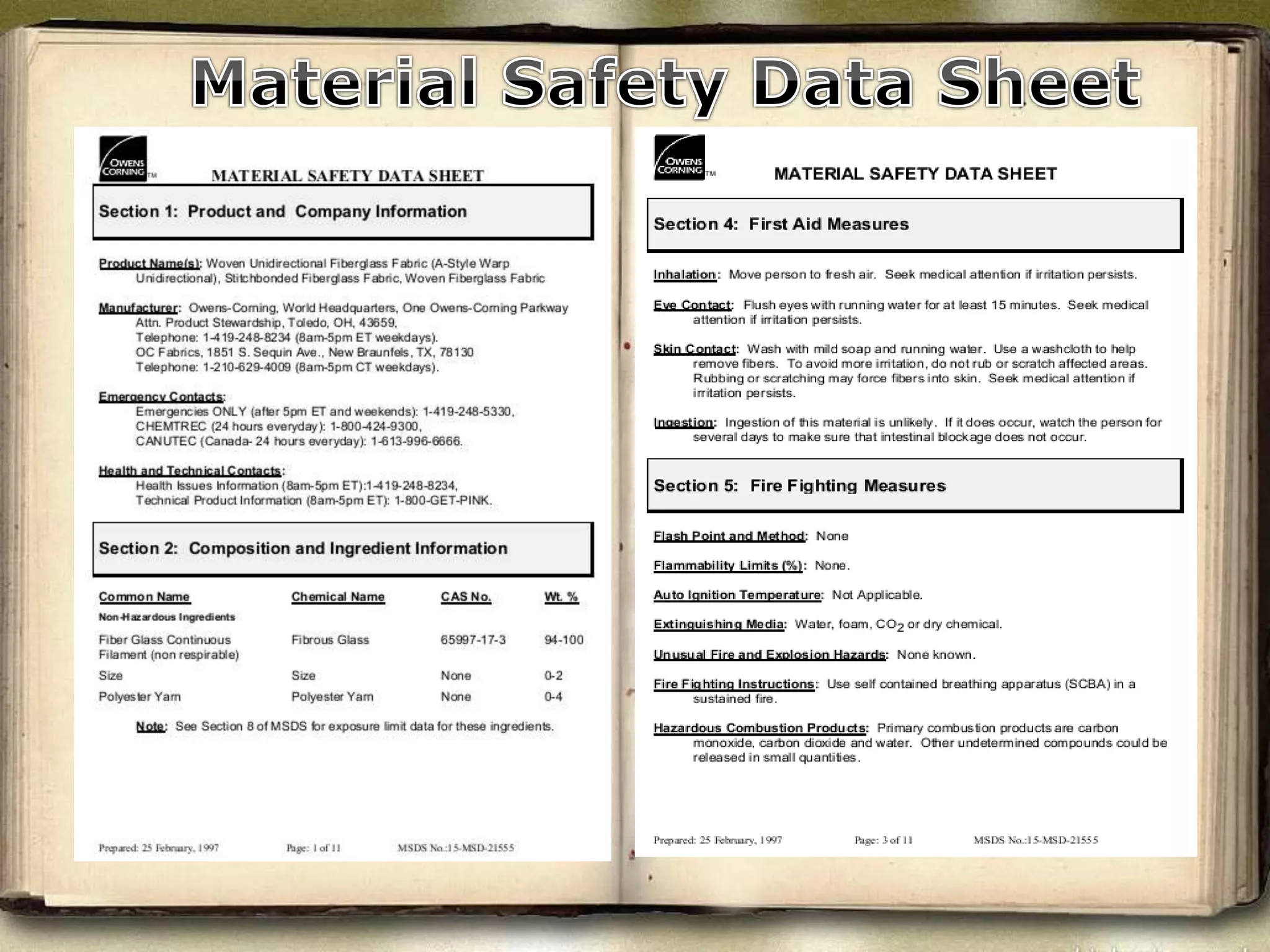
This document discusses safety measures for working with fiberglass. It notes that fiberglass can cause skin, eye, and respiratory irritation upon contact or inhalation. It recommends engineering controls like exhaust ventilation, administrative controls like scheduling to reduce exposure, use of personal protective equipment like gloves, suits, and respirators, and material safety data sheets to communicate chemical hazards. Proper clean-up and disposal of fiberglass dust and waste is also advised to improve safety.