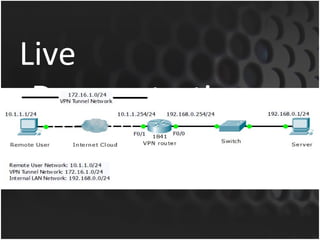
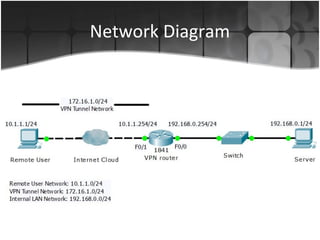
Cisco routers can serve as VPN servers to provide secure remote access to internal networks. The router must be configured with AAA authentication and authorization, virtual templates to dynamically assign interfaces, and VPN protocols like IPSec or VPDN to encrypt traffic and establish secure tunnels. Example configurations showed setting IKE/IPSec policies, client pools, dynamic maps, and applying the crypto map to the external interface to enable VPN connectivity.







![Basic Router Configuration
• Creating Local Login Users for VPN.
Router(config)# username [loginID] privilege [1-15] password 0 [password]
• Configure Fast Ethernet Interfaces
Router#config t
Router(config)#int f0/0
Router(config-if)# description Internal LAN (192.168.0.0/24)
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.254 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config)#int f0/1
Router(config-if)# description VPN INT (10.1.1.0/24)
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.254 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-130415063838-phpapp02/85/Ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-9-320.jpg)
![Configuring AAA
• aaa-model
Enables the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) access control
model.
Router(config)#aaa new-model
• aaa session-id [common | unique]
Ensures that all session identification (ID) information that is sent out for a given
call will be made identical. The default behavior is common.
Router(config)#aaa session-id common](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-130415063838-phpapp02/85/Ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-11-320.jpg)
![Configuring AAA (contd)
• aaa authentication login [list-name] local
Sets (AAA) authentication at login. ‘Local’ keyword tells the AAA to use local
username database for authentication.
Router(config)# aaa authentication login vpn_xauth local
• aaa authorization network [list-name] local
Creates a list for authorization of all network-related service requests . ‘Local’
keyword tells the AAA to use local username database for authentication
Router(config)# aaa authorization network vpn_group local](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-130415063838-phpapp02/85/Ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-12-320.jpg)



![VPDN
• A virtual private dial−up network (VPDN) allows a
private network dial in service to span across to
remote access servers (defined as the L2TP Access
Concentrator [LAC]).
• LAC forwards the PPP session on to an L2TP
Network Server (LNS). The LNS then authenticates
the user and starts the PPP negotiation.
• VPDN uses the Layer 2 Forwarding protocol (L2F)
which permits the tunneling of link level frames](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-130415063838-phpapp02/85/Ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-16-320.jpg)
![Configuring VPDN
• enable vpdn
Enables virtual private networking.
Router(config)#enable vpdn
• vpdn-group [group name]
Ceates a vpdn group which specifies the protocol, dialup mode and interface
Router(config)# vpdn-group VPN_Server
Router(config)# accept-dialin
Router(config)# protocol pptp
Router(config)# virtual-template 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-130415063838-phpapp02/85/Ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-17-320.jpg)

![Configuring IPSec based VPN
• crypto isakmp policy [priority]
Defines an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) policy. IKE policies define a set of
parameters to be used during the IKE negotiation
Router(config)#crypto isakmp policy 1
Router(config-crypto-isakmp)# encr 3des
Router(config-crypto-isakmp)# authentication pre-share
Router(config-crypto-isakmp)# group 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-130415063838-phpapp02/85/Ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-19-320.jpg)

![Configuring IPSec based VPN (contd)
• crypto isakmp client configuration group [name]
Specify which group’s policy profile will be defined by defining key and ip address
pool.
Router(config)#crypto isakmp client configuration group ipsec_group
Router(config-crypto-isakmp )# key ipsec
Router(config-crypto-isakmp )# pool ip_pool
Router(config-crypto-isakmp )# netmask 255.255.255.255](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-130415063838-phpapp02/85/Ciscorouterasavpnserver-100218045815-phpapp01-21-320.jpg)