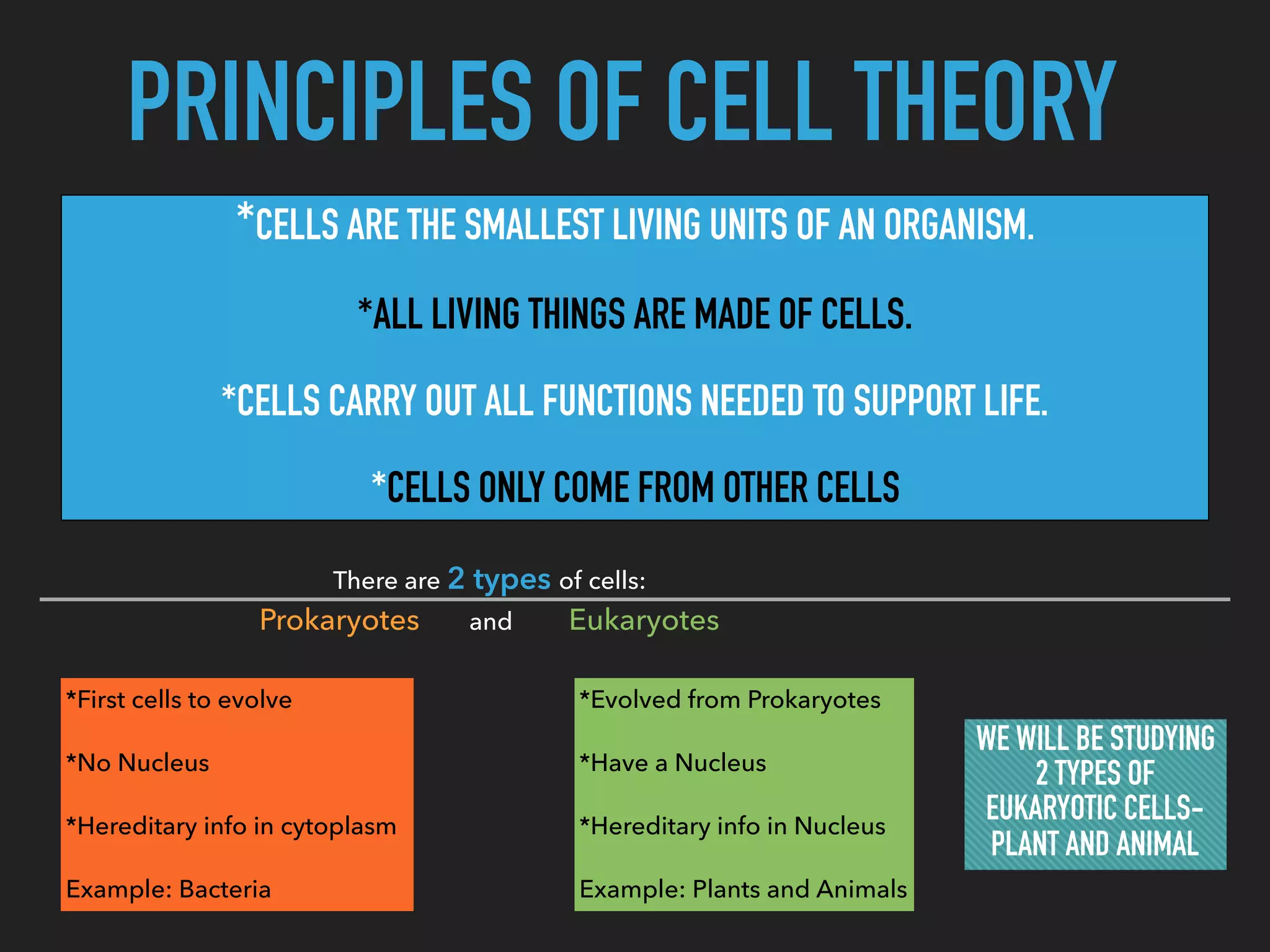
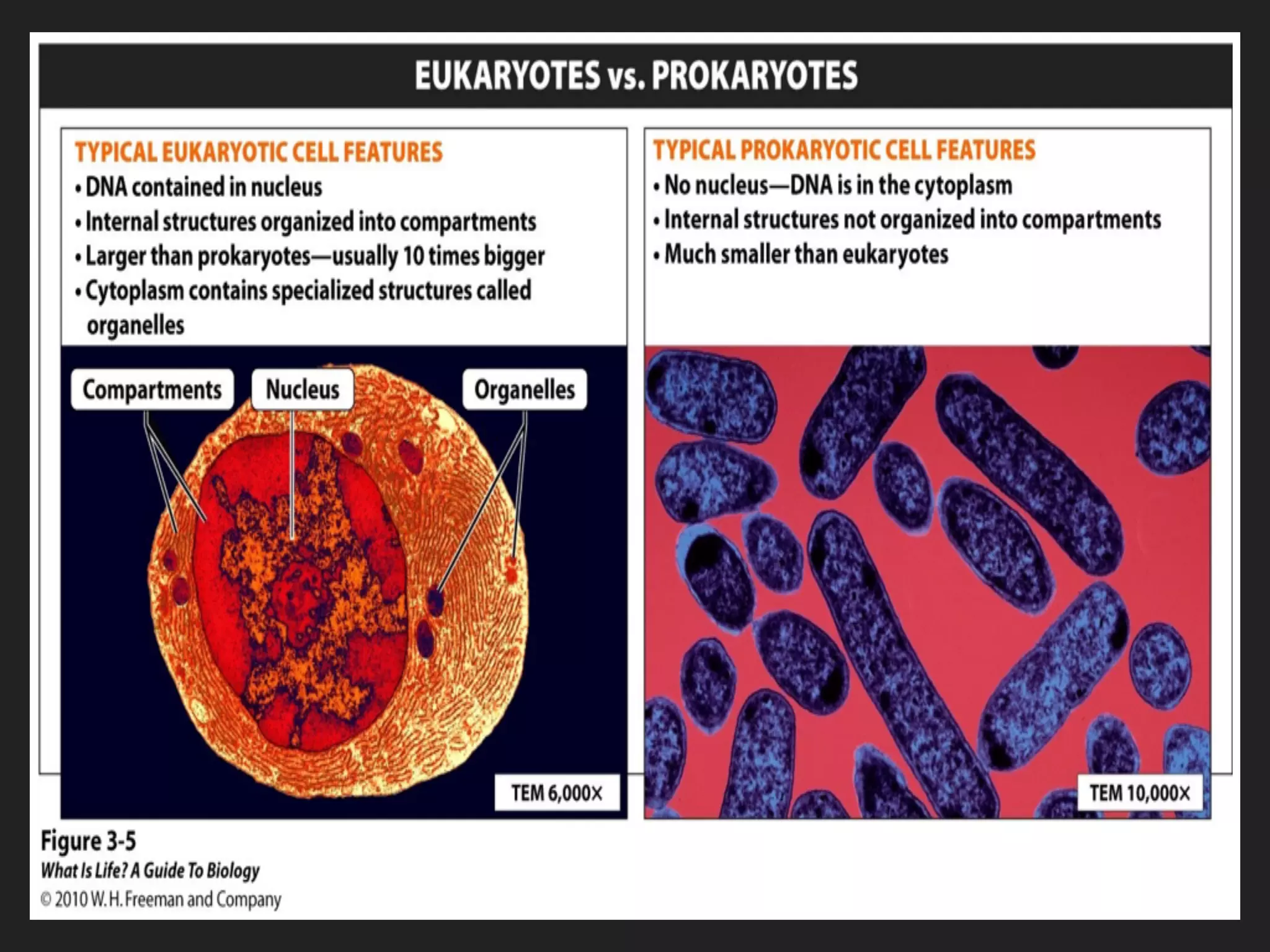
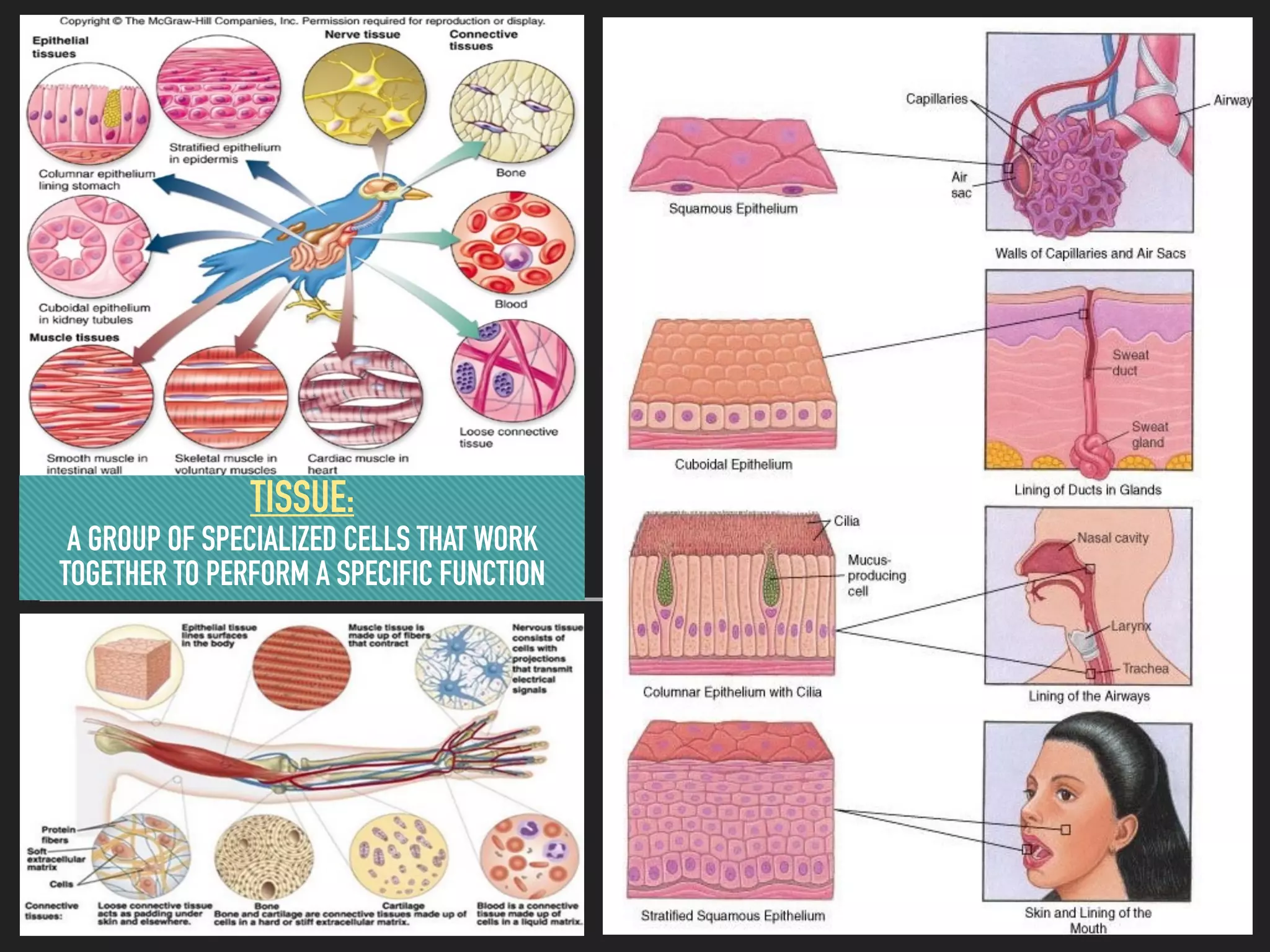
