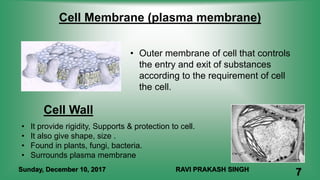
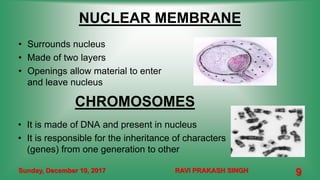
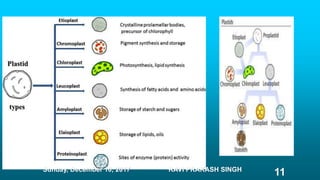
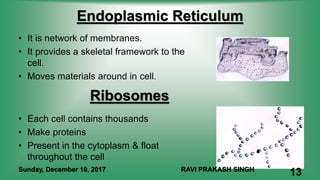
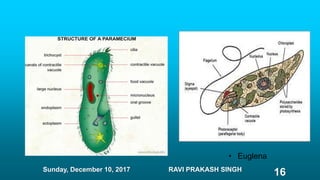
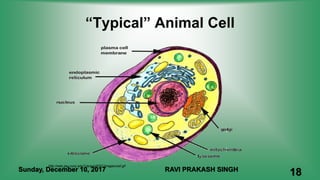
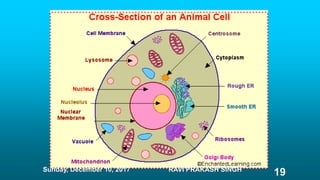
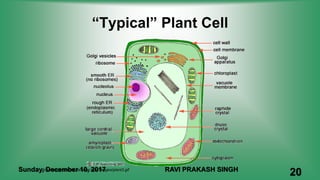
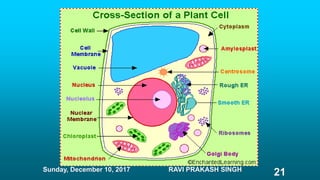
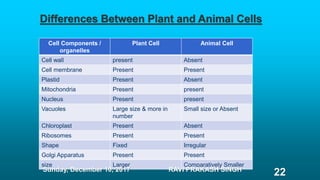
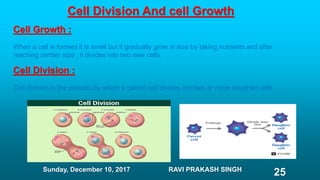
Chapter 8 discusses cell structure and functions, introducing the cell as the basic unit of life and describing the roles of various organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum. It categorizes living organisms into unicellular and multicellular types, highlights differences between plant and animal cells, and explains levels of organization from cells to organisms. The chapter also touches on cell division and growth, emphasizing the importance of cells in biological processes.