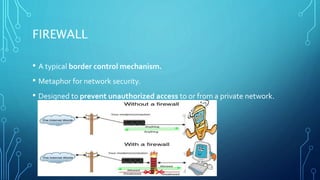
Network security involves protecting computer networks from unauthorized access and system threats. The document outlines the history and objectives of network security, as well as current and emerging types of network security technologies. These include encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, and biometric authentication. The future of network security is envisioned to function more like the human immune system, adapting rapidly to new threats through advancements in security software, hardware, and policy.