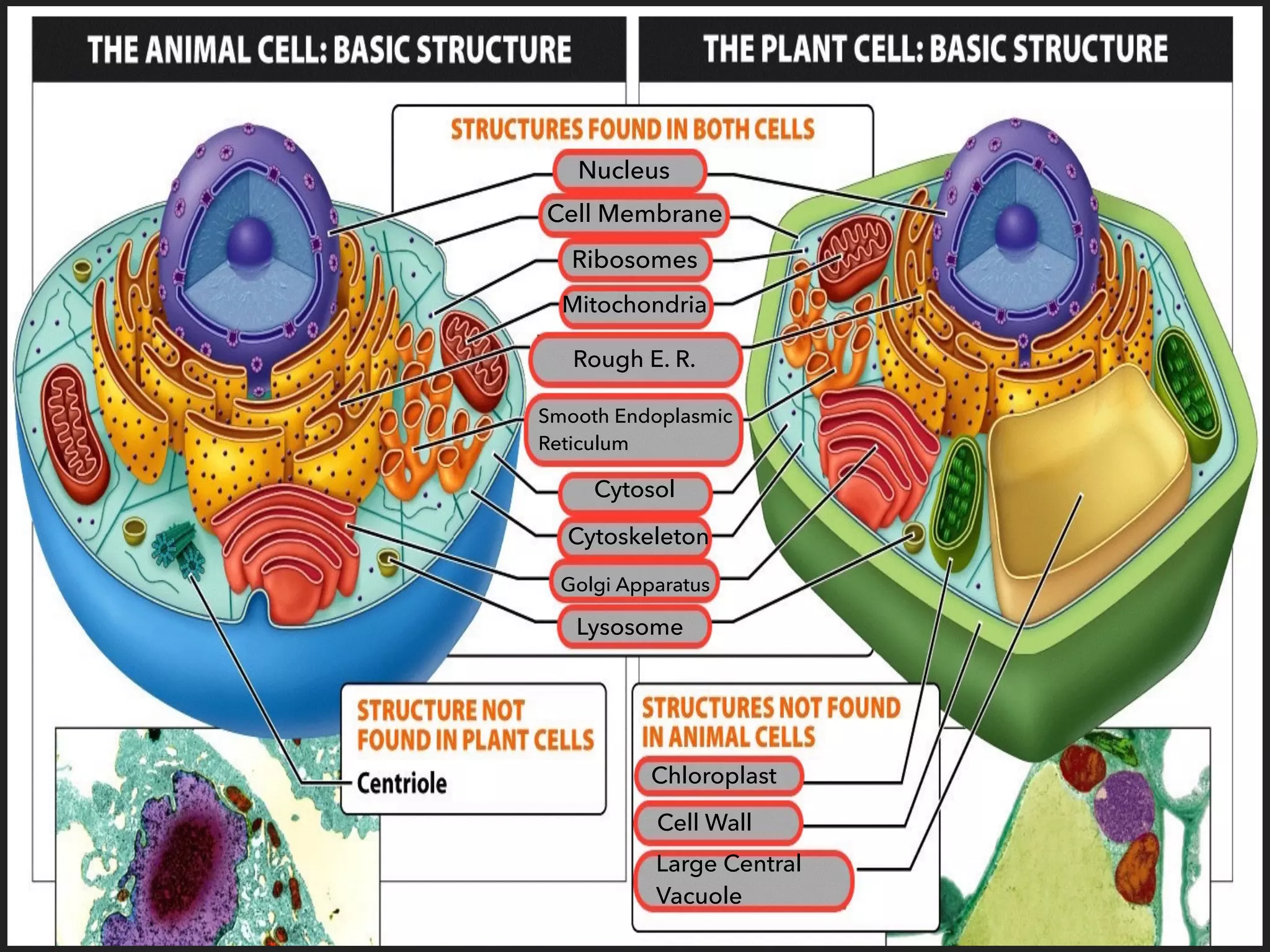
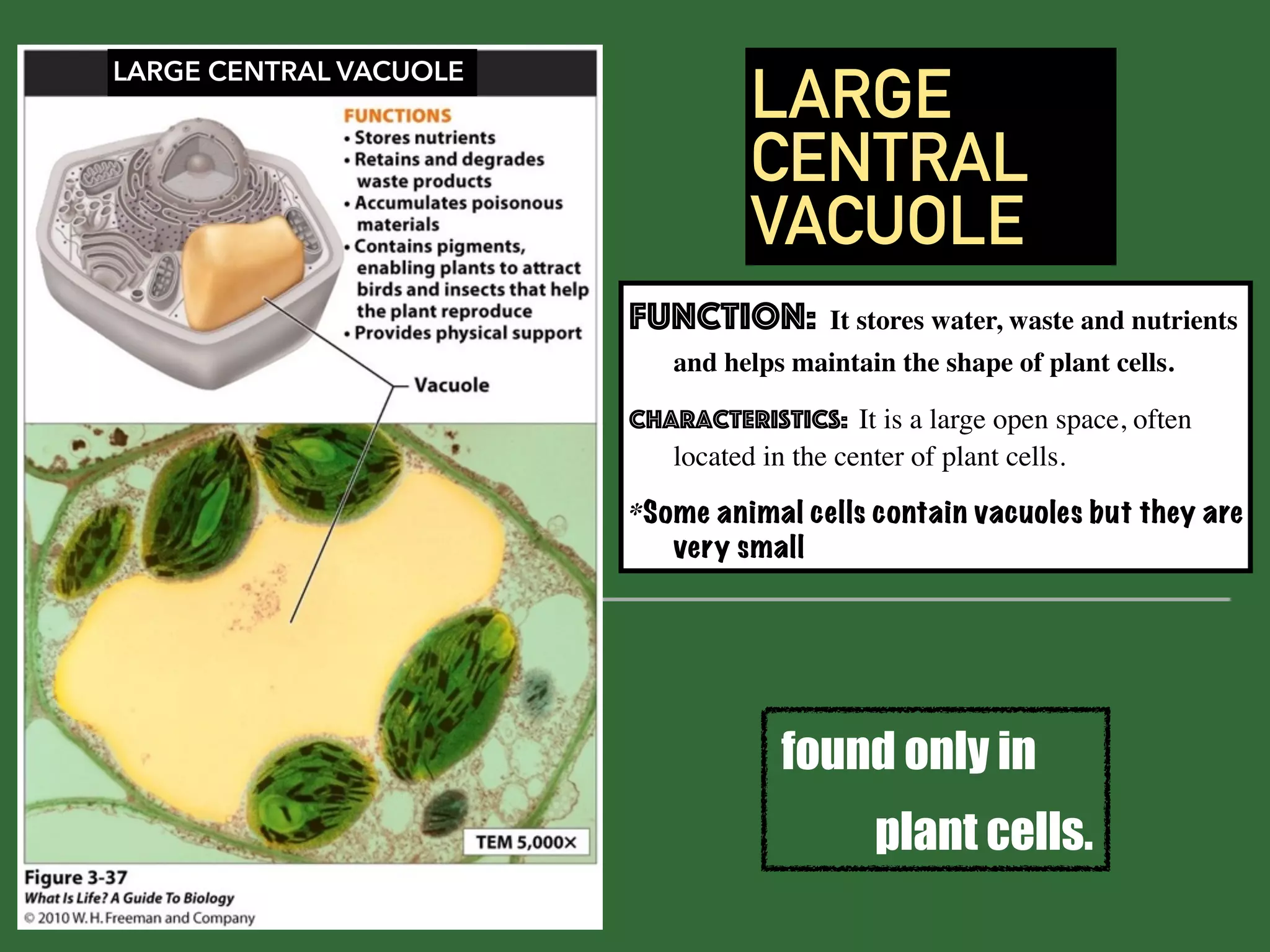
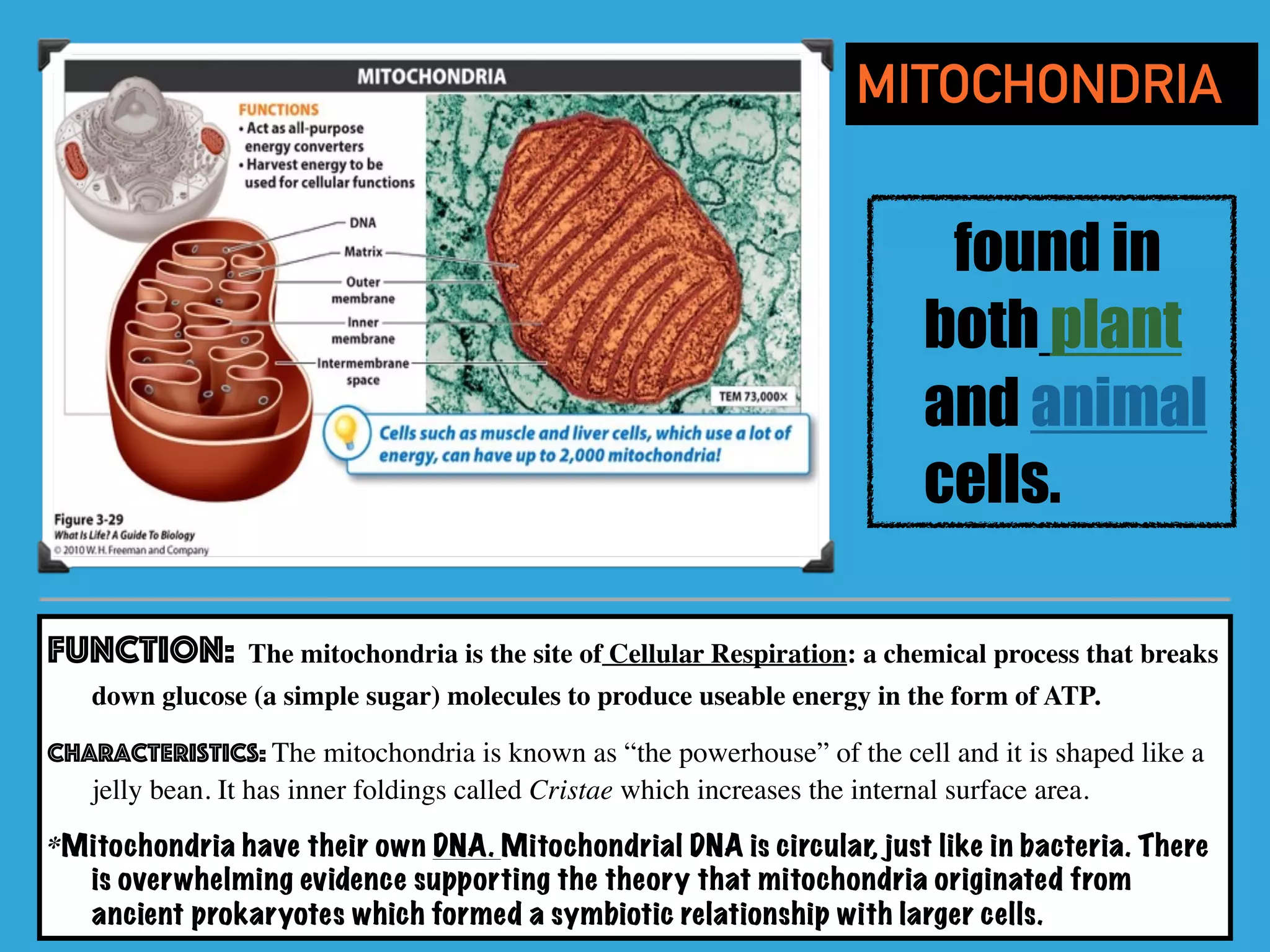
