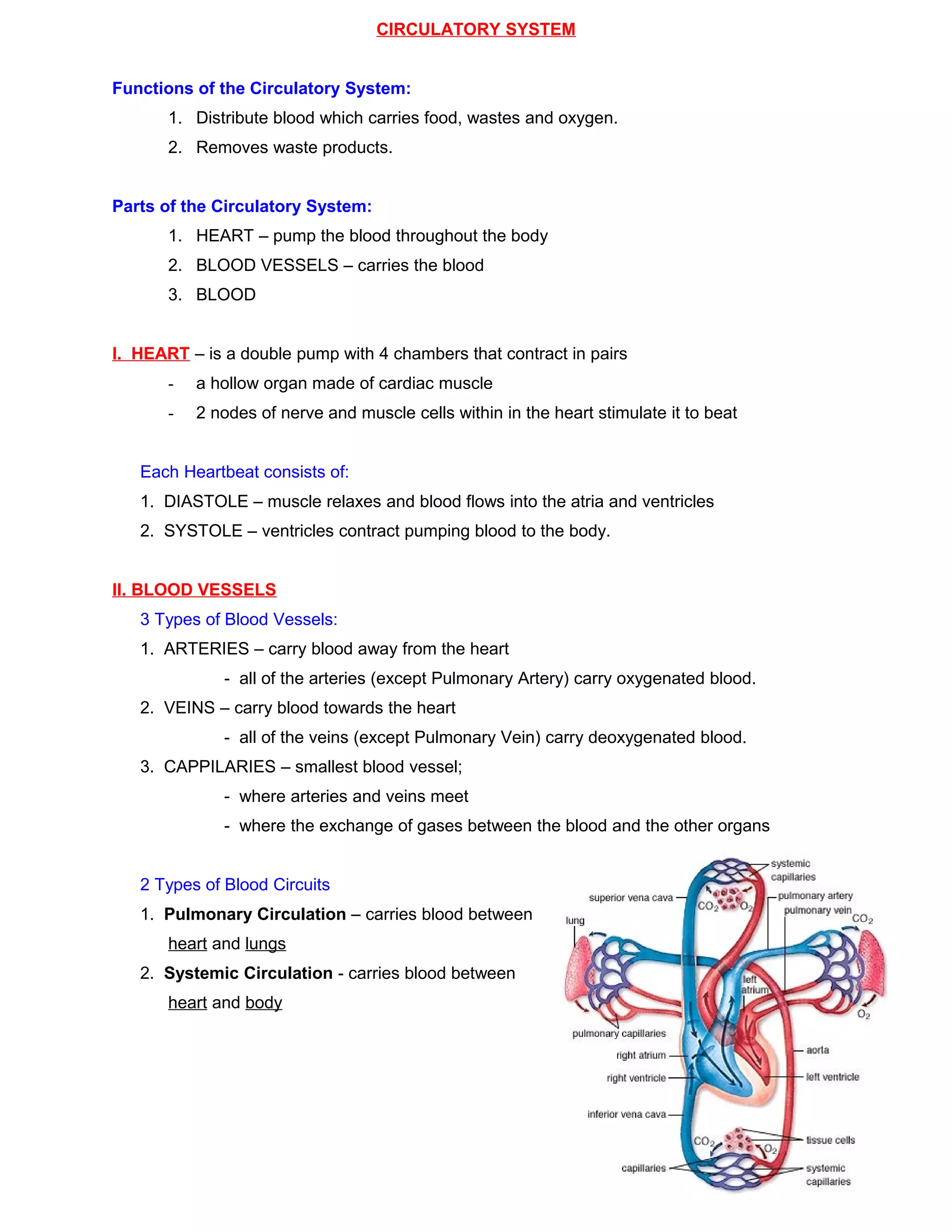
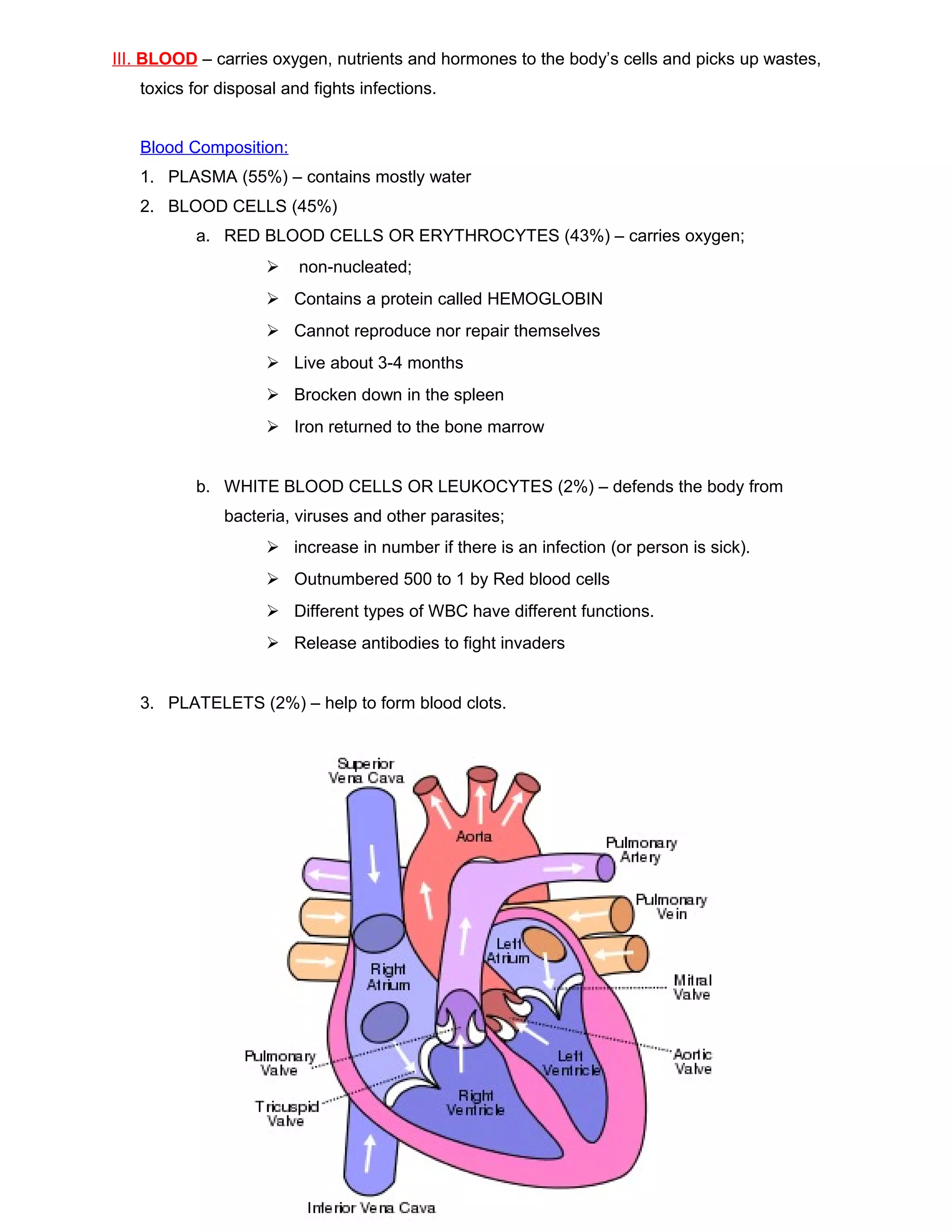
The circulatory system functions to distribute oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other materials to tissues and remove wastes. It consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart is a muscular pump made of cardiac tissue with four chambers that contract rhythmically to circulate blood. Blood vessels include arteries, which carry blood away from the heart; veins, which carry blood toward the heart; and capillaries, where gas and nutrient exchange occurs. Blood contains plasma, red blood cells to carry oxygen, white blood cells to fight infection, and platelets to help clotting. Deoxygenated blood enters the heart's right side and is pumped to the lungs, where it receives oxygen and returns to the left side