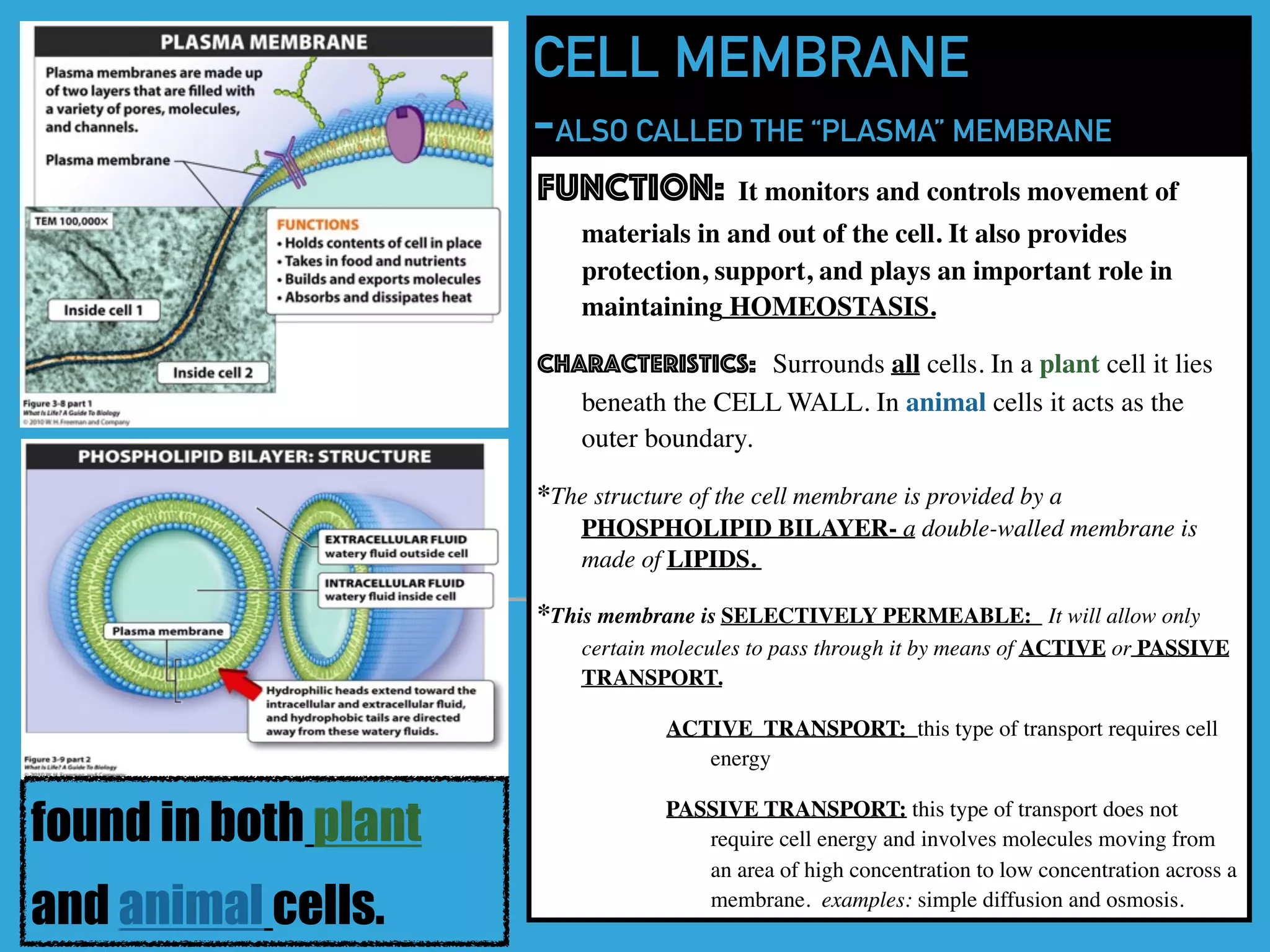
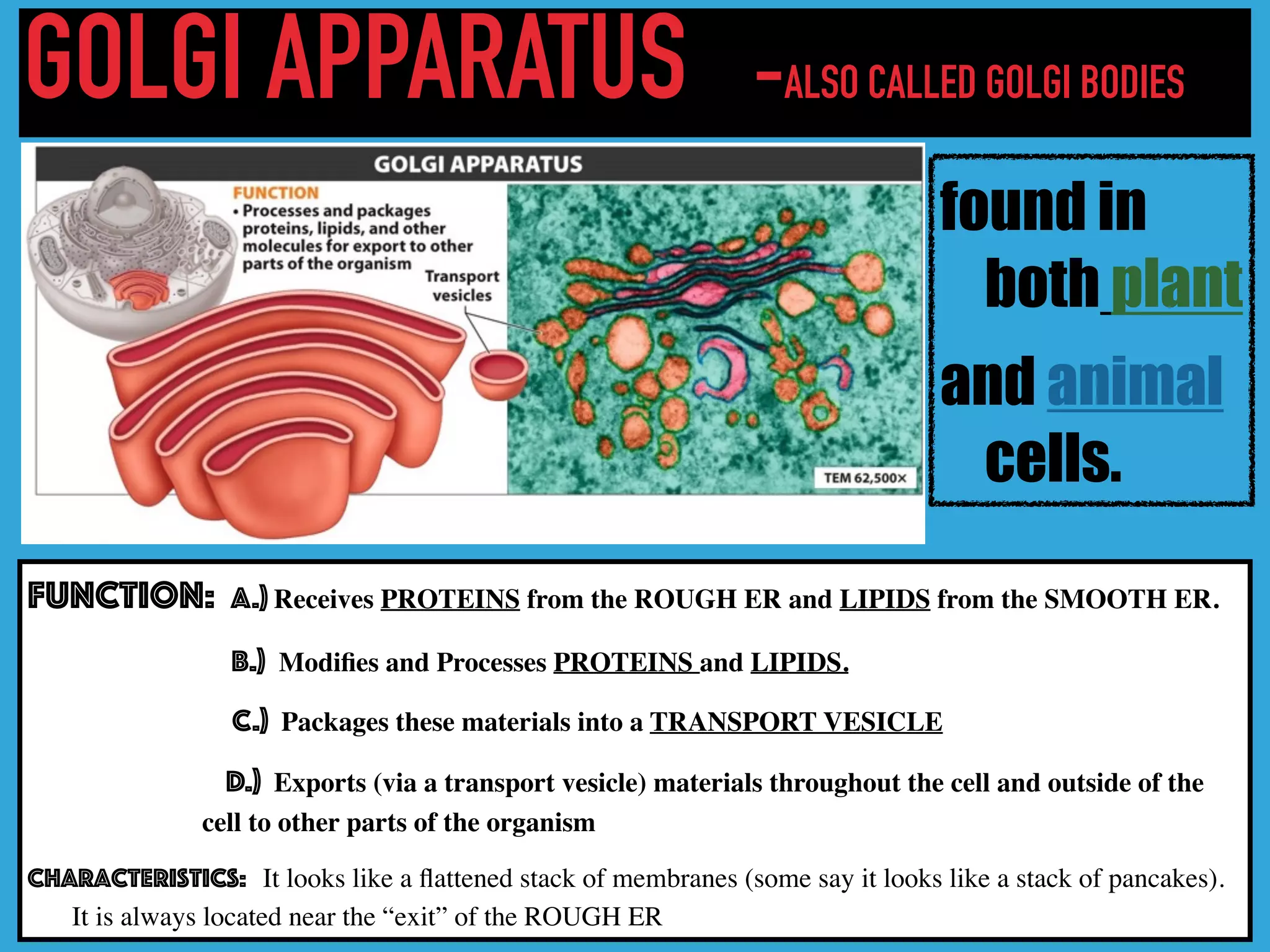
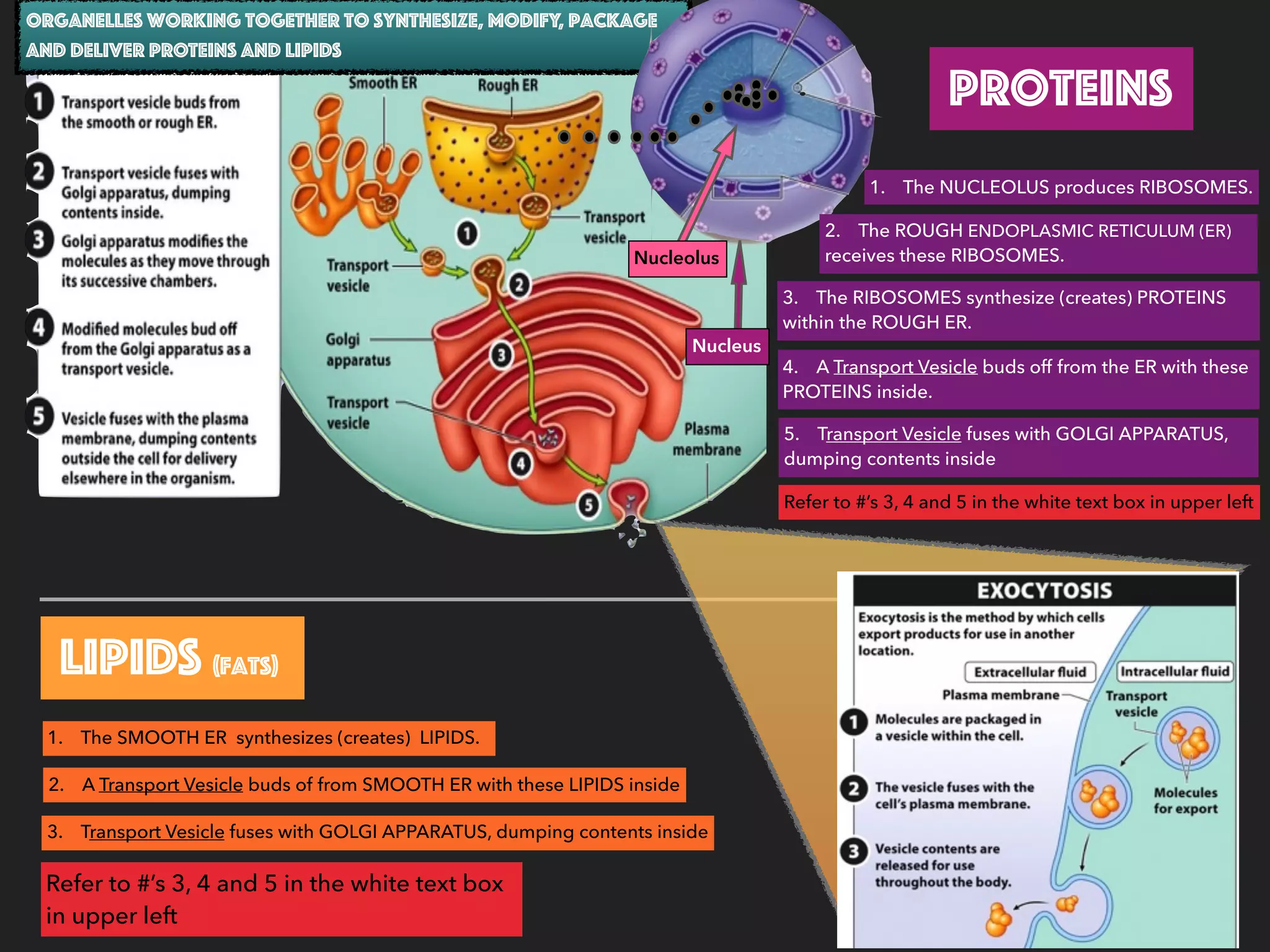
This document provides information about organelles found in plant and animal cells. It explains that organelles are tiny structures within cells that perform life functions. Some key organelles discussed include the nucleus, which controls cell functions; mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell; chloroplasts, which perform photosynthesis in plant cells; the cell membrane, which regulates what enters and exits the cell; and the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus, which work together to synthesize, modify and transport proteins and lipids. The document emphasizes that organelles work cooperatively to carry out the functions necessary to sustain life.